Simple Machines
A simple machine is a non-powered mechanical device that changes the direction or magnitude of a force. In general, they can be defined as the simplest mechanisms that use mechanical advantage (also called leverage) to multiply force. A simple machine uses a single applied force to do work against a single load force. Ignoring friction losses, the work done on the load is equal to the work done by the applied force.
Concept of Simple Machines
Nowadays man can do many things without necessarily using much of his own energy. Many can fly by using aeroplane, raise a heavy load, and drive a nail into wood by using a hammer. All of these are achieved using machines.
The Concept of a Simple Machine
Explain the concept of a simple machine
Machine:
Machine is any device, which is used for simplifying work. Examples of machines are: a crowbar, a seesaw, a claw hammer, a pulley and an inclined plane.
Types of machine:
There are two types of machines
- Simple machine
- Complex machine
What is simple machine?
Simple
machine is any device, which requires single force in operation to
simplify work e.g. Claw hammer, a pulley, and an inclined plane. In a
simple machine, a force is applied at one convenient point to overcome
another force acting at another point.
machine is any device, which requires single force in operation to
simplify work e.g. Claw hammer, a pulley, and an inclined plane. In a
simple machine, a force is applied at one convenient point to overcome
another force acting at another point.
Simple Machine
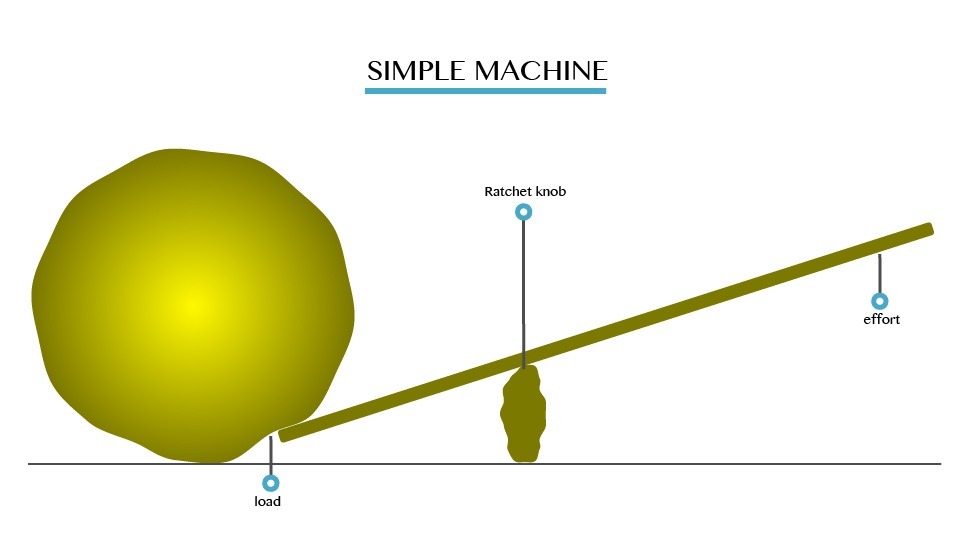
The
diagram above shows a stone being shifted. Force is applied at one end
of the bar in order to exert an upward force on the stone. The down ward
force is called effort and the weight of the stone is called load.
diagram above shows a stone being shifted. Force is applied at one end
of the bar in order to exert an upward force on the stone. The down ward
force is called effort and the weight of the stone is called load.
Effort is the force used to operate a machine. And Load is the resistance, which machines overcome.
The terms Applied in Simple Machine
Explain the terms applied in simple machine
Terms used in simple machine
Mechanical Advantage
Mechanical advantage (M.A) is the ratio of load and effort
Mathematically:
–
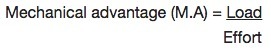
Mechanical advantage has no SI unit.
Example 1
Example 1
A simple machine raises a load of 100N by using a force 50N. Calculate the mechanical advantage.
Solution;
–

Example 2
Example 2.
A force of 20N raises a load of 100kg. Calculate mechanical advantage of the machine.
Solution
–

img4

Velocity ratio
Velocity
ratio is the ratio of distance travelled by effort and distance
travelled by load. Or Velocity ratio is the distance moved by effort per
distance moved by load.
ratio is the ratio of distance travelled by effort and distance
travelled by load. Or Velocity ratio is the distance moved by effort per
distance moved by load.
–

Example 3
Example
In
a certain machine a force of 10N moves down a distance of 5cm in order
to raise a load of 100N through a height of 0.5cm calculated the
velocity ratio (V.R) of the machine.
a certain machine a force of 10N moves down a distance of 5cm in order
to raise a load of 100N through a height of 0.5cm calculated the
velocity ratio (V.R) of the machine.
Solution:
Distance by Effort = 5cm
Distance moved by load = 0.5cm.
From
–

Efficiency of Machine
Efficiency of machine is the ratio of work output and work input.
Work output = Load x Distance moved by Load
Work input = Effort x Distance moved by Effort
–
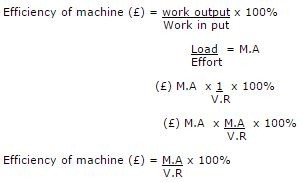
A perfect machine has 100% Efficiency. Therefore M.A is equal to V.R.
Note:
most machines are imperfect machines since efficiency is less than 100%
this is due to the friction and heat and loss of energy.
most machines are imperfect machines since efficiency is less than 100%
this is due to the friction and heat and loss of energy.
Example 4
Example1:
A certain machine with force of 10N moves down a distance of 5cm in order to raise a load of 100N through a height of 0.5cm.
Calculate:
- M.A
- V.R
- Efficiency of machine
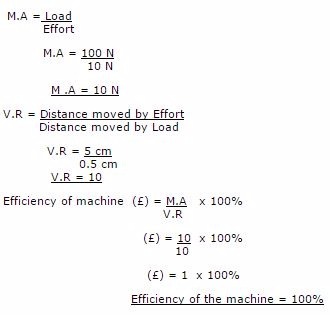
Solution:
Date given:
Effort = 10N
Load = 100N
Distance moved by effort = 5cm
Distance of load= 0.5cm
Efficiency machine?
Efficiency of machine () = M.A x 100%
–
Different Kinds of Simple Machine
Identify the different kinds of simple machines
Different Kinds of Simple Machines
Types of Simple Machines
- LEVERS
- PULLEYS
- INCLINED PLANE
- THE SCREW AND SCREW JACK
- WHEEL AND AXLE
- HYDRAULIC PRESS
Levers
A lever is a rigid body, which when used turns about a fixed point called a fulcrum or pivot. It is used to shift heavy loads.
The Three Classes of Levers
Identify the three classes of levers
Classes of Levers
There are three classes of levers:
- First class lever
- Second class lever
- Third class lever
First Class Lever
Is
the class lever whereby the pivot is between load and effort. Examples
of first class levers are: see-saw, crowbar, pair of scissors and claw
hammer.
the class lever whereby the pivot is between load and effort. Examples
of first class levers are: see-saw, crowbar, pair of scissors and claw
hammer.
First Class Lever
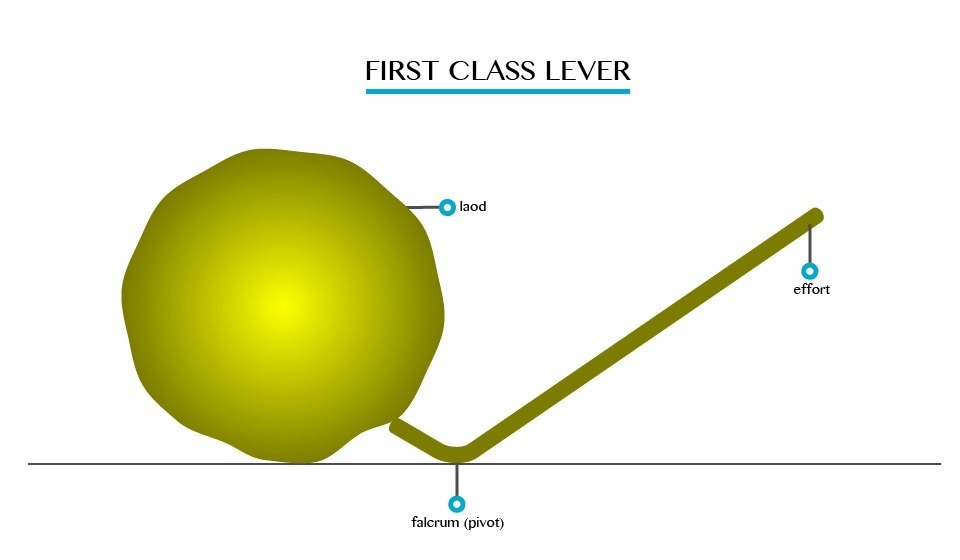
Second Class Lever
Is the class lever where by load is between pivot and load. eg, wheel barrow, tongs, nutcracker, bottle opener.
Second Class Lever
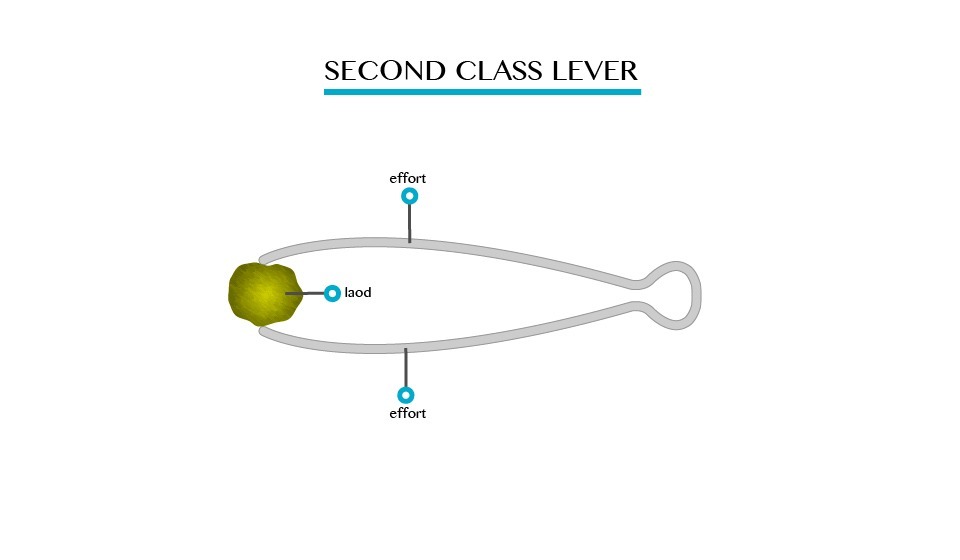
Third Class Lever
Is the class lever whereby Effort is between load and pivot. Eg, fishing load.
Third Class Lever
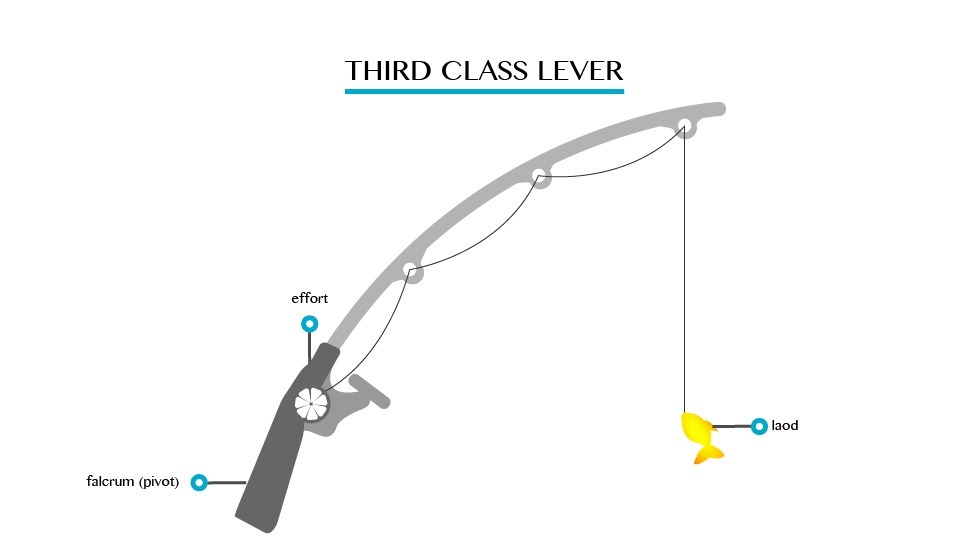
The Mechanical Advantage, Velocity Ratio and Efficiency of Lever
Determine the mechanical advantage, velocity ratio and efficiency of lever
Mechanical Advantage of Lever
M.A =X/Y
M.A =Load arm/Effort arm
Levers in Daily Life
Use of levers in daily life
The reason for a lever is that you can use it for amechanical advantagein lifting heavy loads, moving things a greater distance or increasing the speed of an object.
- Increase force:You can increase the applied force in order to lift heavier loads.
- Increase distance moved
- Increase speed: You can increase the speed that the load moves with Class 1 or Class 3 levers.
Pulleys
A pulley is a grooved wheel, which is free to turn about an axle that is fixed in a frame.
Different Pulley System
Identify different pulley systems
Types of Pulleys
- Single fixed pulley
- Single movable pulley
- The block and tackle system of pulley
Single fixed pulley
This
is the type of pulley whereby effort is applied at one end of the tape
in order to raise the load. Single fixed pulleys are used to raise small
objects e.g. Flags. Consider the diagram below:-
is the type of pulley whereby effort is applied at one end of the tape
in order to raise the load. Single fixed pulleys are used to raise small
objects e.g. Flags. Consider the diagram below:-
Single fixed Pulley
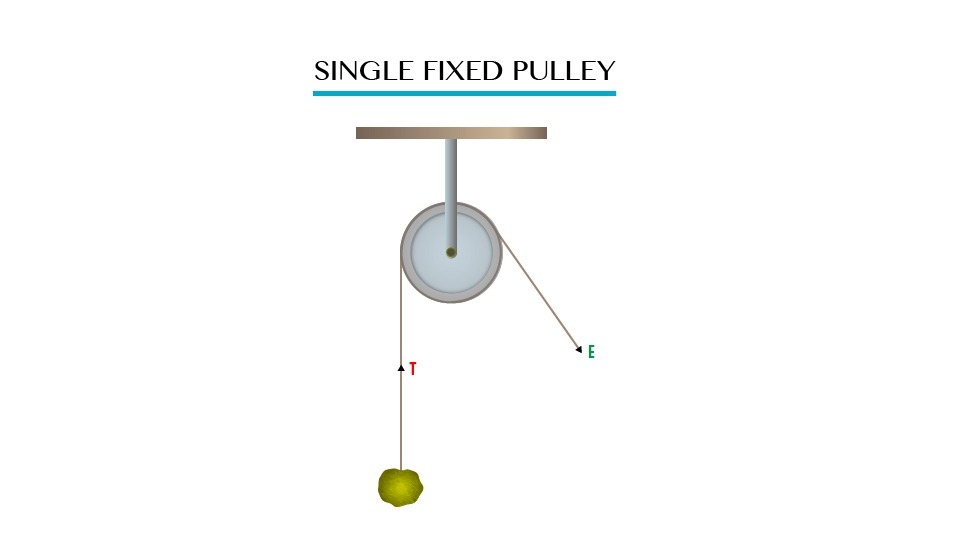
M.A and V.R of single fixed pulley

Single Movable Pulley
Single movable pulley is the one which load is multiple of Effort.
Load = 2E
Consider the following diagram
Single movable pulley
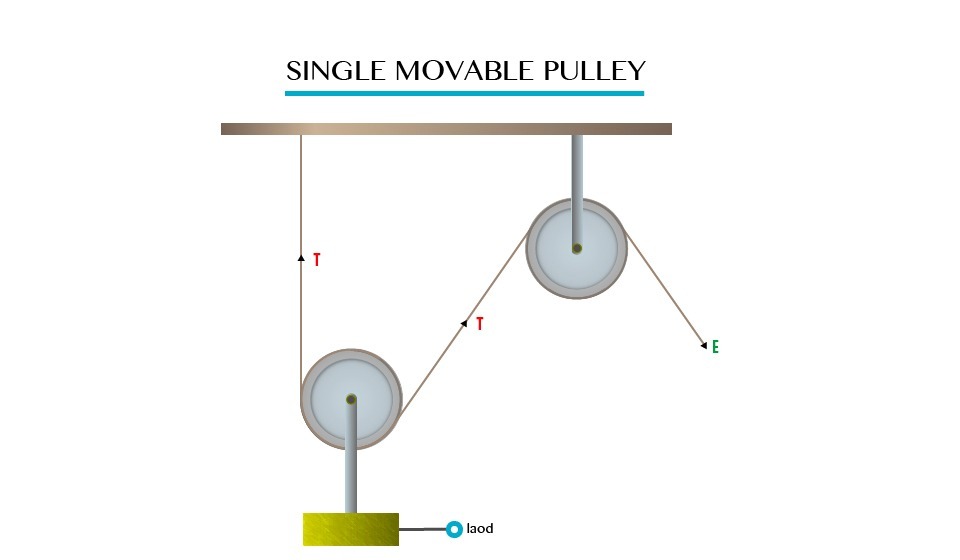
M.A and V.R of single movable pulley

The block and tackle system of pulley
When
two or more pulleys are fixed in a frame, a block is formed. The
pulleys in each block are fixed independently on separate axles.
Consider the diagram below:-
two or more pulleys are fixed in a frame, a block is formed. The
pulleys in each block are fixed independently on separate axles.
Consider the diagram below:-
Block and tackle system of pulley
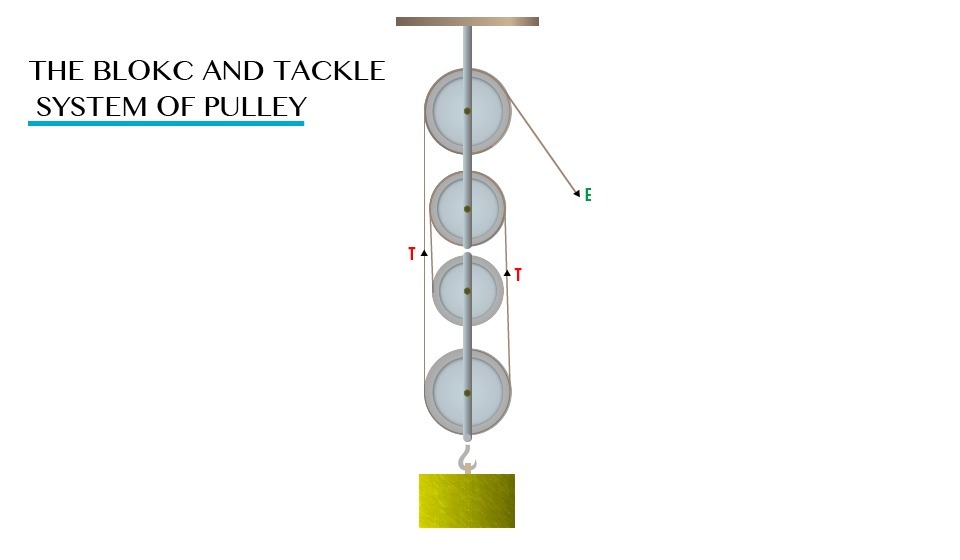
Note; mechanical advantage = Load/Effort
Velocity ratio of Block and tackle system is equal to the number of pulleys.
Example 5
Example 1
A
block and tackle pulley system has a velocity ratio of 4. If a load of
200N is raised by using a force of 75N. Calculate the mechanical (i)
Advantage of the system (ii) efficiency of the system.
block and tackle pulley system has a velocity ratio of 4. If a load of
200N is raised by using a force of 75N. Calculate the mechanical (i)
Advantage of the system (ii) efficiency of the system.
Solution;
Data given
Velocity ratio (V.R) = 4
Load = 200N
Effort = 75N
M.A =?
M.A and Efficiency of block and tackle pulley system
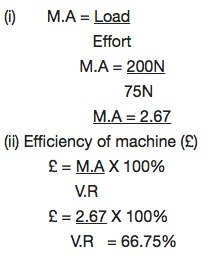
Mechanical Advantage, Velocity Ratio and Efficiency of Pulley System
Determine mechanical advantage, velocity ratio and efficiency of pulley system
VR of block and tackle
When
the lower two pulleys move up a vertical distance y, corresponding to
movement y of the load L, each pulley releases a length y of the rope on
each side giving a total length 2y.
the lower two pulleys move up a vertical distance y, corresponding to
movement y of the load L, each pulley releases a length y of the rope on
each side giving a total length 2y.
With
all this movement of pulleys, the effort E is moved down a distance of 2
x 2y or 4y.Thus, VR = (distance moved by effort)/(distance moved by
load at the same time) = 4y/y = 4
all this movement of pulleys, the effort E is moved down a distance of 2
x 2y or 4y.Thus, VR = (distance moved by effort)/(distance moved by
load at the same time) = 4y/y = 4
VR = Number of pulleys of the system.
Efficiency of block and tackle
From, ε = MA/VR X 100%
ε = (number of pulleys )/(number of pulleys) x 100%
Note:Then, for a perfect block and tackle pulley system, ε = 100%.
But
in practical case the MA is less than the number of pulleys, hence the
efficiency of pulleys system is less than 100% due to friction losses.
in practical case the MA is less than the number of pulleys, hence the
efficiency of pulleys system is less than 100% due to friction losses.
MA of block and tackle.
From MA = load/effort
MA = (Effort x Number of pulleys of the system)/Effort
MA = Number of pulleys of the system.
Pulley in Daily Life
Use of pulley in daily life
Uses of Pulleys
Pulleys
have been used for lifting for thousands of years. The most prevalent
and oldest example are their uses on ships and boats. The block and
tackle have been a key tool for raising sails and cargo. Another major
use for pulleys is withcranes.
have been used for lifting for thousands of years. The most prevalent
and oldest example are their uses on ships and boats. The block and
tackle have been a key tool for raising sails and cargo. Another major
use for pulleys is withcranes.
Pulleys
have been used also in modern times with various machines and systems.
Even in the space age, pulleys have been an important aspect for the
construction and operations of spacecraft and aircraft. It is with a
pulley system that rudders for an aircraft are controlled.
have been used also in modern times with various machines and systems.
Even in the space age, pulleys have been an important aspect for the
construction and operations of spacecraft and aircraft. It is with a
pulley system that rudders for an aircraft are controlled.
Pulleys are used in everyday life, from vehicles to moving equipment such as cranes.
Inclined Plane
The Concept of Inclined Plane
State the concept of inclined plane
An
inclined plane is a sloping plane surface, usually a wooden plank used
to raise heavy load by pulling or pushing them along the surface of the
plane.
inclined plane is a sloping plane surface, usually a wooden plank used
to raise heavy load by pulling or pushing them along the surface of the
plane.
An inclined plane
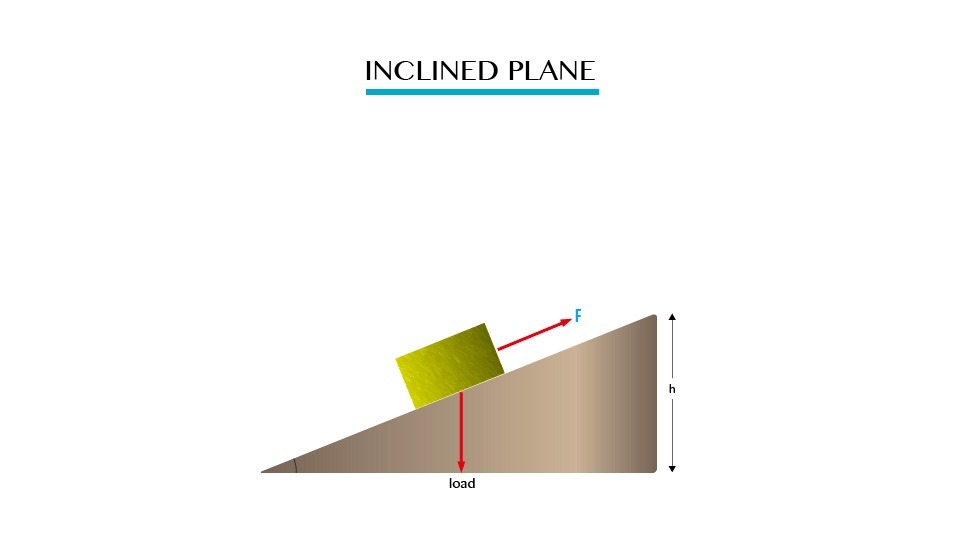
Mechanical Advantage, Velocity Ratio and Efficiency of Inclined Plane
Determine mechanical advantage, velocity ratio and efficiency of inclined plane
Mechanical advantage of the inclined plane
M.A = Load/Effort
V.R of inclined plane = Length of the plane/Height of the plane
Example 6
Example:
A
loaded wheelbarrow of weight 800N is pushed up an inclined plane by a
force of 150N parallel to the plane. If the plane rises by 50cm for
every 400cm distance measured along the plane, find the velocity ratio,
mechanical advantage and efficiency of the plane.
loaded wheelbarrow of weight 800N is pushed up an inclined plane by a
force of 150N parallel to the plane. If the plane rises by 50cm for
every 400cm distance measured along the plane, find the velocity ratio,
mechanical advantage and efficiency of the plane.
Solution:
Data given
Load = 800N
Effort = 150N
Length of plane = 400cm
Height of the plane = 50cm
V.R =?
M.A=?
=?
M.A, V.R and Efficiency of Inclined Plane
Inclined Plane in Daily Life
Apply inclined plane in daily life
Application of Inclined Plane
Inclined planes are widely used in the form ofloading rampsto
load and unload goods on trucks, ships, and planes.Wheelchair rampsare
used to allow people inwheelchairsto get over vertical obstacles without
exceeding their strength.Escalatorsand slantedconveyor beltsare also
forms of inclined plane.
load and unload goods on trucks, ships, and planes.Wheelchair rampsare
used to allow people inwheelchairsto get over vertical obstacles without
exceeding their strength.Escalatorsand slantedconveyor beltsare also
forms of inclined plane.
In
a funicular or cable railway a railroad car is pulled up a steep
inclined plane using cables. Inclined planes also allow heavy fragile
objects, including humans, to be safely lowered down a vertical distance
by using the normal force of the plane to reduce the gravitational
force. Aircraft evacuation slides allow people to rapidly and safely
reach the ground from the height of a passenger airliner.
a funicular or cable railway a railroad car is pulled up a steep
inclined plane using cables. Inclined planes also allow heavy fragile
objects, including humans, to be safely lowered down a vertical distance
by using the normal force of the plane to reduce the gravitational
force. Aircraft evacuation slides allow people to rapidly and safely
reach the ground from the height of a passenger airliner.
Screw Jack
The Structure of a Screw Jack
Describe the structure of a Screw Jack
Structure of Screw Jack
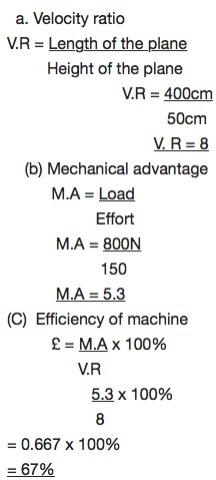
A
screw Jack consist of a cylinder with a spiral ridge runs round it. The
spiral is called the thread (T) and the distance between two adjacent
threads is called the pitch (p) of the screw.
screw Jack consist of a cylinder with a spiral ridge runs round it. The
spiral is called the thread (T) and the distance between two adjacent
threads is called the pitch (p) of the screw.
Consider the following diagram.
The bolt and screw

The Screw Jack
The Mechanichal Advantage, Velocity Ratio and Efficiency of a Screw Jack
Determine the mechanical advantage, velocity ratio and efficiency of a Screw Jack
Mechanical advantage of the screw jack
M.A = Load/Effort
Velocity ratio (V.R)
V.R = Circumference of circle of radius (R)/Pitch of screw
V.R = 2pR/P
Example 7
Example 1
A screw jack with a pitch of 0.2cm and a handle of length 50cm is used to lift a car of weight 1.2 x 104N. If the efficiency of the screw is 30%, find:
- The velocity ratio and mechanical Advantage of the machine
- The effort required to raise the car
Solution;
Date given
Pitch = 0.2cm
Radius= 50cm
Load = 1.2 x104N
Efficiency of jack =30%
V.R=?
M.A=?
Effort+?
–

The Screw Jack in Daily Life
Use the Screw Jack in daily life
Screw
jacks are used to lift heavy loads despite the large friction they
produce. The heavier the load the higher the friction force. They are
self-locking, meaning that when the applied force is removed, they do
not rotate backwards. They are used in adjusting workplace chairs and
tables. They also help in pulling and pushing machine equipment as well
as tightening mechanical parts.
jacks are used to lift heavy loads despite the large friction they
produce. The heavier the load the higher the friction force. They are
self-locking, meaning that when the applied force is removed, they do
not rotate backwards. They are used in adjusting workplace chairs and
tables. They also help in pulling and pushing machine equipment as well
as tightening mechanical parts.
Wheel and Axle
The Structure of a Wheel and Axle
Describe the structure of a wheel and axle
Structure of Wheel and Axle
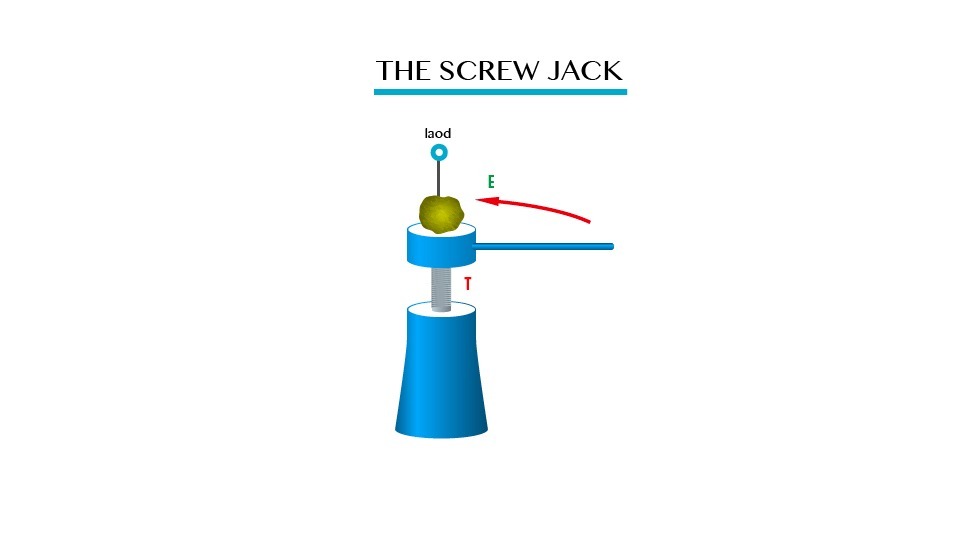
A
wheel and axle is a simple machine that consists of a wheel and axle
mounted with the same axis of rotation. The radius of the wheel is
always greater than that of the axle.
wheel and axle is a simple machine that consists of a wheel and axle
mounted with the same axis of rotation. The radius of the wheel is
always greater than that of the axle.
Consider the diagram below:
Wheel and Axle
The Mechanical Advantage, Velocity Ratio and Efficiency of a Wheel and Axle
Determine the mechanical advantage, velocity ratio and efficiency of a wheel and axle
Mechanical advantage of Wheel and Axle
M.A = Load/Effort
Velocity ratio ( V.R)= radius of wheel (R)/radius of axle (r)
Example 8
Example 1
A
wheel and axle of efficiency 80% is used to raise a load of 2000N. If
the radius of the wheel is 50cm, and that of the axle is 2cm, calculate
wheel and axle of efficiency 80% is used to raise a load of 2000N. If
the radius of the wheel is 50cm, and that of the axle is 2cm, calculate
- The velocity ratio and mechanical Advantage of machine
- The effort required to overcome the load
Solution
Data given
Efficiency = 80%
Load = 2000N
Radius of wheel (R)= 50cm
Radius of axle (r) = 2cm
V.R=?
M.A=?
Effort?
–

The Wheel and Axle in Daily Life
Use the wheel and axle in daily life
Application of Wheel and Axle
Wheels
help people do work in two ways. First, likeleversorinclined planes,
wheels allow you to do something easy for a longer time, instead of
doing something hard for a shorter time. If you turn a large wheel fixed
to an axle, the axle will also turn. You can turn the large wheel
easily (but it takes a lot of turning to go all the way around).
help people do work in two ways. First, likeleversorinclined planes,
wheels allow you to do something easy for a longer time, instead of
doing something hard for a shorter time. If you turn a large wheel fixed
to an axle, the axle will also turn. You can turn the large wheel
easily (but it takes a lot of turning to go all the way around).
The
axle will go around a much shorter distance, but with more force. So
you can use a wheel to create a mechanical advantage – you can turn
something heavy, by spinning a large wheel attached to an axle that is
attached to the heavy thing.
axle will go around a much shorter distance, but with more force. So
you can use a wheel to create a mechanical advantage – you can turn
something heavy, by spinning a large wheel attached to an axle that is
attached to the heavy thing.
That’s
how a pencil sharpener works. Or, you can do it the other way around –
use a lot of force to turn the axle, and that will spin the wheels
really fast. That’s what cars do.Wheels are the most important part of
pottery wheels, wagons and cars, but also ofwheelbarrows,spinning
wheels, water wheels, windmills, andpulleys.
how a pencil sharpener works. Or, you can do it the other way around –
use a lot of force to turn the axle, and that will spin the wheels
really fast. That’s what cars do.Wheels are the most important part of
pottery wheels, wagons and cars, but also ofwheelbarrows,spinning
wheels, water wheels, windmills, andpulleys.
Also,
wheels on a wagon only touch the ground at one spot at a time, keeping
the rest of the wagon off the ground. This makes lessfriction, so that
the wagon is easier to move than if you were pulling it along like a
sled.
wheels on a wagon only touch the ground at one spot at a time, keeping
the rest of the wagon off the ground. This makes lessfriction, so that
the wagon is easier to move than if you were pulling it along like a
sled.
Hydraulic press
The Structure of Hydraulic Press
Describe the structure of Hydraulic Press
Structure of Hydraulic Press
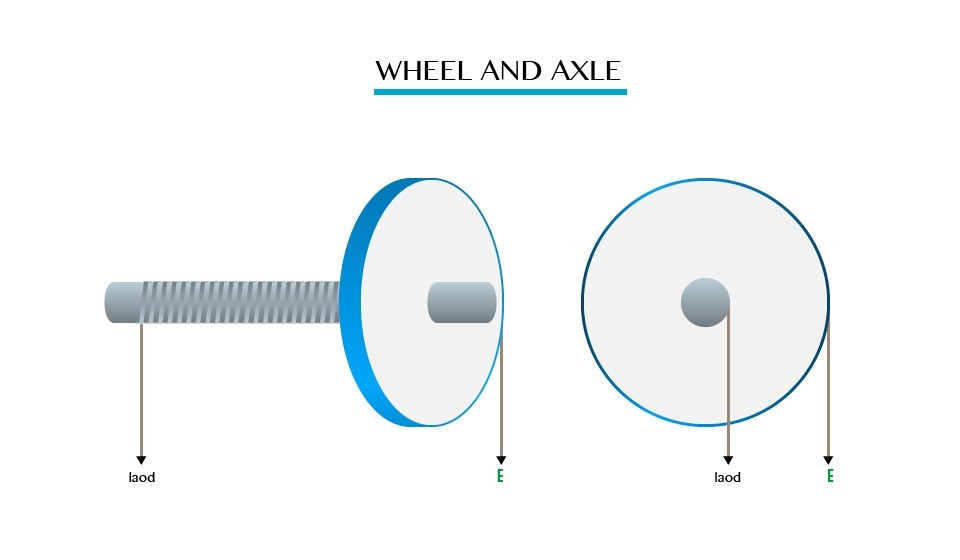
A
hydraulic press is a machine that has a bed or a plate in which the
metallic material is placed so that it can be crushed, straightened or
moulded.
hydraulic press is a machine that has a bed or a plate in which the
metallic material is placed so that it can be crushed, straightened or
moulded.
Mechanical Advantage, Velocity Ratio and Efficiency of a Hydraulic Press
Determine mechanical advantage, velocity ratio and efficiency of a Hydraulic Press
In
hydraulic press small force (Effort) applied on the small piston is
used to overcome a much greater force (load) on the large piston.
hydraulic press small force (Effort) applied on the small piston is
used to overcome a much greater force (load) on the large piston.
When
a small effort (E) is applied downwards on the effort piston of radius
(r) the load piston of radius (R) lifts the load (L).
a small effort (E) is applied downwards on the effort piston of radius
(r) the load piston of radius (R) lifts the load (L).
Consider the diagram below:
Hydraulic Press
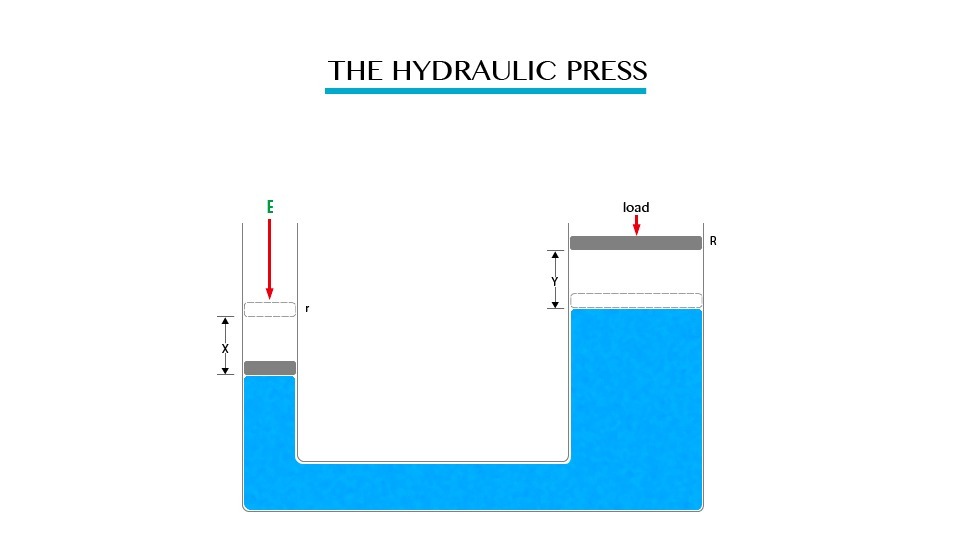
By the principle of transmission of pressure in liquid, the pressure on effort piston is equal to the load piston.
–

VELOCITY RATIO OF HYDRAULIC PRESS
If
friction is neglected the work done by the effort E is equal to the
work done on the load (L). So if the effort piston is moved by distance x
and the load piston raised up by a corresponding distance Y, it
follows:
friction is neglected the work done by the effort E is equal to the
work done on the load (L). So if the effort piston is moved by distance x
and the load piston raised up by a corresponding distance Y, it
follows:
–

Note: Due to friction, efficiency of the hydraulic press is not 100%
The Hydraulic Press in Daily Life
Use the Hydraulic Press in daily life
Uses of a Hydraulic Press
A
hydraulic press is used for almost all industrial purposes. But
basically it is used for transforming metallic objects into sheets of
metal. In other industries, it is used for the thinning of glass, making
powders in case of the cosmetic industry and for forming the tablets
for medical use. The other common uses of the hydraulic presses are as
follows:
hydraulic press is used for almost all industrial purposes. But
basically it is used for transforming metallic objects into sheets of
metal. In other industries, it is used for the thinning of glass, making
powders in case of the cosmetic industry and for forming the tablets
for medical use. The other common uses of the hydraulic presses are as
follows:
For crushing cars
A
hydraulic press is the heart of any car crushing system. In this
process, a hydraulic motor applies a large pressure on the fluids into
the cylinders. The fluid pressure makes the plates rise and with a large
force, the plate is driven on the car thereby crushing it.
hydraulic press is the heart of any car crushing system. In this
process, a hydraulic motor applies a large pressure on the fluids into
the cylinders. The fluid pressure makes the plates rise and with a large
force, the plate is driven on the car thereby crushing it.
Fat-free cocoa powder
While
processing the cocoa beans, a liquid known as chocolate liquor is
derived. For making fat-free cocoa powder, this liquid is squeezed out
in a hydraulic press. After this stage, this liquid is processed further
to make a powder. The powder thus derived is cocoa powder, which is
fat-free.
processing the cocoa beans, a liquid known as chocolate liquor is
derived. For making fat-free cocoa powder, this liquid is squeezed out
in a hydraulic press. After this stage, this liquid is processed further
to make a powder. The powder thus derived is cocoa powder, which is
fat-free.
For sword making
In the process of making swords, a hydraulic press is used to give a flat shape to the raw steel.



