TOPIC 11: INCOMPLETE RECORDS | B/KEEPING FORM 3
Statements Showing Profit or Loss From Incomplete Records
Draw up statements to show profit or loss from incomplete records Some times, businesses, especially small businesses do not maintain a full set of double entry records. Consequently, no trial balance will be produced and a complete set of final accounts cannot be prepared without further analysis of the records that do exist.
This would have been called a Balance Sheet if it had been drawn up from
a set of double entry records. Like a Balance Sheet, a Statement of
Affairs can be prepared horizontally or vertically.
only way the profit for the year can be found is by comparing the
capital shown in the opening Statement of Affairs with the capital shown
in the closing Statement of Affairs.The basic formula is:
may be that the owner has made drawings during the year, which will
account for some of the difference in the capital figures. Similarly the
owner might have brought in additional capital during the year, which
will also account for some of the difference in the capital figures. In
this case the formula must again be modified:-
or Loss = Closing Capital + Drawings during the year – Additional
Capital during the year – Opening Capital (Positive figure means Profit
and Negative figure means Loss)
In
this case, in order to calculate the profit or loss of the business
during the year, the Trading and Profit and Loss accounts are prepared.
For preparing the Trading and Profit and Loss accounts, all necessary
information is not available in the books. So first the missing items
have to be calculated which are necessary for the preparation of Trading
and Profit and Loss accounts.
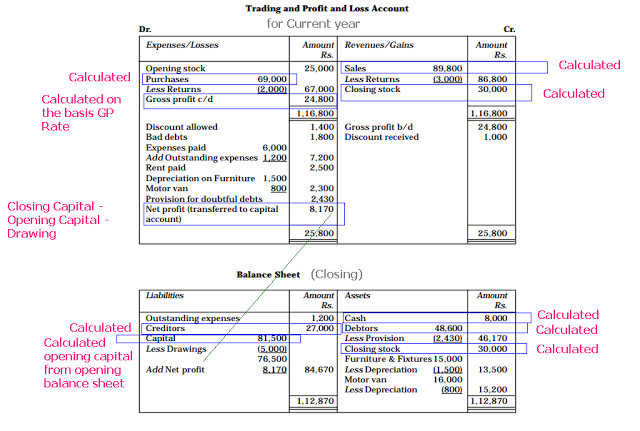
Trading, Profit and Loss Account
Prepare trading, profit and loss account
Example 2
From the following balances extracted from the books of X & Co.,prepare a trading and profit and loss accounton 31st December, 1991.
| $ | $ | ||
| Stock on 1st January | 11,000 | Returns outwards | 500 |
| Bills receivables | 4,500 | Trade expenses | 200 |
| Purchases | 39,000 | Office fixtures | 1,000 |
| Wages | 2,800 | Cash in hand | 500 |
| Insurance | 700 | Cash at bank | 4,750 |
| Sundry debtors | 30,000 | Tent and taxes | 1,100 |
| Carriage inwards | 800 | Carriage outwards | 1,450 |
| Commission (Dr.) | 800 | Sales | 60,000 |
| Interest on capital | 700 | Bills payable | 3,000 |
| Stationary | 450 | Creditors | 19,650 |
| Returns inwards | 1,300 | Capital | 17,900 |
The stock on 21st December, 1991 was valued at $25,000.
Solution
X & Co.Trading and Profit and Loss Account For the year ended 31st December, 1991
| To Opening stock | 11,000 | | | By Sales | 60,000 | ||
| To Purchases | 39,000 | | | Less returns i/w | 1,300 | ||
| Less returns o/w | 500 | | | 58,700 | |||
| 38,500 | | | By Closing stock | 25,000 | |||
| To Carriage inwards | 800 | | | ||||
| To Wages | 2,800 | | | ||||
| To Gross profit c/d | 30,600 | | | ||||
| | | ||||||
| 83,700 | | | 83,700 | ||||
| | | ||||||
| To Stationary | 450 | | | By Gross profit b/d | 30,600 | ||
| To Rent and rates | 1,100 | | | ||||
| To Carriage outwards | 1,450 | | | ||||
| To Insurance | 700 | | | ||||
| To Trade expenses | 200 | | | ||||
| To Commission | 800 | | | ||||
| To Interest on capital | 700 | | | ||||
| To Net profit transferred to capital a/c | 25,200 | | | ||||
| | | ||||||
| | | ||||||
| 30,600 | | | 30,600 | ||||
Preparation of Balance Sheet
Prepare balance sheet
Example 3
From the following balances extracted from the books of X & Co.,prepare a balance sheeton 31st December, 1991.
| $ | $ | ||
| Stock on 1st January | 11,000 | Returns outwards | 500 |
| Bills receivables | 4,500 | Trade expenses | 200 |
| Purchases | 39,000 | Office fixtures | 1,000 |
| Wages | 2,800 | Cash in hand | 500 |
| Insurance | 700 | Cash at bank | 4,750 |
| Sundry debtors | 30,000 | Tent and taxes | 1,100 |
| Carriage inwards | 800 | Carriage outwards | 1,450 |
| Commission (Dr.) | 800 | Sales | 60,000 |
| Interest on capital | 700 | Bills payable | 3,000 |
| Stationary | 450 | Creditors | 19,650 |
| Returns inwards | 1,300 | Capital | 17,900 |
The stock on 21st December, 1991 was valued at $25,000.
Solution
X & Co. Balance Sheet as at 31st December, 1991
| Liabilities | $ | | | Assets | $ | |
| Creditors | 19,650 | | | Cash in hand | 500 | |
| Bills payable | 3,000 | | | Cash at bank | 4,750 | |
| Capital | 17,900 | | | Sundry debtors | 30,000 | |
| Add Net profit | 25,200 | | | Bill receivable | 4,500 | |
| 43,100 | | | Stock | 25,000 | ||
| | | Office equipment | 1,000 | |||
| | | |||||
| 65,750 | | | 65,750 | |||
| | | |||||
Calculating Amount of Cash Stolen
Calculate amount of cash stolen
The loss on theft of cash and any other assets may be simply be expensed to the income statement net of any insurance claim received or receivable. Following accounting entries would therefore be required:
| Debit | Loss on asset theft (balancing amount) |
| Debit | Accumulated Depreciation |
| Credit | Asset (carrying amount) |
Calculating the Value of Stock at Cost which had been Stolen
Calculate the value of stock at cost which had been stolen
Activity 1 (INCOMPLETE RECORDS)
Calculate the value of stock at cost which had been stolen







