Download & Install
Darasa Huru App
DOWNLOAD
TOPIC 1: INTRODUCTION TO BIOLOGY | BIOLOGY FORM 1
Biology is the science that deals with the study of living things. The word Biology is derived from two Greek words, Bios which means Life, and logos which means study of. Thus biology is a study of life and living organisms.
Basic Concepts and Terminologies of Biology
The Meaning of Basic Biological Concepts and Terminologies
Explain the meaning of basic biological concepts and terminologies
Biology
Biology is derived from two Greek words, that is, bios which means life and logos or logia which means study or knowledge.
So
biology can be defined as a branch of science which deals with the
study of life. The term biology can also be defined as a branch of
science which deals with the study of living things or organisms.
biology can be defined as a branch of science which deals with the
study of life. The term biology can also be defined as a branch of
science which deals with the study of living things or organisms.
Biologist
A person specialized in the study of biology
Life
Life
means being alive or existing. Something is alive or existing if it
possesses life processes. The life processes are growth, movement or
locomotion, respiration, excretion, reproduction, sensitivity and
nutrition.
means being alive or existing. Something is alive or existing if it
possesses life processes. The life processes are growth, movement or
locomotion, respiration, excretion, reproduction, sensitivity and
nutrition.
Organism
Organism is anything which has life. It is the other name of a living thing.Organisms are made up of cells.
Cell
A cell is a basic unit of living things. The cell has three main parts, cell membrane, cytoplasm and nucleus. Cells which make up plants are called plant cells and those which make up animals are called animal cells.
Some
organisms are made up of one cell. They are called unicellular or
single-celled organisms e.g. amoeba, euglena and yeast. Some organisms
are made up of many cells, they are called multi cellular organisms e.g.
animals, plants, and most fungi.
organisms are made up of one cell. They are called unicellular or
single-celled organisms e.g. amoeba, euglena and yeast. Some organisms
are made up of many cells, they are called multi cellular organisms e.g.
animals, plants, and most fungi.
The Characteristics of Living Things
Outline the characteristics of living things
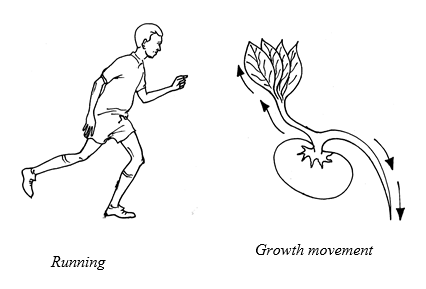
Movement/locomotion
All
living organisms are capable of movement. Movement is the change of
position of the whole organism or just part of an organism. For animals
and unicellular organisms the movement is of the whole body. This is
known as locomotion. Most animals move about using legs, wings
or fins. Unicellular organisms such as amoeba, paramecium and euglena
use the locomotory structures pseudopodia, cilia and flagella
respectively.
living organisms are capable of movement. Movement is the change of
position of the whole organism or just part of an organism. For animals
and unicellular organisms the movement is of the whole body. This is
known as locomotion. Most animals move about using legs, wings
or fins. Unicellular organisms such as amoeba, paramecium and euglena
use the locomotory structures pseudopodia, cilia and flagella
respectively.
In
plants only part of it may move towards different factors such as
light, water, gravity etc. They move by growing. Their roots grow down
in the soil and their shoots grow up into the air or towards a source of
light.
plants only part of it may move towards different factors such as
light, water, gravity etc. They move by growing. Their roots grow down
in the soil and their shoots grow up into the air or towards a source of
light.
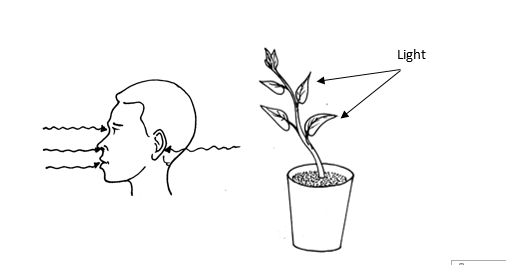
Irritability (sensitivity)
Irritability
is the ability of an organism to respond to a stimulus. Stimulus
(plural; stimuli) is anything that causes a response in an organism.
is the ability of an organism to respond to a stimulus. Stimulus
(plural; stimuli) is anything that causes a response in an organism.
Examples of stimuli include: an alarm clock, a smell of breakfast cooking and a fly landing on your skin.
All
living things are sensitive to certain changes in their surroundings,
that is, they are aware of what is happening around them. This is
possible because they have special organs known as sense organs by which
they detect these changes.
living things are sensitive to certain changes in their surroundings,
that is, they are aware of what is happening around them. This is
possible because they have special organs known as sense organs by which
they detect these changes.
Examples of sense organs include: eyes for vision (sight); skin for temperature, touch, pressure detection; tongue for tasting; nose for smelling; and ears for hearing and body balance.
Plants do not have sense organs but are still able to detect and respond to things like gravity, water and light.
Feeding (Nutrition)
All living things need food to provide energy for such activities such as growth, repair and health.
Animals
get their food by eating other living things or food materials that
were once living things. Herbivores (e.g. rabbits) eat plants,
carnivores (e.g. lions) eat other animals, and omnivores (e.g. humans)
eat animals and plants. Plants make their own food through the process
called photosynthesis.
get their food by eating other living things or food materials that
were once living things. Herbivores (e.g. rabbits) eat plants,
carnivores (e.g. lions) eat other animals, and omnivores (e.g. humans)
eat animals and plants. Plants make their own food through the process
called photosynthesis.
The process of taking in food, synthesizing it, digesting and oxidizing it to release energy or build the body is called nutrition.
Respiration
Respiration is the breaking down of food materials within cells to release energy.
Respiration
usually involves the use of oxygen. All living things need energy for
movement, growth and development, and functioning of body organs.
usually involves the use of oxygen. All living things need energy for
movement, growth and development, and functioning of body organs.

Excretion
All
living things produce wastes such as carbon dioxide, water, urea,
ammonia etc.. Some of these chemicals if left to accumulate in the cells
would seriously poison the living organism hence they need to be
removed. The process of removing metabolic waste products from the body
of living organisms is called excretion.
living things produce wastes such as carbon dioxide, water, urea,
ammonia etc.. Some of these chemicals if left to accumulate in the cells
would seriously poison the living organism hence they need to be
removed. The process of removing metabolic waste products from the body
of living organisms is called excretion.
Waste products are removed from the body by excretory organs such skin, kidneys, lungs and liver.
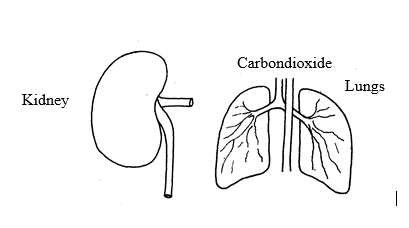
Reproduction
Reproduction
is the process by which living things produce new individuals of their
kind. All living things reproduce, to replace organisms lost by death.
If a group of organisms does not reproduce fast enough to replace those
which die, the group becomes extinct. Reproduction ensures continuation
of life when parent generation dies.
is the process by which living things produce new individuals of their
kind. All living things reproduce, to replace organisms lost by death.
If a group of organisms does not reproduce fast enough to replace those
which die, the group becomes extinct. Reproduction ensures continuation
of life when parent generation dies.
Human
beings bear babies; birds hatch chicks; and plants produce seedlings as
new organisms, which eventually grow to mature organisms to replace
those lost by deaths.
beings bear babies; birds hatch chicks; and plants produce seedlings as
new organisms, which eventually grow to mature organisms to replace
those lost by deaths.
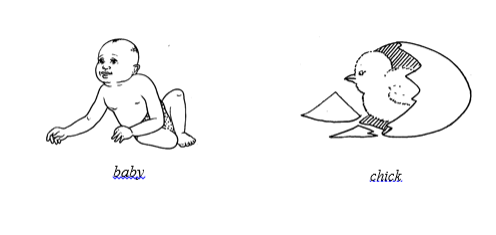
Growth
Growth
is defined as an irreversible (permanent) increase in size and dry
weight of an organism involving differentiation. All living things need
food in order to grow and build up their bodies.
is defined as an irreversible (permanent) increase in size and dry
weight of an organism involving differentiation. All living things need
food in order to grow and build up their bodies.
Animals grow until they reach certain adult size, but most plants can grow continuously throughout their lives.
Examples of growth in living things
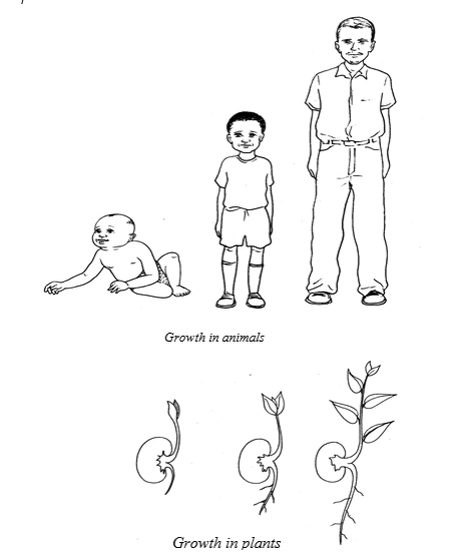
Example 1
Examples of living things
Fucus (bladderwrack)
Streptococci
Diplococci
Streptobacilli
Grass snake

Man
Cow
Flagellate bacilli

Mushroom
Male fern
Oak

Amoeba
Fucus (bladderwrack)

Dog fish
Spider
Butterfly
Crab
Millipede

Frog

A table of differences between living things and non-living things
| Living things | Non-living things |
| They respire | Do not respire |
| They grow | Do not grow |
| They respond to stimuli | Do not respond to stimuli |
| They reproduce | Do not reproduce |
| They excrete | Do not excrete |
| They feed | Do not feed |
| They move | Do not move |
Branches of biology
Biology is a subject and it has many branches. The main branches are botany and zoology Botany is a branch of biology which deals with the study of plants. A person who studies botany is called a botanist Zoology is a branch of biology which deals with the study of animals. A person who studies zoology is called a Zoologist
Other branches of biology
Mycology: this is the study of fungi. A person who studies mycology is called a mycologist
Bacteriology: this is the study of bacteria. A person who studies bacteriology is called a bacteriologist.
Virology: this branch of biology deals with the study of viruses. A person who studies virology is called a virologist.
Immunology: is concerned with body defense against diseases and foreign substances. A person who studies immunology is called an immunologist.
Entomology: refers to the study of insects A person who studies entomology is called an entomologist.
Parasitology:this branch deals with study of parasites and their effects on living organisms. A person who studies parasitology is called a parasitologist.
Dermatology: It is concerned with medical study of skin and its diseases. A person who studies dermatology is called a dermatologist
Ecology: Is
a branch of biology that deals with relationship among living things
and between organisms and their surroundings. A person who studies
ecology is called an ecologist
a branch of biology that deals with relationship among living things
and between organisms and their surroundings. A person who studies
ecology is called an ecologist
Anatomy:Is the study which deals with structure of living things. A person who studies anatomy is called anatomist
Diagram representing branches of Biology
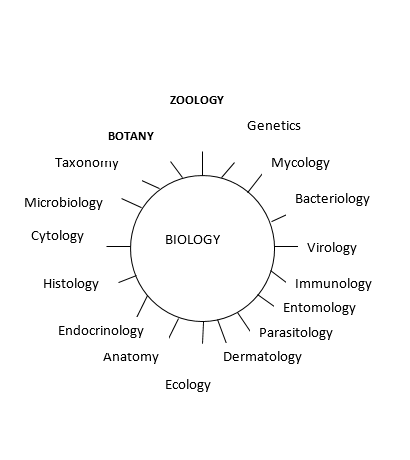
Endocrinology:
This is the study of structure of endocrine glands and the hormones
associated by them. A person who studies endocrinology is called an endocrinologist.
This is the study of structure of endocrine glands and the hormones
associated by them. A person who studies endocrinology is called an endocrinologist.
Histology: Is the study of structure of tissues A person who studies histology is called an histologist
Cytology: Is the study of structure, composition and function of cells. A person who studies cytology is called a cytologist.
Microbiology:
Is devoted to the study of organisms that can be seen only with a
microscope e.g. bacteria, viruses, some fungi and some protoctists. A
person who studies microbiology is called a microbiologist.
Is devoted to the study of organisms that can be seen only with a
microscope e.g. bacteria, viruses, some fungi and some protoctists. A
person who studies microbiology is called a microbiologist.
Taxonomy: Is the scientific classification of organisms. A person who studies taxonomy is called a taxonomist.
Genetics: Study of heredity and variation in organisms. A person who studies genetics is called geneticist.
The Importance of Studying Biology
Explain the importance of studying biology
The study of biology is very important to man.
The following is an outlines of why the study of biology is important:
- It helps us to understand ourselves better since we are living things.
- Skills
and knowledge of biology can be applied to other scientific fields such
as agriculture, forestry medicine, nutrition, pharmacy and veterinary
science. - It helps us to understand our environment better and principles of conserving it.
- Biology
helps to answer some important questions such as, what do living things
need, why do we resemble with a monkey, why do frogs lay many eggs but
only few become adults? - Knowledge of biology helps us to improve
our health since causes, symptoms, transmission and treatment are of
various diseases are studied in biology. - Knowledge of biology helps us to avoid our selves from magical beliefs, superstitions and other traditional taboos.
- Knowledge
of genetics helps us to clear some common doubts about certain
inherited characteristics e.g. albinism, sickle cell anaemia,
haemophilia, etc. - Knowledge of the structure and chemical composition of the organisms enable us to acquire food, clothes and shelter from them.
Relationship between Biological Science with other Related Fields
Relate biological science with other related fields
Veterinary science (Veterinary medicine)
Veterinary medicine is the branch of medicine that deals with the diseases of animals. Doctors that treat animals are called Veterinarians.
Veterinarians are trained to prevent, diagnose and treat illness in
large and small animals. Their work is valuable because many animal
diseases can be transmitted to human beings e.g. rabies, tuberculosis,
tularemia (rabbit fever) anthrax etc. Basic knowledge of biology is
required for successful study of veterinary science.
Veterinarians are trained to prevent, diagnose and treat illness in
large and small animals. Their work is valuable because many animal
diseases can be transmitted to human beings e.g. rabies, tuberculosis,
tularemia (rabbit fever) anthrax etc. Basic knowledge of biology is
required for successful study of veterinary science.
Agriculture
Agriculture
is concerned with production of useful plants and animals through
farming system. Agriculture provides us with almost all our food. It
provides materials for clothing and shelter. It provides materials used
for making many industrial products such as paints and medicines.
Agriculture uses knowledge of biology to improve plant and animal
breeding. Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) ensure better quality,
early maturity and high yield products. Crop and animal diseases and
pests can only be overcome by applying biological knowledge.
is concerned with production of useful plants and animals through
farming system. Agriculture provides us with almost all our food. It
provides materials for clothing and shelter. It provides materials used
for making many industrial products such as paints and medicines.
Agriculture uses knowledge of biology to improve plant and animal
breeding. Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) ensure better quality,
early maturity and high yield products. Crop and animal diseases and
pests can only be overcome by applying biological knowledge.
Forestry
A forest
is a large area of land covered with trees. It is much more than just
trees. It also includes smaller plants such as mosses, shrubs and wild
flowers. Forestry is the science of managing forest resources for human
benefit. The practice of forestry helps maintain an adequate supply of
timber and management of such valuable forest resources such as water,
wildlife, grazing areas and recreational areas.
is a large area of land covered with trees. It is much more than just
trees. It also includes smaller plants such as mosses, shrubs and wild
flowers. Forestry is the science of managing forest resources for human
benefit. The practice of forestry helps maintain an adequate supply of
timber and management of such valuable forest resources such as water,
wildlife, grazing areas and recreational areas.
Biology
helps in improving the qualities of the trees through manipulating the
genetic constitution of the particular plant species.
helps in improving the qualities of the trees through manipulating the
genetic constitution of the particular plant species.
Climate,
soil and water determine the type of plants to be grown which entirely
applies biological knowledge. Use of biological control to combat tree
pests applies biological principles.
soil and water determine the type of plants to be grown which entirely
applies biological knowledge. Use of biological control to combat tree
pests applies biological principles.
Pharmacy
Pharmacy is the profession concerned with the preparation, distribution and use of drugs. Members of this profession are called pharmacists or druggists.
Pharmacy also refers to a place where drugs are prepared or sold The
drugs are made depending on the chemical composition of the body of an
organism and how they can react with such medicines. Knowledge of
biology also helps to know the effects of drugs on living things
(pharmacology) and possible remedies to be taken.
Pharmacy also refers to a place where drugs are prepared or sold The
drugs are made depending on the chemical composition of the body of an
organism and how they can react with such medicines. Knowledge of
biology also helps to know the effects of drugs on living things
(pharmacology) and possible remedies to be taken.
Medicine
Medicine
is the science and art of preserving health and treating illness.
Medicine is a science because it is based on knowledge gained through
careful study and experimentation. It is an art because its success
depends on how skilfully medical practitioners apply their knowledge in
dealing with patients. The goal of medicine include saving lives,
relieving suffering and maintaining the dignity of sick people.
Biological knowledge helps the doctors, surgeons and nurses to diagnose,
treat and prescribe the right medicine to cure the disease.
is the science and art of preserving health and treating illness.
Medicine is a science because it is based on knowledge gained through
careful study and experimentation. It is an art because its success
depends on how skilfully medical practitioners apply their knowledge in
dealing with patients. The goal of medicine include saving lives,
relieving suffering and maintaining the dignity of sick people.
Biological knowledge helps the doctors, surgeons and nurses to diagnose,
treat and prescribe the right medicine to cure the disease.
Biological
knowledge will also help them to offer education to the patients on how
to prevent themselves from the diseases e.g. purifying drinking water,
vaccination against polio, measles and other diseases.
knowledge will also help them to offer education to the patients on how
to prevent themselves from the diseases e.g. purifying drinking water,
vaccination against polio, measles and other diseases.
Nutrition
Nutrition
is the science which deals with food and how the body uses it. People,
like all living things need food to live. Food provides substances that
the body needs to build and repair its tissues and to regulate its
organs and systems. Food also supplies energy for every action we
perform. Knowledge of biology helps to identify the type of food
required by an individual based on its quality and quantity.
is the science which deals with food and how the body uses it. People,
like all living things need food to live. Food provides substances that
the body needs to build and repair its tissues and to regulate its
organs and systems. Food also supplies energy for every action we
perform. Knowledge of biology helps to identify the type of food
required by an individual based on its quality and quantity.
A table showing differences between plants and animals
| PLANTS | ANIMALS |
| (i)They are autotrophic, i.e. they can make their own food | They are heterotrophic i.e. they feed on complex organic compounds |
| (ii)Contain chlorophyll, can undergo photosynthesis. | No chlorophyll, cannot undergo photosynthesis |
| (iii)Growth occurs in some parts only i.e. root and shoot tips. | Growth occurs in all parts of the body. |
| (iv)They have branched bodies | They have compact bodies |
| (v)No nerves, muscles, blood system or special sensory cells. | Have nerves, muscles, blood system and special sensory cells. |
| (vi)Usually rooted in the ground and do not move from place to place. | Not rooted in the ground, move to get food and escape enemies. |
| (vii)Have no digestive system | Have digestive system needed to break down food |
| (viii)Cells of plants have cell walls | Cells of animals have no cell walls |
Activity 1
Living and non-living things
Aim: to explore living and non-living things around the school
Procedure:Go around the school surroundings. Identify varieties of living and non living things you see.
Make a list of living and non – living things in a tabular form as shown below.
| List of living things | List of non-living things |
Exercise 1
Self test questions
1. Biology is derived from two Greek words namely,
- Logos and Lagos
- Logos and phyla
- Bios and logos
- Bios and phyla
2. The following are characteristics of living things except
- Nutrition
- Reproduction
- Growth
- Dancing
3. A branch of biology which deals with the study of plants is called
- Botany
- Dermatology
- Ecology
- Zoology
4. A person who studies zoology is called
- Botanist
- Virologist
- Zoologist
- Ecologist
5. All of the following are living things except
- Bean plant
- Sand
- Lizard
- Rat
6. Which of the following is the most important basic difference between plants and animals?
- Growth
- Reproduction
- Nutrition
- Movement
7. Which of the following is out of place?
- Excretion
- Virology
- Endocrinology
- Zoology
8. The following is the best description about irritability
- Removal of waste products
- Ability to move from one place to another
- Increase in size of an organism
- Ability to respond to environmental changes
9. The picture below best represents
- Reproduction
- Movement
- Nutrition
- Sensitivity
Picture
10.
A person picks up a telephone after hearing it ringing. Which
characteristics of living things is the person showing by this action?
A person picks up a telephone after hearing it ringing. Which
characteristics of living things is the person showing by this action?
- Excretion and reproduction
- Respiration and nutrition
- Irritability and movement
- Respiration and growth
11. For each of the following write TRUE if the statement is true and FALSE if the statement is not true.
- Biology is a branch of science which deals with the study of living things__________________
- Dancing is one of the characteristics of living things _________________
- A person who studies ecology is called mycologist _________________
- Knowledge of biology can help us to improve our health ________________
- Living things normally increase in size. The process of increasing in size is called growth ________________
12 (a). What do you understand by the following terms?
- Biology
- Cell
- Bacteriology
(b) List down seven (7) characteristics of living things.
13. Give seven differences between living things and non living things.
- Outline the importance of studying biology
- Why are a mosquito and a dog considered to be living things?
14. Give four differences between plants and animals.
- A
motor car moves from place to place, obtains energy by combining petrol
with oxygen and produces waste gases. Does this mean cars are alive?
Look through the seven features, of living things and list those which
do not apply to cars.
15. (a) What do you understand by the following terms?
- Pharmacy
- Forestry
- Veterinary medicine.
(b) State how biology is related to the following science fields
- Pharmacy
- Veterinary medicine
- Agriculture
- Forestry
- Nutrition
- Medicine
Scientific Processes in Biology
Biology,
just like other science subjects, involves carrying out experiments.
When studying living things simple observation can be made by using our
own senses i.e. sight, smell, touch, taste and hearing. The senses can
be detected by our sense organs i.e. eye for sight, nose for smell, skin
for touch, tongue for taste and ear for hearing.
just like other science subjects, involves carrying out experiments.
When studying living things simple observation can be made by using our
own senses i.e. sight, smell, touch, taste and hearing. The senses can
be detected by our sense organs i.e. eye for sight, nose for smell, skin
for touch, tongue for taste and ear for hearing.
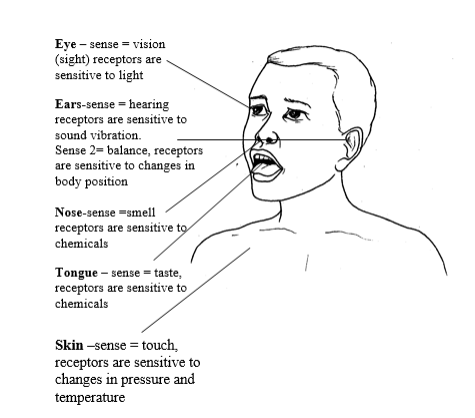
To Use Own Sense Organs to Make Correct Observations
Use own sense organs to make correct observations
The body sense organs
Measurements of Mass, Length, Temperature and Pulse Rate
Take measurements of mass, length, temperature and pulse rate
Measurements: When carrying out biological investigation measurements like mass, time, temperature, and length are unavoidable.
Instruments used for various measurements:
- Beam balance – for measuring mass
- Thermometer – for measuring temperature
- Clock/stopwatch – for measuring time
- Ruler – for measuring length
- Pulse rate can be measured by using a stethoscope or by pressing the fingers firmly on the skin.
The
study of biology like any the science subject involves scientific
processes. The scientific processes involved in the study of biology
include observation, measurement and experimentation. Through these processes the study of biology becomes possible.
study of biology like any the science subject involves scientific
processes. The scientific processes involved in the study of biology
include observation, measurement and experimentation. Through these processes the study of biology becomes possible.
OBSERVATION
Through
observation we can learn many scientific phenomena. Observation is made
by using our own sense organs. There are five sense organs in the human
body which are eyes, ears, the nose, the tongue, and the skin. Each of
these organs is specific to a certain type of observation.
observation we can learn many scientific phenomena. Observation is made
by using our own sense organs. There are five sense organs in the human
body which are eyes, ears, the nose, the tongue, and the skin. Each of
these organs is specific to a certain type of observation.
The following are sense organs and their associated functions in observation.
Eyes
How
can you differentiate between the colors of an egg from that of a ripe
pawpaw? In this case in order to answer this question correctly, you
must be able to make correct observation. By using your eyes you can
observe differences in colors of the two things given and then tell
their differences.
can you differentiate between the colors of an egg from that of a ripe
pawpaw? In this case in order to answer this question correctly, you
must be able to make correct observation. By using your eyes you can
observe differences in colors of the two things given and then tell
their differences.
We
use our eyes as a sense organ for vision. By using our eyes we are able
to see and differentiate sizes, colours and shapes of various organisms
and hence we can learn about them.
use our eyes as a sense organ for vision. By using our eyes we are able
to see and differentiate sizes, colours and shapes of various organisms
and hence we can learn about them.
Ears
How
can you distinguish between the sound produced by a singing bird and a
roaring lion? Sometimes you can just use your ears to study various
biological concepts. For example many organisms produce different sounds
which we can use to identify them.
can you distinguish between the sound produced by a singing bird and a
roaring lion? Sometimes you can just use your ears to study various
biological concepts. For example many organisms produce different sounds
which we can use to identify them.
Therefore,
it is easy for a biologist to know an organism just by hearing the
sound without even seeing it. This proves how your ears are very
important organs in scientific studies because they are used to identify
and differentiate sounds of various living organisms.
it is easy for a biologist to know an organism just by hearing the
sound without even seeing it. This proves how your ears are very
important organs in scientific studies because they are used to identify
and differentiate sounds of various living organisms.
Nose
Sometimes
in the scientific study we need to smell in order to identify and
distinguish between various things. For example, how can you distinguish
the smell of a ripe banana from that of a ripe pineapple? As a
scientist you must be able to use your nose as a sense organ effectively
and successfully. BUT avoid smelling anything in the laboratory without
the permission from your teacher or laboratory technician.
in the scientific study we need to smell in order to identify and
distinguish between various things. For example, how can you distinguish
the smell of a ripe banana from that of a ripe pineapple? As a
scientist you must be able to use your nose as a sense organ effectively
and successfully. BUT avoid smelling anything in the laboratory without
the permission from your teacher or laboratory technician.
Tongue
We
use tongue to taste various things. By use of tongue we can
differentiate various tastes and be able to discover the type of the
taste concerned. For example, one can differentiate salt from sugar
solutions by just tasting using the tongue. BUT avoid tasting anything
in the laboratory unless you are told do so by the teacher or laboratory
technician.
use tongue to taste various things. By use of tongue we can
differentiate various tastes and be able to discover the type of the
taste concerned. For example, one can differentiate salt from sugar
solutions by just tasting using the tongue. BUT avoid tasting anything
in the laboratory unless you are told do so by the teacher or laboratory
technician.
Skin
We
can use the skin as a sense organ to detect heat, temperature, pressure
and even pain. For example, during a hot day you feel hot while during
cold days you feel cold. Even if you close your eyes, and someone rubs
your skin using a block of ice, you can simply tell it by just feeling
the coldness it imparts to the surface of your skin.
can use the skin as a sense organ to detect heat, temperature, pressure
and even pain. For example, during a hot day you feel hot while during
cold days you feel cold. Even if you close your eyes, and someone rubs
your skin using a block of ice, you can simply tell it by just feeling
the coldness it imparts to the surface of your skin.
This
group of students are conducting an experiment on ‘food tests’ in the
school laboratory. Can you tell the sense organs they are using in their
study?
group of students are conducting an experiment on ‘food tests’ in the
school laboratory. Can you tell the sense organs they are using in their
study?
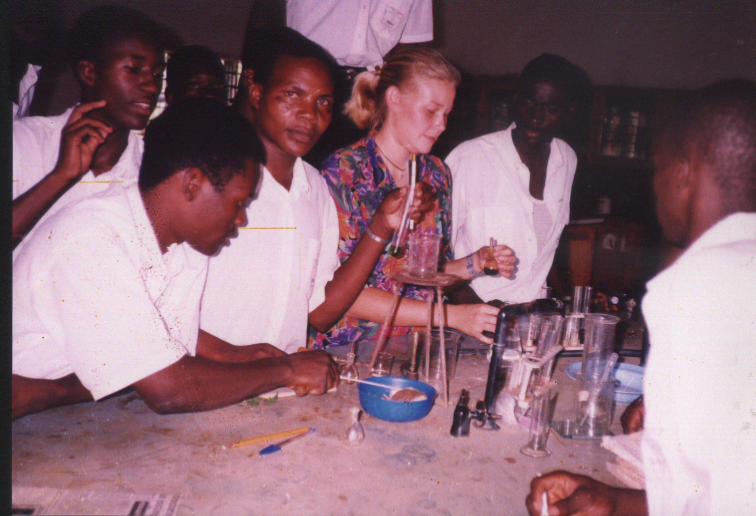

MEASUREMENT
Though
we can use our sense organs to make observations, the observations
alone are not so reliable. Every sense organ has its weakness. Since
science lies upon measurable quantities there is a need of measurement.
Scientists have been able to design ways to take measurements of various
things. Some of the quantities which can successfully be measured
include mass, temperature, length and pulse rate.
we can use our sense organs to make observations, the observations
alone are not so reliable. Every sense organ has its weakness. Since
science lies upon measurable quantities there is a need of measurement.
Scientists have been able to design ways to take measurements of various
things. Some of the quantities which can successfully be measured
include mass, temperature, length and pulse rate.
Measurement of length
We
can use eyes to observe the length of various objects. However, our
eyes can just tell which object is longer than the other but can not
tell us what the exact length of each object is. Tape measure is one of
the common instruments that are used for measuring length in our every
day life.
can use eyes to observe the length of various objects. However, our
eyes can just tell which object is longer than the other but can not
tell us what the exact length of each object is. Tape measure is one of
the common instruments that are used for measuring length in our every
day life.
Tape measure, an instrument for measuring length
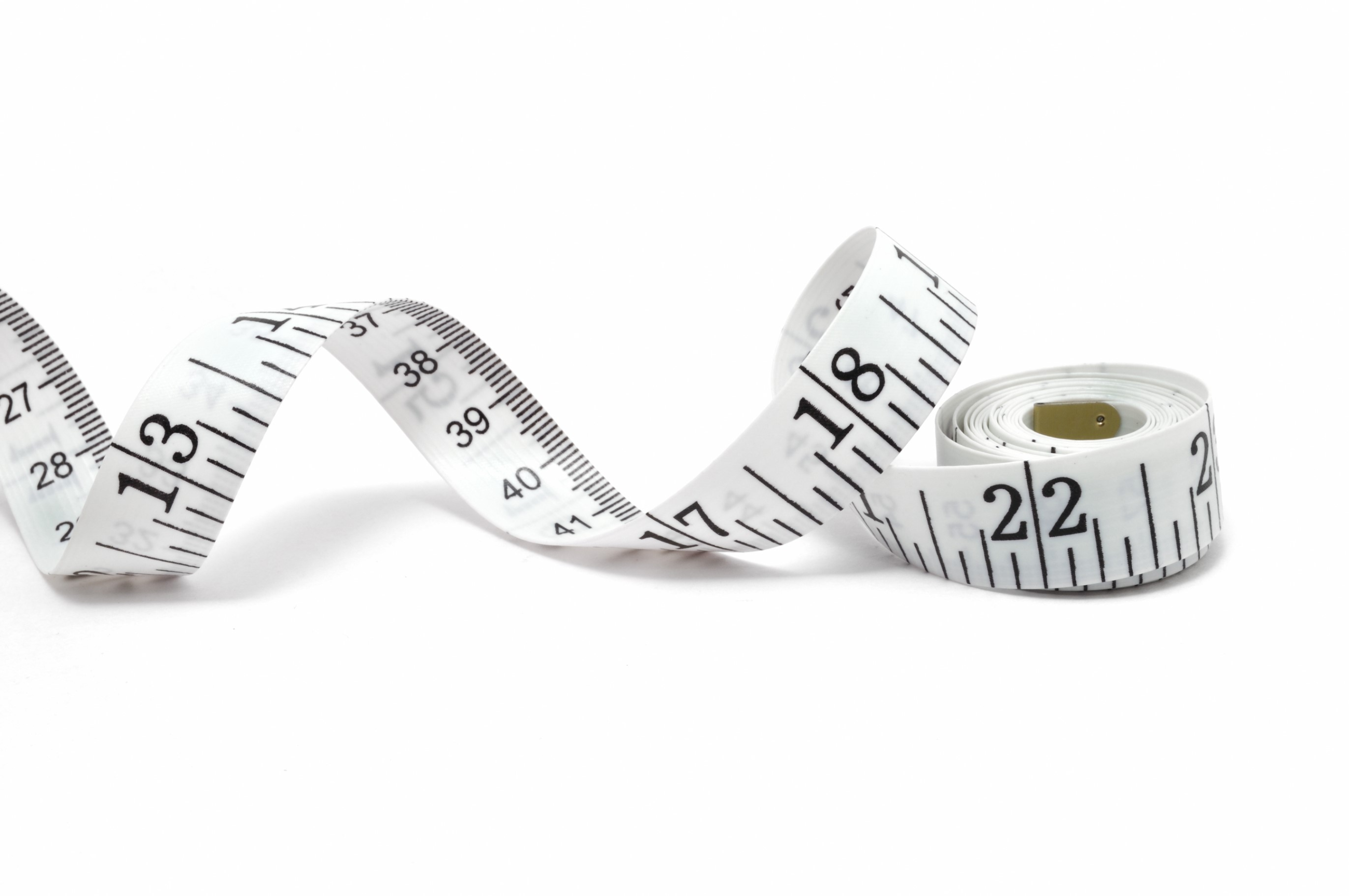

Measurement of mass
A
scientist or biologist must have a standard way of measuring mass of a
substance. Sense organs cannot give us the true value of mass of a
substance. This can be done by using beam balance which is a special
instrument for measuring mass of a substance.
scientist or biologist must have a standard way of measuring mass of a
substance. Sense organs cannot give us the true value of mass of a
substance. This can be done by using beam balance which is a special
instrument for measuring mass of a substance.
Beam balance

Measurement of temperature
We
can take the measurement of temperature of a substance just by using
our sense organs. For example, by touching something you can tell
whether a particular thing is hot or cold. However, you cannot tell
exact temperature of an object.
can take the measurement of temperature of a substance just by using
our sense organs. For example, by touching something you can tell
whether a particular thing is hot or cold. However, you cannot tell
exact temperature of an object.
Therefore,
to be able to know the exact temperature you need to use an instrument
specially designed for measuring the temperature. This is instrument is
the thermometer. Using thermometers we are able to know the exact
temperature of an object.
to be able to know the exact temperature you need to use an instrument
specially designed for measuring the temperature. This is instrument is
the thermometer. Using thermometers we are able to know the exact
temperature of an object.
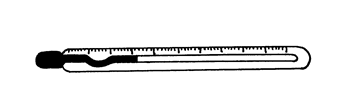
Thermometer

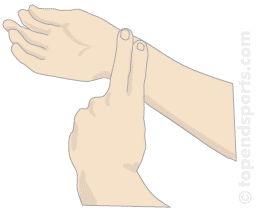
Measurement of pulse rate
Pulse
rate refers to average beating of your heart. You can find how fast
your heart is beating, that is your heart rate, by feeling your pulse.
rate refers to average beating of your heart. You can find how fast
your heart is beating, that is your heart rate, by feeling your pulse.
How to measure your pulse rate
- Sit down comfortably on a chair with the palm of your hand facing upwards.
- Gently
place the index and middle fingers of your other hand on your wrist
(see the diagram below). Can you feel your pulse as a repeated throb? - If
necessary change the position of your finger until you can feel your
pulse rate well. Count the number of heart beats in one minute. - Repeat step 3 four times.
- Write down the number of beats per minute.
- Work out the average. This is what is called average heart rate per minute. It tells you how fast your heat is beating.
Measuring the pulse rate
EXPERIMENTATION
Biology
as a science subject involves practical work. In every area of biology,
experimentation is necessary. However, there are several procedures to
be followed in conducting any scientific investigation. These procedures
include the following:
as a science subject involves practical work. In every area of biology,
experimentation is necessary. However, there are several procedures to
be followed in conducting any scientific investigation. These procedures
include the following:
Identification of a problem (problem statement)
In
our day to day life we often come across questions or phenomena which
require explanations. Such questions or phenomena are of interest to a
biologist who will seek to provide answers to them.
our day to day life we often come across questions or phenomena which
require explanations. Such questions or phenomena are of interest to a
biologist who will seek to provide answers to them.
The phenomena could be for example; it
was observed that the harvest of tomatoes in Juma’s garden was low
despite frequent irrigation, correct planting techniques, timely
planting and adequate sunlight. So, what was the problem with Juma’s garden?
was observed that the harvest of tomatoes in Juma’s garden was low
despite frequent irrigation, correct planting techniques, timely
planting and adequate sunlight. So, what was the problem with Juma’s garden?
This is the problem to be investigated by the biologist in order to come up with an answer.
Hypothesis formulation
Hypothesis
is a tentative explanation for the observation made. Using your example
of low yield in the tomato garden, the possible hypothesis could be poor
yield could have been caused by low soil fertility and therefore
application of the fertilizer could increase harvest of the tomatoes in
the garden. This hypothesis must therefore be tested by experimentation if it has to be a scientifically acceptable explanation.
is a tentative explanation for the observation made. Using your example
of low yield in the tomato garden, the possible hypothesis could be poor
yield could have been caused by low soil fertility and therefore
application of the fertilizer could increase harvest of the tomatoes in
the garden. This hypothesis must therefore be tested by experimentation if it has to be a scientifically acceptable explanation.
Experimentation
An
experiment is a series of investigation intended to discover
relationship or certain facts that may lead to finding a problem. In the
case of low harvest of tomatoes, you are first supposed to construct a
plan of investigation as follows:
experiment is a series of investigation intended to discover
relationship or certain facts that may lead to finding a problem. In the
case of low harvest of tomatoes, you are first supposed to construct a
plan of investigation as follows:
Select
two plots, A and B, from the same garden and subject both of them to
the same conditions as before. In plot B apply fertilizers while in plot
A don’t put any fertilizers (plot A will be your control plot).
two plots, A and B, from the same garden and subject both of them to
the same conditions as before. In plot B apply fertilizers while in plot
A don’t put any fertilizers (plot A will be your control plot).
Observation and data recording
After
setting up an experiment, a researcher must observe and record data.
Observation is done by using sense organs such as ears, eyes, nose and
skin. The researcher must record whatever he observes. The researcher
obtained X kg in plot A and Y kg in plot B.
setting up an experiment, a researcher must observe and record data.
Observation is done by using sense organs such as ears, eyes, nose and
skin. The researcher must record whatever he observes. The researcher
obtained X kg in plot A and Y kg in plot B.
Interpretation of data
Once
a researcher has collected data, he should try to explain the meaning
of data in relation to the purpose of the experiment. In the tomato
garden experiment, the harvest in plot A was little compared to the
harvest in plot B.
a researcher has collected data, he should try to explain the meaning
of data in relation to the purpose of the experiment. In the tomato
garden experiment, the harvest in plot A was little compared to the
harvest in plot B.
In
these plots, all the conditions were the same except that in plot A no
fertilizers were applied while in plot B fertilizers were applied.
Therefore, high harvest in plot B was a result of applying fertilizers.
If this experimentation is correct, then the same results should be
obtained if the experiment is repeated under the same conditions.
these plots, all the conditions were the same except that in plot A no
fertilizers were applied while in plot B fertilizers were applied.
Therefore, high harvest in plot B was a result of applying fertilizers.
If this experimentation is correct, then the same results should be
obtained if the experiment is repeated under the same conditions.
Conclusion
At
the end of investigation, a researcher must draw conclusion. This
conclusion is based on the collected data. The conclusion is either
confirmation or rejection of the hypothesis under investigation.
the end of investigation, a researcher must draw conclusion. This
conclusion is based on the collected data. The conclusion is either
confirmation or rejection of the hypothesis under investigation.
In
the tomato garden experiment, the results have shown that application
of fertilizers has increased the harvest of tomatoes. Therefore, low
harvest of tomatoes was caused by poor soil fertility.
the tomato garden experiment, the results have shown that application
of fertilizers has increased the harvest of tomatoes. Therefore, low
harvest of tomatoes was caused by poor soil fertility.
Summary
The following diagram summarizes the scientific process.
The scientific process
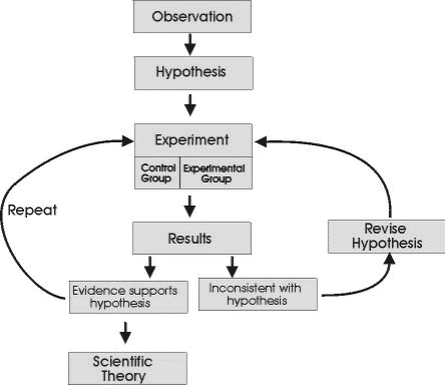
Activity 2
Aim: observing different conditions and substances using various sense organs: Materials: flowers of different colors, hot water, ice, a bottle of perfume, whistle, lemon, knife.
Procedure:
- Take the different flowers provided. Name the color of each flower.
- Open the bottle of perfume, try to smell it. What is the smell of the perfume?
- Use a knife to cut the onion. Where in your body do you feel sensation when cutting the onion?
- Take
two beakers. One of the beakers put hot water and the other put ice
block with a little amount of water. Dip a finger in a beaker containing
hot water and do the same for a beaker containing ice block. What
sensation did you feel in the two beakers? - Take a whistle and try to blow it using your mouth. What is coming out of the blow?
For
each of the stimulus experienced in procedures 1-5 name the sense organ
involved in detection of each stimulus and present your results as
shown in the table below. The first option has been done for you as an
example.
each of the stimulus experienced in procedures 1-5 name the sense organ
involved in detection of each stimulus and present your results as
shown in the table below. The first option has been done for you as an
example.
| Procedure | Stimulus | Sense organ involved for detection |
| 1 | Colour | Eyes |
| 2 | ||
| 3 | ||
| 4 | ||
| 5 |
Activity 3
Aim: measurement of length and masses Materials: meter rule, Tilapia fishes, board, weighing scale
Procedure:
- Take 5 Tilapia fishes and number them as 1 to 5.
- Take Tilapia fish number 1, place it on a board and measure its length.
- Take Tilapia fish number 1, put it on a weighing scale and record its mass.
- Repeat steps 2 and 3 for Tilapia fish number 2, 3, 4, and 5.
Present your results in a tabular form as shown
| Tilapia fish no | Length (cm) | Mass (g) |
| 1 | ||
| 2 | ||
| 3 | ||
| 4 | ||
| 5 |
Activity 4
Questions
- Which Tilapia has the greatest length?
- Which Tilapia has a greatest mass?
- Is there any Tilapia fish which has a shorter length but has a greater mass than the longer one?
- Arrange the fishes in order of their increasing
One of the following can be used to make observation during scientific investigation
- Nose
- Blood vessels
- Teeth
- Lung
All of the following are used for various measurements except
- Beam balance
- Thermometer
- Ruler
- Hand lens
Which of the following is not true?
- Eye for sight
- Skin for touch
- Tongue for vision
- Nose for smell
Body temperature can be measured using
- Chemical balance
- Stop watch
- Measuring cylinder
- Thermometer
A third step in scientific investigation is
- Hypothesis
- Problem identification
- Experimentation
- Conclusion
Hypothesis means
- An idea
- A school of thought
- An intelligent guess
- An opinion
Which of the following will be a sequence to follow in a scientific procedure after ‘experimentation’?
- Problem identification
- Conclusion
- Observation and data recording
- Hypothesis formulation
An experiment is carried out to test
- Hypothesis
- Theory
- Law
- Conclusion
Name the instruments used to measure
- Mass
- Length
- Pulse rate
- Temperature
Name
the five sense organs used to make observation during scientific
investigation and state the senses perceived by each sense organ.
the five sense organs used to make observation during scientific
investigation and state the senses perceived by each sense organ.
Outline the six steps involved when carrying out scientific investigation.
Define the following terms:
- Hypothesis
- Experimentation
Simple Biological Experiments
Carry out simple biological experiments
Activity 5
Carry out a simple biological experiment in relation to the above topics.
The Biology Laboratory
The Biology Laboratory
Describe the biology laboratory
A biology laboratory is a room or building specially designed for carrying out biological experiments.
A biology laboratory has:
- Large windows and big space to allow enough air and light for better ventilation and visibility respectively.
- Shelves – for keeping chemicals, specimens, apparatus and models.
- Supply of gas, electricity and water
- Working benches
- An emergence door in case of danger occurs.
- Preparation room
The biology laboratory rules
Biology
laboratory has sophisticated instruments which need to be handled with
special care. Chemicals which are being used are potentially harmful and
they need a special attention when working with them.
laboratory has sophisticated instruments which need to be handled with
special care. Chemicals which are being used are potentially harmful and
they need a special attention when working with them.
The following laboratory rules should be adhered to:
- Don’t enter in the laboratory without permission from the teacher or laboratory technician.
- Do not play, or run unnecessarily in the laboratory.
- Do not eat or drink in the laboratory.
- Do not use chemicals or handle apparatus or specimens without instruction from the teacher or laboratory technician.
- Any accident or damage of apparatus must be reported.
- Label chemicals and specimens to avoid confusion.
- Always keep flammable substances away from flames.
- Turn off water and gas taps after use.
- Never point the open end of the test tube to your fellow or yourself when heating.
- Never smell substances, specimens, chemicals or gases directly.
- Wash your hands with soap after the experiment.
- Clean the apparatus and benches after the experiment.
- Return the apparatus and chemicals to their normal position after use.
The Difference between the Biology Laboratory from other School Facilities
Distinguish the biology laboratory from other school facilities
Difference between biology laboratory and other school facilities:
- Dissecting kits
- Models of different organs and systems
- Refrigerators and ovens for storing and drying specimens
- Animal keeping units
- Chemicals designed for biological experiments
- Preserved specimens of living things
- Gases, electricity and water supply.
Aim: To differentiate biology laboratory from other school laboratories or facilities
Procedure:
let students visit the chemistry laboratory, physics laboratory, the
school library, classroom and school store and allow them to perform the
following.
let students visit the chemistry laboratory, physics laboratory, the
school library, classroom and school store and allow them to perform the
following.
- Make a list of items that are found in each of the above named areas.
- Compare the list with those which are found in the biology laboratory.
- Construct
a table of differences showing a list of items which are found in the
biology laboratory and those which are found in the above named school
facilities as shown below. - List items which are found in both the biology laboratory and other school facilities listed above and compare the differences.
| Facility / Building | Items |
| Biology laboratory | |
| Chemistry laboratory | |
| Physics laboratory | |
| School library | |
| Classroom | |
| School store |
Interpretation of Warning Signs on Containers of Laboratory Chemicals and Apparatus
Interpret warning signs on containers of laboratory chemicals and apparatus
Warning signs on laboratory chemicals and apparatus
Some
of the chemicals and apparatus used in biology laboratory may be
harmful or dangerous. Before starting using any chemical you must know
whether the chemical is toxic, flammable, oxidizing, explosive or
irritant/harmful. To help you recognize such dangerous substances, the
containers of modern chemicals carry special chemical warning signs as
indicated below.
of the chemicals and apparatus used in biology laboratory may be
harmful or dangerous. Before starting using any chemical you must know
whether the chemical is toxic, flammable, oxidizing, explosive or
irritant/harmful. To help you recognize such dangerous substances, the
containers of modern chemicals carry special chemical warning signs as
indicated below.
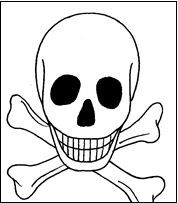
Toxic
Toxic
substances can cause death. They may be poisonous when swallowed,
breathed in or absorbed through the skin. Examples of toxic substances
include acids and alkalis, lead II acetate and potassium dichromate.
substances can cause death. They may be poisonous when swallowed,
breathed in or absorbed through the skin. Examples of toxic substances
include acids and alkalis, lead II acetate and potassium dichromate.
The symbol for toxic substances is represented as shown above.
Flammable
Flammable
substances are substances which can catch fire easily. Examples of such
substances include petrol, alcohol, Thomas Baker (Phosphorus yellow or
phosphorus red) and potassium metal. These substances normally evaporate
fast and therefore should not be brought near open flames. The symbol
is as indicated above.
substances are substances which can catch fire easily. Examples of such
substances include petrol, alcohol, Thomas Baker (Phosphorus yellow or
phosphorus red) and potassium metal. These substances normally evaporate
fast and therefore should not be brought near open flames. The symbol
is as indicated above.

Corrosive
Corrosive
substances attack and destroy living tissues. They may destroy the
floor, desks as well as metals, examples of corrosive substances are
concentrated acids, e.g. sulphuric acid, hydrochloric acid, nitric acid
and concentrated alkalis e.g. sodium, potassium and ammonium hydroxides.
If by accident a corrosive substance comes into contact with your skin,
go to the sink and wash with a lot of water. The symbol is shown above.
substances attack and destroy living tissues. They may destroy the
floor, desks as well as metals, examples of corrosive substances are
concentrated acids, e.g. sulphuric acid, hydrochloric acid, nitric acid
and concentrated alkalis e.g. sodium, potassium and ammonium hydroxides.
If by accident a corrosive substance comes into contact with your skin,
go to the sink and wash with a lot of water. The symbol is shown above.
Oxidant
An
oxidant is a chemical or substance which accelerates burning. Small
fires can be made big in the presence of oxidizing agent. Examples of
oxidizing agents include potassium permanganate, potassium chlorate, and
zinc nitrate.
oxidant is a chemical or substance which accelerates burning. Small
fires can be made big in the presence of oxidizing agent. Examples of
oxidizing agents include potassium permanganate, potassium chlorate, and
zinc nitrate.

Explosive
An explosion is a forceful rapid reaction which involves random throwing of particles
Harmful or irritant
Harmful
substances have a long term effect. They do not kill immediately. They
have a cumulative effect. Therefore careful handling is required.
substances have a long term effect. They do not kill immediately. They
have a cumulative effect. Therefore careful handling is required.
Irritant
substances cause pains on the skin or eyes. They can endanger one’s
health if they come into contact with the skin or eyes for too long.
Examples of harmful substances include lead chloride, lead nitrate, lime
water ferrous sulphate and manganese (IV) oxide
substances cause pains on the skin or eyes. They can endanger one’s
health if they come into contact with the skin or eyes for too long.
Examples of harmful substances include lead chloride, lead nitrate, lime
water ferrous sulphate and manganese (IV) oxide
Examples above of some chemical containers with their warning signs.

Activity 6
Aim: to investigate chemical warning signs Requirements: varieties of chemical containers Procedure: collect chemical containers. Observe them carefully and identify chemical warning signs on them.
Record your results as shown in the table that follows.
| Chemical container | Warning sign |
The Common Apparatus and Equipment of Biology Laboratory
Identify common apparatus and equipment of biology laboratory
Some apparatus and equipment used in the biology laboratory.
- Microscopes
- Hand lenses
- Thermometers
- Dissecting kits
- Mortar and pestle
- Dissecting trays
- Delivery tubes
- Measuring cylinders
- Bunsen burners
- Test tubes
- Specimen bottles
- Ovens
- A pair of scissors
- Chemical balance
- Funnel
- Test tube racks
- Test tube holders
- Beakers
- Forceps
- Surgical blades
- Microscope slides
- Droppers
- Spatula
- Corks
- Glass straws
- Fridge/refrigerator
- Mounted needle
- Beam balances
- Glass rods
- Scalpels
Microscope

Thermometers
Hand lenses
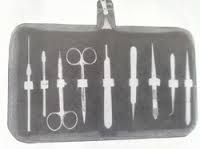
Dissecting kit
Motor and Pestle
Dissecting tray

Delivery tube
Measuring cylinder
Bunsen Burner
Test tube
Specimen Bottles

Oven

Pair of scissors
Funnel
Surgical blades

Microscopic blades

Spatula
Cork
Glass straws

Mounted Needle
Beam balance

Glass rod

Scalpels
Dropping pipette
Fridge/refrigerator

Some common chemicals used in the biology laboratory
- Benedict’s solution
- Lime water (calcium hydroxide)
- Sodium hydroxide (slaked lime)
- Cobalt chloride
- Hydrochloric acid
- Copper (II) sulphate
- Sudan III
- Alcohol
- Stains e.g. carmine red, methylene blue
- Sodium bicarbonate
- Potassium permanganate
- Iodine solution
Exercise 2
In each of the following questions write TRUE for correct statement and FALSE for incorrect statement.
- A biology laboratory is a place where biological experiments are conducted……………………………….
- Everything in the laboratory can be tasted ………………
- Warning signs can help someone to avoid accident in the laboratory…………………………………………………
One of the following is not a basic quality of the biology laboratory.
- Working benches
- Large windows and big space
- Supply of gas, electricity and water
- Kitchen
Substances which may catch fire easily are said to be
- Toxic
- Flammable
- Explosive
- Irritant
An instrument used to measure temperature of the body is called
- Chemical balance
- Measuring cylinder
- Thermometer
- Barometer
One of the following is a common reagent used in the biology laboratory
- Benedict’s solution
- Potassium iodide
- Sodium acetate
- Barium chloride
Which of the following list of instruments is not related to biology laboratory?
- Fridge, a pair of scissors, surgical blades
- Microscope, test tube, thermometer
- Dissecting kit, scalpel, beaker
- Meter bridge, pendulum bob and burette.
The warning sign shown indicates
- Explosive substance
- Oxidizing agent
- Flammable substance
- Corrosive substance

Match the items in list A with the corresponding items in list B.
LIST A
- Used for placing specimen during dissection
- An apparatus used for stirring solution
- A substance which accelerates burning
- Do not play or run in the laboratory
- A common reagent in the biology laboratory
LIST B
- Laboratory rule
- Oxidant
- Sudan III
- Dissecting kit
- Glass rod
What do you understand by the following terms?
- Laboratory
- Warning sign
Draw warning signs which may be used in bottles carrying a substance which is
- toxic
- flammable
- explosive
- harmful
List down any six (6) laboratory rules
State the use of the following apparatus
- Specimen bottles
- Test tube holders
- Beam balance
- Beaker
- Mortar and pestle
Draw the following apparatus:
- Measuring cylinder
- Mortar and pestle
- Funnel
- Tripod stand.
THE MICROSCOPE
Much
of the living world is too small for human eyes to see. Our eyes can
only see objects that are larger than 0.1mm. Objects with sizes smaller
than 0.1mm can be viewed by using microscopes.
of the living world is too small for human eyes to see. Our eyes can
only see objects that are larger than 0.1mm. Objects with sizes smaller
than 0.1mm can be viewed by using microscopes.
What is a microscope?
A
microscope is an instrument used for viewing objects which are too
small to be seen by our naked eyes. It ranks as one of the most
important tools of science.
microscope is an instrument used for viewing objects which are too
small to be seen by our naked eyes. It ranks as one of the most
important tools of science.
- Physicians and biologists, for example, use microscopes to examine bacteria and blood cells.
- Material
scientists and engineers use microscopes to study the crystal
structures within metals and alloys (metal mixtures) and to examine
computer chips and other tiny electronic devices.
There are two types of microscopes
- Compound or light microscope
- Electron microscope
Optical or light microscope
An
optical microscope has one or more lenses that refract (bend) the light
rays that shine through or are reflected by the specimen being
observed. The refracted light rays make the specimen appear much larger
than it is.
optical microscope has one or more lenses that refract (bend) the light
rays that shine through or are reflected by the specimen being
observed. The refracted light rays make the specimen appear much larger
than it is.
Magnifying
glass is the simplest optical microscope, has only one lens. The best
magnifying glasses can magnify an object by 10 to 20 times.
glass is the simplest optical microscope, has only one lens. The best
magnifying glasses can magnify an object by 10 to 20 times.
The compound or light microscope
The
compound or light microscope uses two or more sets of lenses to provide
higher magnifications. Each set of lenses functions as a unit and is
referred to as lens system. In microscopes with only
one objective, the lens system and ocular are mounted at opposite ends
of a tube. In microscopes with two or more objectives the objectives are
mounted in a rotating nose piece connecting to the end of the tube
opposite the ocular. The person operating the microscope rotates the
nose piece to align one of the objectives with the opening in the end of
the tube.
compound or light microscope uses two or more sets of lenses to provide
higher magnifications. Each set of lenses functions as a unit and is
referred to as lens system. In microscopes with only
one objective, the lens system and ocular are mounted at opposite ends
of a tube. In microscopes with two or more objectives the objectives are
mounted in a rotating nose piece connecting to the end of the tube
opposite the ocular. The person operating the microscope rotates the
nose piece to align one of the objectives with the opening in the end of
the tube.
The workings of electron and compound microscope
Electron microscope – Uses electrons to illuminate the specimen and can
reveal much more structures than light microscope can do.
Electron microscope – Uses electrons to illuminate the specimen and can
reveal much more structures than light microscope can do.
Light microscope – Uses light to illuminate the specimen
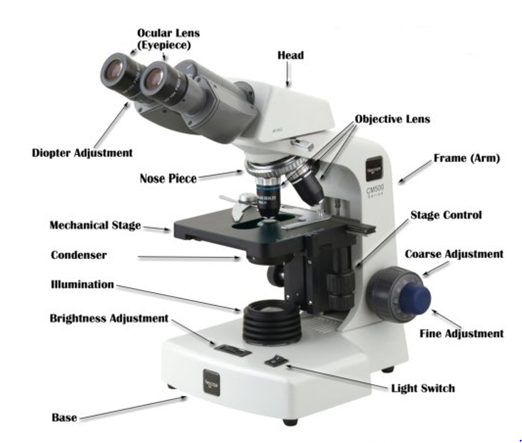
Parts of the light microscope and their functions
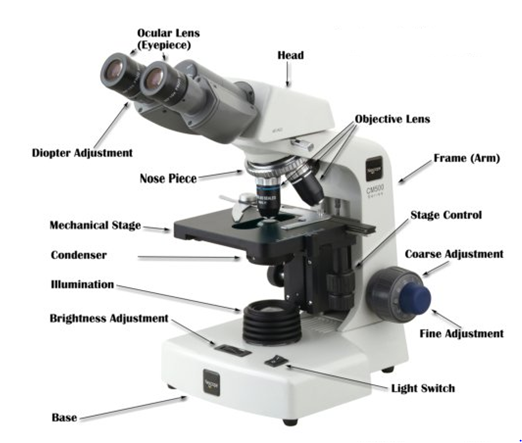

Parts of the light microscope has the following functions:
- Eyepiece – Magnify objects under observation since it consists of magnifying lenses.
- Body tube – Hollow tube attached to the arm. Its function is to hold eyepiece lens and revolving nose piece.
- Revolving nose piece – Holds objective lenses in place. Position of the objective lenses can be changed by manipulating the revolving nose piece.
- Coarse adjustment knob – It lowers and raises the body tube so that a clear image is obtained.
- Fine adjustment knob – Raises and lowers the body tube to obtain a fine focus.
- Objective lens – Brings image into focus and magnifies it.
- Stage – This is a place where specimen to be observed is placed
- Clips – Hold the slide or specimen in position
- Mirror – Reflects and directs light to the object under observation.
- Diaphragm – Is an aperture that regulates the amount of light passing through the condenser to illuminate the specimen
- Condenser – Concentrates light reflected by the mirror.
- Base or stand – Supports the microscope steadily
- Arm or limb – Supports the body tube and stage. It is used to hold the microscope
- Hinge screw – Raises and lowers the stage.
Magnification
Magnification
power is symbolized by a number and abbreviation X. For example a 10X
magnifying glass magnifies an object by 10 times. An object is magnified
by multiplying the eyepiece lens magnification and objective lens
magnification.
power is symbolized by a number and abbreviation X. For example a 10X
magnifying glass magnifies an object by 10 times. An object is magnified
by multiplying the eyepiece lens magnification and objective lens
magnification.
Example:
Magnification = eyepiece lens x objective lens magnification
= 10 × 20= X200
A table of magnification
| Eye piece lens magnification | Objective lens magnification | Total magnification |
| 5 | 20 | X100 |
| 10 | 20 | X200 |
| 15 | 10 | X150 |
| 10 | 25 | X250 |
| 20 | 20 | X400 |
How to use a microscope
- Turn on your microscope light
- Turn the nose piece so that the small (low power) objective lens clicks into place. Always start with low power lens in place.
- Place
the prepared slide on the center of the stage under the clips so that
the object is in the center of the opening. Make sure the cover slip is
on top - With your eye at stage level, use the coarse adjustment
to bring the object and the low power objective lens as near to each
other as possible. The objective lens should not touch the cover slip - Now
with your eye to the eyepiece, slowly move the coarse adjustment to
increase the distance between the object and the lens. Continue this
until the image is focused. - Adjust the diaphragm so that the object can be seen as clearly as possible
- To
observe the object under medium and high powers, rotate the revolving
nose piece to bring the next highest objective lens into position. Make
sure you hear the ‘click’ to ensure that the objective lens is in place.
Then, focus using the fine adjustment only.
Ways of handling and carrying a light microscope
- Use both hands to carry the microscope. One hand should hold the base and the other hand should hold the arm.
- Always place the microscope on the desk or table carefully and gently and never place it at the edge of the bench.
- Keep the microscope in an upright position when using liquids or when not in use.
- Keep the stage clean and dry. If any liquids are spilled on the microscope, wipe them up immediately with a piece of tissue.
- Focus with the low-power objective lens first.
- Focus by moving the lens away from the slide, that is, by increasing the working distance.
- Consult your teacher if the lenses are dirty.(viii) Consult your teacher if the adjustments do not work freely.
- When your work is completed, move the low power objective lens into place and remove your slide.
- Keep your microscope covered when it is not in use and keep your work area clean and tidy.
ELECTRON MICROSCOPE
This
type of microscope uses a beam of electrons rather than a beam of light
to produce magnified images. Electron wave lengths are much shorter
than those of visible light. As a result electron microscopes can
resolve much finer detail than light microscope can do.
type of microscope uses a beam of electrons rather than a beam of light
to produce magnified images. Electron wave lengths are much shorter
than those of visible light. As a result electron microscopes can
resolve much finer detail than light microscope can do.

Types of electron microscopes
- Transmission
electron microscope (TEM) This type of a microscope passes a broad beam
of electrons through a specimen slice a few hundred angstroms thick. - Scanning electron microscope (S E M) This microscope scans a focused beam across the surface of the specimen.
Other kinds of microscopes
Scanning probe microscope The microscope scans a specimen with a sharp point called a probe.
The ion microscope (field -ion microscope)
It is used to examine metals. It creates an image of the crystal
structure of the tip of an extremely sharp metal needle. An electric
field applied to the tip repels charged helium, neon or argon atoms
which spread out and strike a special screen. The screen glows where the
atoms strike it, forming an image of the arrangement of atoms in the
metal.
It is used to examine metals. It creates an image of the crystal
structure of the tip of an extremely sharp metal needle. An electric
field applied to the tip repels charged helium, neon or argon atoms
which spread out and strike a special screen. The screen glows where the
atoms strike it, forming an image of the arrangement of atoms in the
metal.
Exercise 3
Which kind of microscope uses electrons to illuminate the specimen?
- Electron microscope
- Metal microscope
- Light microscope
- Compound microscope
Which part of the microscope holds objective lenses?