Download & Install
Darasa Huru App
DOWNLOAD
TOPIC 2: GENETICS | BIOLOGY FORM 4
Concept of Genetics
is the study of heredity and variations in organism. Through this
statement there are two common words that are heredity and variation.
state of possessing two identical forms of a particular gene, one
inherited from each parent. For example, a girl who is homozygous
forcystic fibrosis(CF) received the cystic fibrosis gene from both of
her parents and therefore she has cystic fibrosis.
Heterozygosity
Thestateofbeingheterozygous;havingtwodifferentallelesofthesamegene
is a condition where an allele can express itself in the presences of
other alleles. Example: ‘Tt’ where ‘T’ is the dominant that expresses
its effect in the presence of ‘t’.
condition where an allele can only express itself when they are in
homozygous form but does not express its effect on the presence of other
alleles.
Genetics Materials
characteristics are passed from parents to their offspring through
distinct units called genes.There are a lot of genes in an organism’s
body. Genes are arranged in a linear manner, making chromosomes.
Chromosomes
are thread like structures found in the nuclei of all body cells. Gene
is made up of chemical substances called Nucleic acid.
- Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
- Ribonucleic acid (RNA)
These
acids are made up of building blocks called nucleotides. Each
nucleotide consists of three molecules linked together, that is a
pentose sugar, phosphoric acid and organic base.
is called the “molecule of life”. This is because it determines the
physical and behavioural characteristics of an organism. The DNA
determines example the colour of your hair, eyes, skin, ears and nose,
height, ability or inability to roll the tongue all.
is a double stranded helical (spiral) molecular chain of a nucleic
found within the nucleus of a cell.By “double stranded helical” it means
that the DNA consists of two strands, which twist around each other in a
spiral fashion.
The
polynucleotide chain runs in the opposite direction. Each chain is
joined to the other by pairs of bases. There are four bases namely
Guanine (G), Cytosine ©, Adenine (A) and Thymine (T)
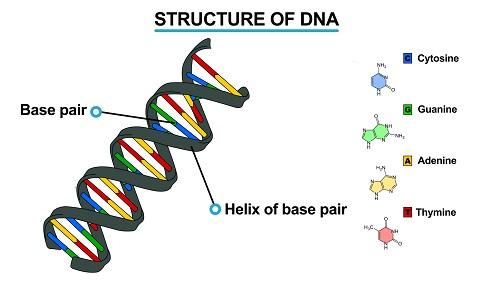
Note:
pairs with cytosine and adenine pairs with thymine.DNA plays a key role
in inheritance because it replicates itself during mitosis and meiosis.
DNA also undergoes changes and has genetic information the
characteristics of a species.
chromosomes determine the type of protein synthesized. The genes
determine the actual characteristics of the organisms. In protein
synthesis deoxyribonucleic acid acts as a template for the formation of
ribonucleic acid (RNA).
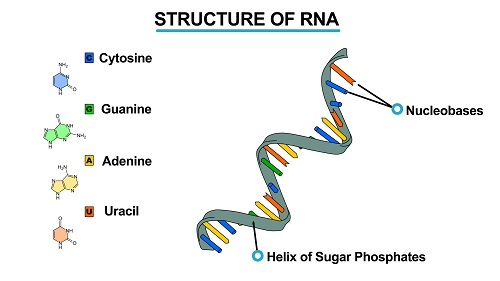
RNA
consists of only a single strand of polynucleotide. The polynucleotide
is made up of many nucleotides. Each nucleotide consists of a
nucleobase, ribose sugar and phosphate group.The RNA sugar is ribose and
not deoxyribose. Its nucleotides contain only one of four bases that
are:
- Guanine (G)
- Cytosine (C)
- Adenine (A)
- Uracyl (U)
- Messenger (mRNA)
- Transfer (tRNA)
- Ribosomal (rRNA)
| DNA | RNA | |
|---|---|---|
| Stands For | DeoxyriboNucleicAcid. | RiboNucleicAcid. |
| Definition | A nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all modern living organisms. DNA’s genes are expressed, or manifested, through the proteins that its nucleotides produce with the help of RNA. |
Theinformation found in DNA determines which traits are to be created, activated, or deactivated, while the various forms of RNA do the work. |
| Function | The blueprint of biological guidelines that a living organism must follow to exist and remain functional. Medium of long-term, stable storage and transmission of genetic information. |
Helps carry out DNA’s blueprint guidelines. Transfers genetic code needed for the creation of proteins from the nucleus to the ribosome. |
| Structure | Double-stranded. It has two nucleotide strands which consist of its phosphate group, five-carbon sugar (the stable 2-deoxyribose), and four nitrogen-containing nucleobases: adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine. |
Single-stranded. Like DNA, RNA is composed of its phosphate group, five-carbon sugar (the less stable ribose), and four nitrogen-containing nucleobases: adenine, uracil (not thymine), guanine, and cytosine. |
| Base Pairing | Adenine links to thymine (A-T) and cytosine links to guanine (C-G). | Adenine links to uracil (A-U) and cytosine links to guanine (C-G). |
| Location | DNA is found in the nucleus of a cell and in mitochondria. | Depending on the type of RNA, this molecule is found in a cell’s nucleus, its cytoplasm, and its ribosome. |
| Stability | Deoxyribose sugar in DNA is less reactive because of C-H bonds. Stable in alkaline conditions. DNA has smaller grooves, which makes it harder for enzymes to “attack.” |
Ribose sugar is more reactive because of C-OH (hydroxyl) bonds. Not stable in alkaline conditions. RNA has larger grooves, which makes it easier to be “attacked” by enzymes. |
| Propagation | DNA is self-replicating. | RNA is synthesized from DNA when needed. |
| Unique Features | The helix geometry of DNA is of B-Form. DNA is protected in the nucleus, as it is tightly packed. DNA can be damaged by exposure to ultra-violet rays. |
The helix geometry of RNA is of A-Form. RNA strands are continually made, broken down and reused. RNA is more resistant to damage by Ultra-violet rays. |
Principle of Inheritance, Concept of Inheritance
Gregor
John Mendel advanced the principles of inheritance. In 1856 – 1863
Mendel grew and tested some 29,000-pea plants. From these studies, he
formulated the law of segregation and the law of assortment.
After
his work on peas, Mendel began to experiment with honeybees. However,
he failed to produce a clear picture of their heredity because of
difficulties in controlling the mating behaviour of queen bees.Mendes
works was largely criticized and generally rejected during his lifetime.
It was only after his death that his work gained broad recognition. He
is now considered the father of modern genetics, Mendel diedMendel died
on January 6th, 1884.
- It is self-pollinating but can be cross-pollinated
- It matures very fast
- It produces many seeds and hence many off springs
- It has several physical properties
- Height of the stem-tall or dwarfs
- Texture of the seed coat – smooth or wrinkled
- Colour of flowers – purple or white
- Colour of pods – green or yellow
- Position of flowers – axial or terminal
law is also called Mendel’s first law of inheritance or law of
segregation. The law states, “An organism’s characteristics are
determined by internal factors which occur in pair”. Only one of the
factors can be contained in a single gamete.
modern terms this means that genes occurring in pairs control the
characteristics of an organism but only one gene can be carried in a
single gamete.
- Genes can exist in more than one form
- An organism inherits two alternative form of a gene for a particular trait, one from each parent
- During the production of gametes pair of alleles separate. Thus each gamete has one allele for each trait.
- When
the two alleles in a pair are different one is dominant while the other
is recessive. This condition is called complete dominance.
When inheritance of one pair of characteristics is studied at a time it is called Monohybrid inheritance.
Download & Install
Darasa Huru App
DOWNLOAD
plants produced are normal and also are known as the first filial
generation (F1).Hence he concluded that the tallness is said to be
dominant which the gene for dwarfness is said to be recessive in the
garden pea. Because the gene of dwarf are masked by the gene for
tallness.Hybrid is an offspring of a cross-between parents showing
unlike characteristics.Test Cross (Back cross) this is the cross that
involves off springs of two different pure lines.
Some
conditions in human follow Mendelian monohybrid inheritance. Example, a
condition that is associated with a simple pair of alleles and are
inherited in Mendelian fashion
- Albinism
- Sickle Cell anemia
- Rhesus blood group
- Haemophilia
- Achondroplasia
continued to study the inheritance of two pairs of characteristics.
This inheritance is known as dihybrid cross.Dihybrid Cross is the
inheritance of two characteristics in which each is controlled by a
different gene, different locus.
- Tall with purple flower
- Dwarf with white flower
- Two phenotypes in the ration 9:3:3:1 resembled one or other of the parent
- Two phenotypes did not resemble any of the parents’ phenotypes but instead had combined the characteristics of both parents
- Ratio of tall to dwarf plants was 3:1 and that of purple flowered plant was 3:1
Non-Mendelism Inheritance
all inheritance follows Mendelian fashion. Mendel only considered
characteristics that were determined by single genes with two alleles in
which one is dominant and the other recessive. Later research showed
that in some alleles neither one is dominant over the other. That
condition is known as co-dominance or incomplete dominance.
is the condition in which no allele is dominant or recessive compared
to the otherExample when red and white flowered varies of the four
o’clock plant are crossed, all the plant of the F1 generation produce
pink flowers.
Dominance is a condition in which a dominant gene completely masks
recessive gene. Example: Homozygous tall plant crossed with the
homozygous short/dwarf plant. chart showing Tall x Dwarf.
all inheritance follows Mendelian fashion. Mendel only considered
characteristics that were determined by single genes with two alleles in
which one is dominant and the other recessive. Later research showed
that in some alleles neither one is dominant over the other. That
condition is known as co-dominance or incomplete dominance.
when red and white flowered varies of the four o’clock plant are
crossed, all the plant of the F1 generation produce pink flowers.
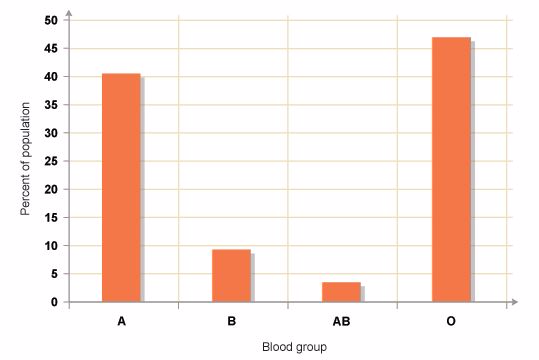
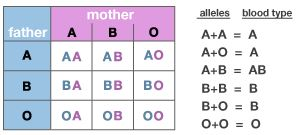
entire human population falls under four main blood group that are –A,
B, AB and O.Allele A and B are condomint white allele O is recessive to
both A and B.
Example:
parents with heterozygous blood group A and B have off spring with
blood group A, B, AB and O as illustrated in the following cross.
Sex Determination and Inheritance
beings have 46 chromosomes (23 pairs of homologous chromosome). In
every body cell of these, two are sex chromosomes while 44 are referred
to as Autosome.
other chromosomes in which each of the homologous chromosomes carries
gene for the same characteristics, X and Y do not carry the same gene.
preference and selection is the tendency of people to like one type of
sex more than the other. This tendency is very common in African
countries and some parts of Asia.
Some
people in a family prefer having boys than girls while others prefer
girls to boys. Those who prefer boys do so in a belief that boys will
perpetuate the linage and take care of the parents when females are
living far away with their husbands. Those who prefer girls argue that,
girls are kind and merciful; therefore they can take care of their
parents in old age.
- Manpower Generation:Some
societies prefer boys to girls because they generate wealth upon
getting married. A family will get a lot of cattle or money as bridal
price. - Generation and protection of wealth:Some
societies prefer girls more than boys because girls will prefer to have
more sons than girls so that they can somehow benefit indirectly
through their son. - Land ownership In some societies a woman cannot own land thus prefers more sons than daughters because they can benefit from the sons.
Variation Among Organisms
in biology, refers to any difference between cells, individual
organisms, or groups of organisms of any species caused either by
genetic differences (genotypic variation) or by the effect of
environmental factors on the expression of the genetic potentials
(phenotypic variation). Variation may be shown in physical appearance,
metabolism, fertility, mode of reproduction, behaviour, learning and
mental ability, and other obvious or measurable characters. If you
consider almost any characteristic, you will find differences between
various people (or other animals or plants) in a population.
Genetic
variation describes naturally occurring genetic differences among
individuals of the same species. This variation permits flexibility and
survival of a population in the face of changing environmental
circumstances. Consequently, genetic variation is often considered an
advantage, as it is a form of preparation for the unexpected. Variation
between different species is always greater than the variation within a
species.
Genetic
variations are caused by differences in number or structure of
chromosomes or by differences in the genes carried by the chromosomes.
Eye colour, body form, and disease resistance are genotypic variations. A
variation cannot be identified as genotypic by observation of the
organism. Breeding experiments must be performed under controlled
environmental conditions to determine whether or not the alteration is
inheritable.
caused variations may result from one factor or the combined effects of
several factors, such as climate, food supply, and actions of other
organisms. These variations do not involve any hereditary alteration and
in general are not transmitted to future generations.
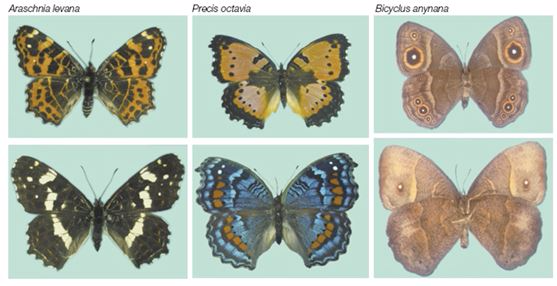
(composed of well-defined classes, as blood groups in man). A
discontinuous variation with several classes, none of which is very
small, is known as a polymorphic variation. The separation of most
higher organisms into males and females and the occurrence of several
forms of a butterfly of the same species, each coloured to blend with a
different vegetation, are examples of polymorphic variation.
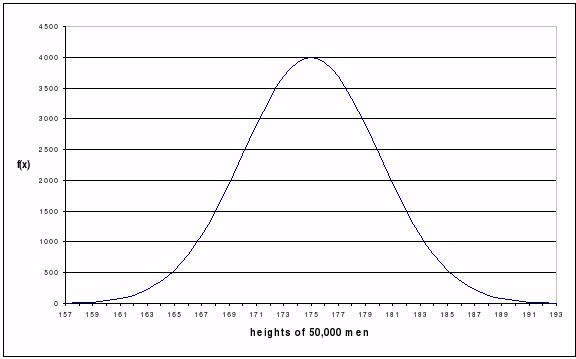
This
type of variation exhibits a wide range of differences for the same
characteristics, from one extreme end to the other. Characteristics
showing continuous variation vary in a general way, with a broad range,
and many intermediate values between the extremes. As a matter of fact,
if you consider a large enough sample from a population, perhaps
plotting frequency as a histogram or as a frequency polygon, you will
find that most of the values are close to the average (mean), and
extreme values are actually rather rare. Examples of continuous
variations in human beings include weight, height and complexion. Height
is an example of continuous variation. People vary in height from very
short to very tall, with many intermediate heights.
Discontinuous variation
variation is a type of variation that shows sharp differences among
individuals of a species, with no intermediate forms.
fall into a number of distinct classes or categories. This is based on
features that cannot be measured across a complete range. A person
either has the characteristic or not. There is no intermediate
condition.
The
ability to roll the tongue (one is either tongue roller or non tongue
roller), fingerprints, sex (one is either male or female) and the ABO
blood group system where one can only have blood group A, B, AB or O.
and blood groups. In plants, a pawpaw tree is either male or female.
These characteristics can be explained much more easily by simple rules
of genetics and are less likely to be affected by other factors.
Discontinuous variations are unchangeable and unaffected by the external
environment.
Difference between Continuous and Discontinuous Variation
Differentiate continuous from discontinuous variation
Continuous Variations:
- The variations fluctuate around an average or mean of species.
- Direction of continuous variations is predictable.
- They are already present in the population.
- Continuous
variations are formed due to chance segregation of chromosomes during
gamete formation, crossing over and chance pairing during fertilization. - They can increase adaptability of the race but cannot form new species.
- Continuous variations are connected with the mean or average of the species by intermediate stages.
- The continuous variations are also called fluctuations.
- When represented graphically, continuous variations give a smooth bell shaped curve.
- They are very common.
- Continuous variations do not disturb the genetic system.
- A mean or average is absent in discontinuous variations.
- The direction of discontinuous variations is unpredictable.
- Discontinuous variations are new variations though similar variations might have occurred previously.
- Discontinuous variations are produced by changes in genome or genes.
- Discontinuous variations are the fountain head of continuous variations as well as evolution
- These variations are not connected with the parental type by intermediate stages.
- Discontinuous variations are also known as mutations or sports.
- A curve is not produced when discontinuous variations are represented graphically.
- These variations appear occasionally.
- They disturb the genetic system of the organism.
Explain causes of variation among organisms
variation within a species is inherited. Variation in a characteristic
that is a result of genetic inheritance from the parents is called
inherited variation. Each egg cell and each sperm cell contains half of
the genetic information needed for an individual. When these join at
fertilisation a new cell is formed with all the genetic information
needed for an individual. Examples of inherited characters in humans
include eye colour, hair colour, skin colour and lobed or lobeless ears.
is inherited variation too, because whether you are male or female is a
result of the genes you inherited from your parents.
variation can be caused by mutation (which can create entirely new
alleles in a population), random mating, random fertilization, and
recombination between homologous chromosomes during meiosis (which
reshuffles alleles within an organism’s offspring). Some of these
variation causes are explained in detail below:
occurs at the time of gamete formation. At the time of gamete formation
during meiosis, the parental chromosomes separate at random hence
forming different gametes with different chromosomes. This independent
assortment gives a wide variety of different gametes and hence
individuals.
Chromosomal
crossover (or crossing over) is the exchange of genetic material
between homologous chromosomes that results in recombinant chromosomes
during sexual reproduction. Crossing over and random segregation during
meiosis can result in the production of new alleles or new combinations
of alleles. Portions of paired chromosomes may be exchanged to form new
chromosomal and gene combinations in gametes resulting into new trait
combinations in offspring.
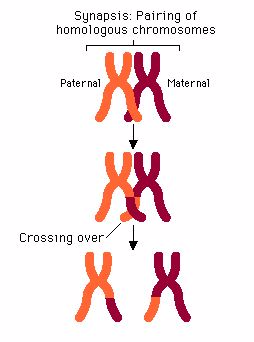
Non-disjunction
Non-disjunction
results into doubling of the chromosome number due to failure of
chromosomes to segregate during meiosis. This leads to increase in cell
size and subsequent increase in size of various parts of the organism,
hence variation.
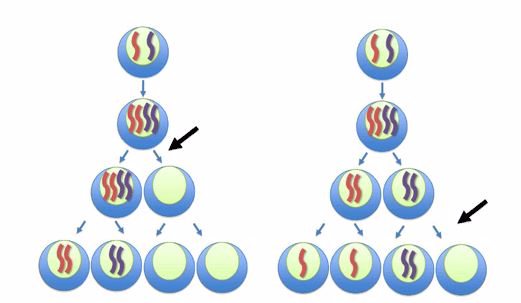
Random fertilization
fertilization that results during the fusion of the gametes also
contributes to variation. Gametes are the egg and sperm, or pollen,
produced by meiosis. Each gamete has a unique set of combination of
genes. A male gamete can fertilize any of the female gametes. The
fertilization between a male gamete and a female gamete occurs randomly
in the fallopian tube. As a result, each zygote is unique and hence
variation occurs due to the different combination of genes from the male
and female gamete.
The
random fusion of gametes is a source of genetic variation in offspring
(with the same parents). For example, a litter of puppies or kittens
sired (bred) by the same father will show variation between individuals
as shown bellow.

Random mating
mating involves individuals pairing by chance, not according to their
genotypes or phenotypes. Random mating is a source of variation in a
population. For example, a population in which mating only occur between
organisms of similar phenotypes, such as red beetles mating with red
beetles and yellow beetles mating with yellow beetles, will tend to show
less variation than a population where crosses are random. For example,
red beetles mating with yellow beetles.
are sudden and permanent changes in the genes and chromosomes which are
then passed on from cell to cell during mitosis. Such changed genes or
chromosomes will produce offspring that differ from parents.
of animal and plant species can be affected by factors such as climate,
diet, accidents, water, temperature, light, diseases, degree of
acidity, soils nutrients, culture and lifestyle. For example, if you eat
too much you will become heavier, and if you eat too little you will
become lighter. A plant in the shade of a big tree will grow taller as
it tries to reach more light. Such variations are produced in the body
(somatic) cells and not in the sex cells hence cannot be inherited.
Variation
caused by the surroundings is called environmental variation. Here are
some other examples of features that show environmental variation:
- Your language and religion
- Flower colour in hydrangeas – these plants produce blue flowers in acidic soil and pink flowers in alkaline soil
Download & Install
Darasa Huru App
DOWNLOAD
The meaning of Genetic Disorders
Give the meaning of genetic disorders
refers to an abnormality, which results from problems in the genes of
an organism, and it is inherited. This means that the genetic disorder
is caused by the change in the gene or chromosomes due to an error in
the person’s genetic materials.
disorders are malfunctioning of the body’s physiological mechanisms due
to changes on gene or chromosomes; for example the change in number of
chromosomes from 46 to 47 chromosomes or below that hence leading to
genetic disorders.
Examples of Genetic Disorders
Cite examples of genetic disorders
- Down’s Syndrome or Mongolism/Mongolia
- Turner Syndrome
- Super male and Super female
- Haemophilia
- Colour blindness
NOTE:
The changes in the genes and chromosomes may be caused by different
factors, which lead to genetic disorder. The sudden change in genetic
materials of the cell that may cause it to differ from other cells is
known as mutation.
organism is affected by mutation, which occurs naturally at a low rate.
A number of factors may contribute to mutation. Such factors include
various chemicals and radiation example X-rays. Mutation can be due to a
change in gene itself i.e. this is called point mutation only or in the
arrangement of gene chromosome. Other causes of mutation include
addition or loss of chromosomes and duplication of genes.
There
are two types of mutation including chromosomal mutation and gene
mutation. Both leads to the genetic disorder is to lead to change in
gene and chromosome. Chromosomal mutation leads to genetic disorder like
Down’s syndrome, Turner Syndrome, Klinefelter’s Syndrome. It affects
the appearance or the number of chromosomes. Gene mutation leads to
genetic disorders like Haemophilia and Colour blindness, which affects
the genes.
This
is a chromosomal abnormality in which there are three copies of
chromosome number 21 instead of the usual 2. The person with Down’s
syndrome therefore has 47 chromosomes in his/her body cells. The
affected individuals have a short broad face, slanted eyes, short
fingers and weak muscles. Such individuals are usually mentally
retarded.
presence of the extra chromosome on chromosome 21 is known as trisomy.
The extra chromosome on chromosome 21 is due to its failure to separate
during meiosis. This is known as non-disjunction. This non-disjunction
occurs when homologous chromosome fail to separate in meiosis II of the
egg. Therefore after the fertilization, chromosome 21 will contain 3
(i.e. the 2 which failed to separate plus the one from the father)
instead of normal two (i.e. each from one parent). In some few cases
non-disjunction may occur in the father’s sperm.
extra chromosome on chromosome 21, thus making three instead of two,
causes this disorder. The extra chromosome on chromosome 21 is caused by
failure to separate during meiosis.
with down’s syndrome are very susceptible to diseases including heart
diseases. They thus die young, mostly not more than 30 years. They may
also suffer discrimination in those societies that consider it as a
curse or something very unusual.
is a genetic disorder of female (women) caused by absence of second sex
chromosome. Such women are XO, rather than the normal XX chromosome. In
this disorder there are only 45 chromosomes, the female lacks secondary
sexual feature, small uterus, the internal genitals never mature and
therefore she is sterile. This disorder is characterized by lack of
ovaries and menstrual cycle.
This
genetic disorder is caused by absence of X chromosome in normal XX
chromosome. This occurs when the second X chromosome lacks i.e. make XO
instead of normal XX chromosome.
- The women who suffer from Turner’s syndrome are abnormally short; their ovaries usually do not develop and hence are infertile.
- They may also suffer mental abnormalities, which may lead to difficulty in learning
- Missing
one copy of this gene causes short stature and skeletal abnormalities
in women with Turner’s syndrome. This is due to the researchers who
identified one gene called SHOX that is important for bone development
and growth, hence when missing it will cause skeletal abnormalities.
Super Male and Super Female
is the genetic disorder caused by the non-disjunction of sex
chromosomes, leading to a male having an extra Y chromosome (XYY) that
is a super male. Also a female having an extra X chromosome (XXX) that
is a super female; hence both male and female have 47 chromosomes
instead of 46.
with an extra X or Y chromosome appear very tall but in most cases they
look normal and do not show any physiological or medical abnormalities.
with the XYY syndrome were previously thought to be overly aggressive
and more likely to become criminals. These original stereotypes came
about because several researchers in the 1960s found a number of men
with XYY syndrome in prisons and mental institutes. Since then, broader,
less biased studies have been done on males with XYY and females with
XXX syndrome.
genetic disorder is caused by the presence of extra Y chromosome (XYY)
or X chromosome (XXX). This causes changes in chromosomes from normal 46
to 47 chromosomes.
the male with XYY chromosomes and the female with XXX chromosome or
syndrome may be taller than average, they appear very tall in some
cases. Also the people with XYY and XXX syndrome they have an increased
risk for learning difficulties especially in reading and speech.
is a non-disjunction or genetic disorder resulting from failure of the
XY or XX chromosomes of the gametes to separate and hence being
inherited together. The victim has 47 chromosomes instead of 46. He is a
male due to the presence of Y chromosome but he develops female
secondary features.
genetic disorder is caused by failure of the XY or XX chromosomes of
the gamete to separate, hence makes XY or XX chromosome to be inherited
together. Hence results from 47 chromosomes instead of normal 46
chromosomes.
individual with Klinefelter’s syndrome usually has low intelligence:
Male with Klinefelter’s syndrome are typically tall and may have small
testes and some breast development, although this is not necessarily
obvious. They may also have difficult in learning and are usually
infertile.
genetic disorders may be caused by the chromosome mutation or gene
mutation. Also the genes can be inherited together hence lead to genetic
disorders. When genes that are inherited together they are said to be
linked that is known as sex linkage. This sex linkage includes
Haemophilia and Red-Green colour blindness.
is the hereditary disorder whereby blood clotting is delayed caused
prolonged bleeding. People suffering from haemophilia may bleed for more
than two hours following an injury. Bleeding may occur either in skin,
muscles even in joints due to even a minor injury. Haemophilic girls are
very rare; their chance to survive beyond puberty is minimum due to
excessive bleeding during menstruation.
is caused by a recessive allele “h” carried on the X chromosome. It is
easier for a haemophilic son to be produced from normal parents because a
carrier female with single haemophilic allele on one of X chromosomes
appears phenotypically normal. When she marries a normal man, there is a
chance that they may get a haemophilic son.
causes the failure of blood clotting hence it leads to death. For the
female an individual could not survive beyond the puberty age due to
excessive bleeding during menstruation.
is a condition in which one fails to distinguish red from green colour.
It is a sex linked hereditary disorder whereby an individual fail to
distinguish red from green. As for Haemophilia, colour blindness is
controlled by recessive gene, hence for the disorder to be expressed
phenotypically it must be present in homogenous form in female, though
for male a single allele is enough for the disorder to be expressed
phenotypically.
This
disorder as for haemophilia is caused by a recessive gene/trait carried
by X chromosome. For example: If a heterozygous normal female (carrier)
marries a normal male, the possibility of getting the colourblind son
is expected.
- XcXc – carrier female
- XcY – normal male
- XcY – colourblindness
disorder is characterized by the difficulty in distinguishing Red from
Green colour that may lead to accidents in traffic lights, when an
individual will fail to determine Red light from Green light.
- Genetics
can help us to understand why people look the way they do and why some
people are more prone to certain diseases than others. - Genetics
can help health-care professionals to identify certain conditions in
babies before they are born using techniques such as prenatal testing. - Genetic technologies are also being used to help develop targeted medicinesfor certain diseases.
- In
addition to its use in health care, genetics has a range of other
applications. For example, the police can use genetic fingerprinting to
catch criminals. - Genetic fingerprinting was invented and
developed by Sir Alec Jeffreys at the University of Leicester in 1984.
This technique can identify individuals on the basis of their genetic
information. - Criminals often leave evidence of their identity at
a crime scene: for example, hair follicles, blood or skin cells. The
police can use the genetic information to demonstrate whether or not an
individual was present at the scene of a crime. - Genetic information can prove innocence and help to identify and convict the guilty.
The Importance of Genetics in Biological Science and Related Fields
Explain the importance of genetics in biological science and related fields
is often applied to blood grouping. Blood grouping is very important in
human life as it enables determination of blood groups so as the donor
blood can be transfused to needy patients (recipients) without
agglutination (clotting) or causing any adverse reaction. The four ABO
blood groups are A, B, AB and O.
the surface of the red blood cells are special proteins called antigens
A and B. The A and B antigen molecules on the surface of red blood
cells are made by two different enzymes. These two enzymes are encoded
by different versions, or alleles, of the same gene.
A allele codes for an enzyme that makes the A antigen, and the B allele
codes for an enzyme that makes the B antigen. A third version of this
gene, the O allele, codes for a protein that is not functional; it makes
no surface molecules at all.
The
table below shows all of the possible combinations of blood type
alleles. The blood type for each allele combination is shown on the
right. For example, if you inherit a B allele from your father and an A
allele from your mother, your blood type will be AB.
Blood
plasma is packed with proteins called antibodies. The body produces a
wide variety of antibodies that will recognize and attack foreign
molecules that may enter the body from the outside world. A person’s
plasma does not contain any antibodies that will bind to molecules that
are part of his or her own body.
conducting a blood transfusion, it is important to carefully match the
donor and recipient blood types. If the donor blood cells have surface
molecules that are different from those of the recipient, antibodies in
the recipient’s blood recognize the donor blood as foreign. This
triggers an immune response resulting in blood clotting. If the donor
blood cells have surface moleculesthat are the same as those of the
recipient, the recipient’s body will not see them as foreign and will
not mount an immune response.
are two special blood types when it comes to blood transfusions. People
with type O blood are universal donors because there are no molecules
on the surface of the red blood cells that can trigger an immune
response. People with type AB blood are universal recipients because
they do not have any antibodies that will recognize type A or B surface
molecules.
process of choosing animals and plants with certain desired qualities
such as increased yields, tolerance to drought, resistance to disease
and faster growth is referred to as artificial selection.
involves breeding closely-related organisms. Thus the required qualities
are retained from one generation to another.
with desired qualities are inbred through successive selfing. Excessive
inbreeding reduces genetic diversity, health and fitness.
is also called hybridization. Different varieties of the same species
are interbred in order to combine the advantageous traits of one variety
with those of another.
Plants
are crossbred to introduce traits/genes from one variety or line into a
new genetic background. For example, a mildew-resistant pea may be
crossed with a high-yielding but susceptible pea, the goal of the cross
being to introduce mildew resistance without losing the high-yield
characteristics. Progeny from the cross would then be crossed with the
high-yielding parent to ensure that the progeny were most like the
high-yielding parent, (backcrossing).
- Improved quality, such as increased nutrition, improved flavour, or greater beauty.
- Increased yield of the crop.
- Increased tolerance of environmental pressures (salinity, extreme temperature, and drought).
- Resistance to viruses, fungi and bacteria.
- Increased tolerance to insect pests.
- Increased tolerance of herbicides.
- Longer storage period for the harvested crop.
Artificial
insemination in the livestock industry has helped to produce a wide
variety of cattle breeds which produce higher yields of milk or meat or
both, sheep with high quality wool and poultry which produce good meat
and eggs.
counselling is giving of professional advice and information about
inherited disorders and diseases so as to help people make informed
decisions.
patients or relatives at risk of an inherited disorder are advised of
the consequences and nature of the disorder, the probability of
developing or inheriting it, and the options open to them to avoid
propagating the problem to future generations.
The
advice aims at controlling or preventing inheritable diseases and
disorders like sickle-cell anaemia, albinism, haemophilia, colour
blindness, etc.
- increasing the family’s understanding of a genetic condition;
- discuss options regarding disease management and the risks and benefits of further testing and other options;
- helping the individual and family identify the psychosocial tools required to cope with potential outcomes; and
- reducing the family’s anxiety.
- Before conception, when one or both parents are carriers or sufferers of a certain hereditary disorder.
- During
pregnancy, if an abnormality is detected in the embryo. Genetics can
help health-care professionals to identify certain conditions in babies
before they are born using techniques such as prenatal testing. - If a defect is noticed after birth.
- If a genetic condition sets in during adulthood.
Genetic
counsellors advice parents on how to minimize the risk of passing on
certain traits to their children. For example, marriages between close
relative increases the chances of alleles being homozygous. People with
genetic disorders are also taught how to control them. Genetic
counselling is also used to resolve controversies over parentage.
engineering is the process of manually adding new DNA to an organism.
The goal is to add one or more new traits that are not already found in
that organism. Examples of genetically engineered (transgenic) organisms
currently on the market include plants with resistance to some insects,
plants that can tolerate herbicides, and crops with modified oil
content.
engineering has been applied to produce insulin cheaply using bacteria.
This is done by transferring a gene that determines insulin production
in a human cell into bacteria. Since bacteria reproduce very fast, large
amounts of insulin can be produced within a short time. The insulin is
then extracted from the bacteria and purified in readiness for use in
the treatment of diabetes mellitus in human beings.
engineering is also used in the production of interferons. Genes
responsible for interferon production are inserted into the DNA of
yeast. Interferon is a chemical naturally produced by cells in order to
inhibit viral growth during infection. It is used in the treatment of
cancer and viral diseases.
refers to use of science and technology to investigate and establish
facts in criminal or civil courts of law. The police can use DNA
fingerprinting to catch criminals. This technique can identify
individuals on the basis of their genetic information. In practice, the
test is used to determine whether a family relationship exists between
two people, to identify organisms causing a disease, and to solve
crimes. Only a small sample of cells is needed for DNA fingerprinting. A
drop of blood or the root of a hair contains enough DNA for testing
often leave evidence of their identity at a crime scene: for example,
hair follicles, blood or skin cells. The police can use the genetic
information to demonstrate whether or not an individual was present at
the scene of a crime. Genetic information can prove innocence and help
to identify and convict the guilty.
Also
in cases such as raping, DNA test of sperm remains retrieved from the
victim’s clothes or body may be used to establish evidence that could
lead to conviction or release of the suspected rapist.