Download & Install
Darasa Huru App
DOWNLOAD
TOPIC 2: MOVEMENT | BIOLOGY FORM 3
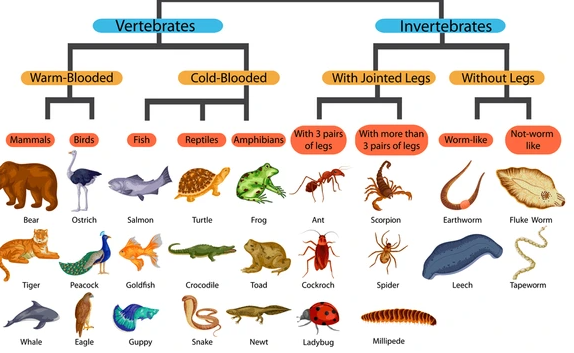
Concept of Movement and Locomotion
The Concept of Movement and Locomotion
Explain the concept of movement and locomotion
refers to change of position and posture. Therefore the change of
position of body parts such as limbs and other body parts.
locomotion involves coordination between nervous muscular and skeletal
system and all these system enable the organism to locomote.
The Importance of Movement in Animals and Plants
Explain the importance of movement in animals and plants
- Find a mate and to reproduce
- Escape danger
- Seek and capture food
- To seek shelter, a suitable habitat/climate
- To avoid competition for food/water, living space etc
- Find water/soil nutrients, and hold leaves to get maximum sunlight
- Seek and capture food
- Obtain support
- Protect themselves from damage from: touch/pressure, pain or sudden temperature change
- Disperse seeds
Demonstrate movement and locomotion actions
Demonstration of movement and locomotion


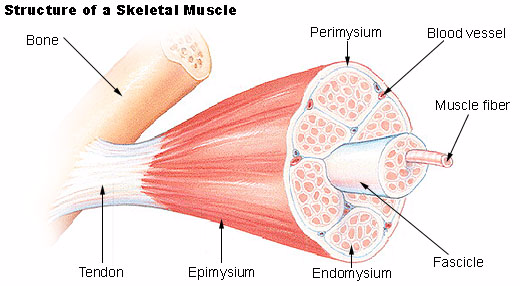
The Structures of Human Skeleton
Describe the structures of human skeleton
contraction and relaxation of muscles cause muscular movement in
vertebrate organisms such as man. The muscles work together with
skeletal system to support or allow movement to occur.BONES, CARTILAGE, JOINTS AND MUSCLES
Bones
consist of living cells embedded in a hard substance made mainly: The
bones are attached together at the joints by tough flexible fibers known
as ligaments
- Short bones these are short bones, which support weight allowing for many smaller movements. Example bones on the human feet.
- Long bones
these are strong, hollow and light containing spongy bone at the end.
And spongy bone has open space and holes, which contain red marrow,
which is where red cells are made. Example bones on the legs and arms. - Flat bones these are bones, which support and protect body organs, these comprises ribs, breastbone, shoulder bones etc.
- Irregular bones these bones are for support and such bones are vertebrae also human ear has three tiny irregular bones, which conduct sound.
bones, the skeletal system has tissue called cartilage. It’s the strong
flexible tissue that gives shape to some parts of the body
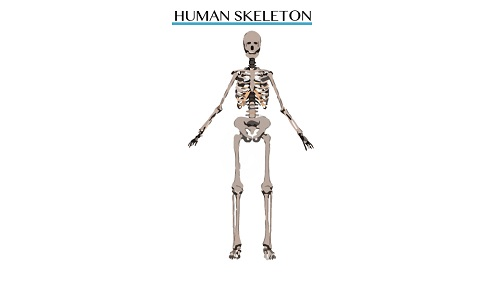
- The human skeleton provides mechanical support for the body
- Protection for internal organs e.g. skeleton of head protects the brain while chest bones protect soft organs such as the heart
- Skeleton functions as framework for anchoring the muscles
- Skeleton, together with muscles, function to bring about movement in an organism
Explain the concept of muscles
muscle is a tissue consisting of cells that have the capacity to
contract and exert a pull. Muscles are made up of specialized tissues,
which are known as contractile tissues. When these tissues contract they
become shorter and tighter, as a result they cause movement. All
muscles are made up of elongated cells called muscle fibers.
are three kinds of muscles in the body of a mammal. These muscles are
skeletal muscles (voluntary), smooth (involuntary) muscles and cardiac
muscles.
How Muscles Facilitate Movement
Download & Install
Darasa Huru App
DOWNLOAD
Demonstrate how muscles facilitate movement
- At one point a muscle is usually attached to an immovable bone and other end to a movable bone.
- Muscles
may be attached directly or indirectly by means of tendons. Tendons are
tough whitish cords of fibrous materials which connect a bone and a
muscle - Muscles can contract and relax, but not expand when
muscle contracts it becomes shorter and thicker and hence, exerts a
pulling force on bone to which it is attached at a point of insertion. - When a muscle relaxes, it lengthens and becomes thinner
- Most
muscles act in pairs in such a manner that when one member of the pair
contracts the other member relaxes. This means that they never contract
or relax at the same time - Muscles acting in pairs in this manner
are known as antagonistic muscles. One member of the pair is called
extensor while the other member is the flexor
figure below shows how the two muscles of the upper arms that is the
biceps and triceps muscles bringing about the bending and straightening
of the limb.
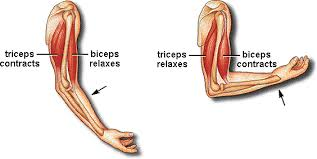
the triceps (extensor) muscle contracts the limb is straightened. The
contraction of the triceps is accompanied by the relaxation of the
biceps (flexor). When the biceps muscle contracts the arm bends.
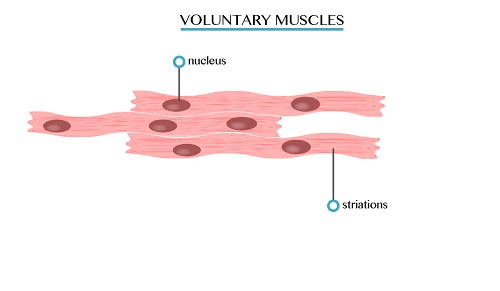
- These are the muscles, which are attached to bones of the skeleton
- The skeletal muscles contract powerfully and fatigue quickly
- Their contractions are controlled by the brain for this reason they are called voluntary muscles
- Skeletal muscles are concerned with the movement of the limbs and parts of the skeleton
- These muscles are made up of cells which taper at both ends (spindle shaped)
- Smooth muscles contract slowly
- The contraction of the smooth muscle is involuntary (it is not controlled by the brain)
smooth muscles, which are formed in different organs contract and relax
to cause movements of materials through them. Example: peristalsis in
alimentary canal causes movements of the materials through the canal
with the help of smooth muscles.

is the type of muscle, which is found only in the heart. These muscles
are made up of muscle fibers which branch and connect to each other like
a network.
- Contraction of cardiac muscles causes the heart to keep on pumping (i.e. heart beat)
muscle cramp is an involuntary and forcibly contracted muscle that does
not relax. The cramp may involve a part of muscle, the entire muscle or
several muscles that usually act together. Any of the muscles that are
not at our voluntary control can cramp.
it occurs when the body lacks salt especially for those people who work
hard in hot weather they sweat a lot and get painful cramps in their
legs, arms or stomach.
- Lack of water or salt in the body
- Lack of oxygen in the muscles (inadequate oxygenation of muscles)
- Cramps from poor breathing (lack of oxygen) can be improved by rapid breathing as well as stretching the muscles
- A
muscle cramp from lack of water or salt can be treated by stretching
the muscles and drinking many glasses of water, which contain salt so as
to replace the amount of salt lost in the body
a soft massage on the cramped muscle, stretching the muscle and
applying oil ointment on the affected area, can treat a muscle cramp.
plants do not show locomotion (movement of the entire organism).
However, movement of individual plant organs is possible and modified by
sensitivity of the plant to external stimuli.
Examples of these movements are metabolic conditions, disease
conditions, vex ages and parental influence Those movements shown by
plants in response to external stimuli are known as induced or irritablemovements.
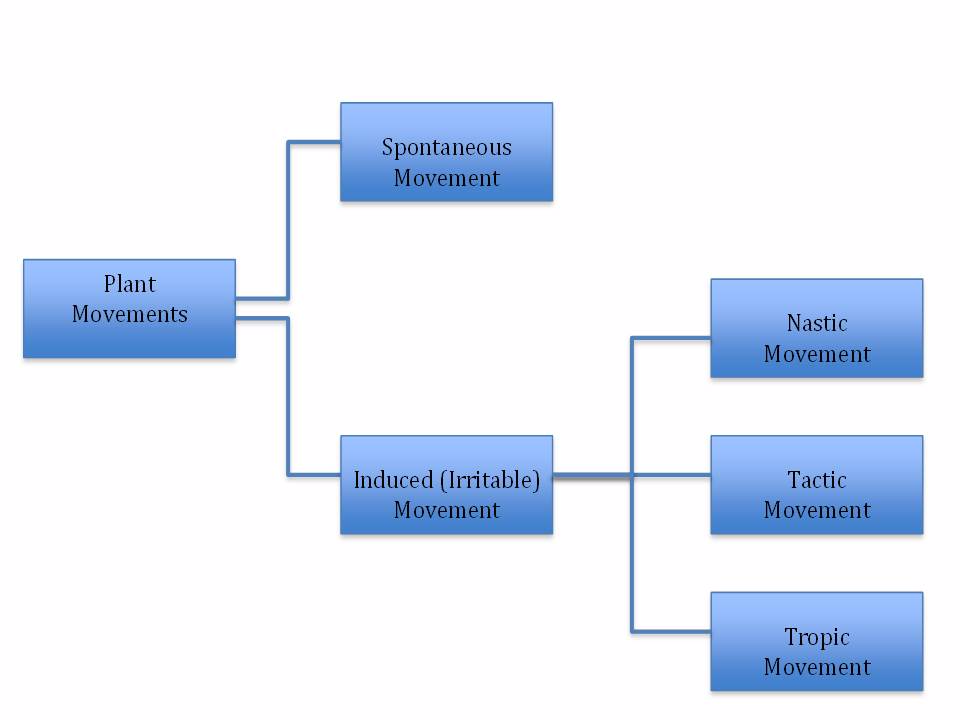
- Spontaneous movement
- Induced (irritable) movement
is plant movement in response to internal stimuli. Example of these
movements are metabolic conditions, disease conditions, vex ages and
parental influences
is the type of plant movement shown by plants in response to external
stimuli. Light, temperature, gravity, touch, water and chemical
substances are examples of induced movement.
- Light
- Chemicals
- Water
- Temperature
- Contact
- Gravity
- Gravitactic or Gravitaxis
Tropic
movements are the growth movements shown by a fixed part of a
stationary plant towards or away from a stimulus coming from one
direction. Tropic movements are also known as tropism movements.
Tropic
(tropism) is growth movements, which take place at a very slow pace.
The growth movement is caused by an increased or decreased rate of
growth on the side of the organ, which is under the influence of the
stimulus, with respect to the opposite side. This results in growth in
curvature.
- Phototropism or phototropic which is a growth movement shown by part of a fixed plant in response to light
- Hydrotropism (Hydrotropic) which is growth movement in a response to water
- Thigmotropism (Thigmotropic) which is the growth movement in response to touch
- Chemotropism (Chemotropic) which is a growth movement made by plants towards chemicals
- Thermotropism (Thermotropic), a growth movement shown in plants in response to heat.
Experiments to Investigate Movement in Plants
Carry out experiments to investigate movement in plants
An experiment to investigate movement in plants