Introduction to Astronomy
The Concept of Astronomy
Explain the concept of astronomy
Astronomy is a branch of science which deals with the study of origin,evolution, composition, distance and the motion of all bodies and scattered matter in the universe.
- Universe is the totality of space and time together with matter and energy.
- Astronomers are the people who deals astronomy.
The Importance of Astronomy in Everyday Life
Explain the importance of astronomy in everyday life
Importance of astronomy include:
- It was the earliest method of measuring time.
- It was used to develop calendars that made it possible to predict the seasons.
- It is used in navigation.-Helps us to understand the earth and the life it supports originated from and how it evolved.
- It presents a new frontier for exploration.
Solar System
Difference between a Star and a Planet
Distinguish between a star and a planet
The
solar system is made up of the sun and the celestial objects bound to
it by gravity.These objects include the eight planets and their known
moons and billions of small bodies that include
asteroids,comets,meteoroids and interplanetary dust.
solar system is made up of the sun and the celestial objects bound to
it by gravity.These objects include the eight planets and their known
moons and billions of small bodies that include
asteroids,comets,meteoroids and interplanetary dust.
Stars and planets
A star is a large celestial body made up of hot gases known as plasma.
Plasma is an ionized gas in which a certain proportion of electrons are free rather than bound to an atom or molecule.
The
sun is a large star. The sun is also the closest star to the earth.
Astronomical unit is the distance between the earth and the sun which is
used to measure distances across the solar system (its value is
approximately 149.60 million kilometers).
sun is a large star. The sun is also the closest star to the earth.
Astronomical unit is the distance between the earth and the sun which is
used to measure distances across the solar system (its value is
approximately 149.60 million kilometers).
A Galaxy is a giant collection of stars,gas and dust.
Most
stars in the universe are in the galaxies. Nearly all of the stars
visible in the night sky are within our own galaxy, sometimes called the
Milky Way Galaxy.
stars in the universe are in the galaxies. Nearly all of the stars
visible in the night sky are within our own galaxy, sometimes called the
Milky Way Galaxy.
Planet
is a major (large) object which is in orbit around a star.There are
eight planets which are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn,
Uranus, and Neptune.
is a major (large) object which is in orbit around a star.There are
eight planets which are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn,
Uranus, and Neptune.
Characteristics of a planet
- It is a celestial body that orbits a star.
- It is massive enough so that its own gravity cause it to assume a spherical shape.
- It has cleared the neighbourhood around its orbit.
Pluto
is not considered as a planet because it resides in an area of space
populated by numerous other objects.It is now designated a dwarf
planet.The dwarf planet does not meet the third characteristic i.e has
not cleared the neighbourhood around its orbit.
is not considered as a planet because it resides in an area of space
populated by numerous other objects.It is now designated a dwarf
planet.The dwarf planet does not meet the third characteristic i.e has
not cleared the neighbourhood around its orbit.
Differences between stars and planets
| Stars | Planets |
| Emit their own light | Do not emit their own light |
| Twinkle at night | Do not twinkle at night |
| Appear to be moving from east to west. | Planets move around the sun from west to east. |
| Their temperatures are usually very high | Their temperature depends on their distances from the sun |
| Countless in number | There are eight in the solar system |
| Very big in size but they appear small because they are very far away | Very small in size as compared to stars. |
Asteroids
(minor planets) are small solar system bodies in orbit around the
sun,especially in the inner solar system.Asteroids are smaller than
planets but larger than a speck of dust.
(minor planets) are small solar system bodies in orbit around the
sun,especially in the inner solar system.Asteroids are smaller than
planets but larger than a speck of dust.
A
comet is a solid body orbiting the sun typically composed of rock dust
or ice. Most comets were formed from condensed interstellar gas and dust
clouds in the early stages of the creation of the universe.
comet is a solid body orbiting the sun typically composed of rock dust
or ice. Most comets were formed from condensed interstellar gas and dust
clouds in the early stages of the creation of the universe.
The Force of Gravitation which Maintains Celestial Bodies in their Orbits
Explain the force of gravitation which maintains celestial bodies in their Orbits
Gravitation
force is the attractive force existing between any two objects that
have mass. It pulls objects together and acts on all matter on the
universe, hence it is sometimes referred to as universal gravitation.
force is the attractive force existing between any two objects that
have mass. It pulls objects together and acts on all matter on the
universe, hence it is sometimes referred to as universal gravitation.
Newton’s law of universal gravitation
It
states that: ‘Every single point mass attracts every other point by a
force directed along the line joining the two masses.’The force is
proportional to the product of the two masses and inversely proportional
to the square of the distance between the point masses.
states that: ‘Every single point mass attracts every other point by a
force directed along the line joining the two masses.’The force is
proportional to the product of the two masses and inversely proportional
to the square of the distance between the point masses.
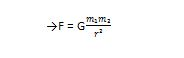
Where:
- F is the magnitude of the attractive force between the two point masses.
- G is the universal gravitation constant.m₁ is the mass of the first point mass.
- m₂ is the mass of the second point mass.
- r is the distance between the centers of the two point masses.
Gravitation
force is actually very weak force.The huge gravitational force of the
nearest star,the sun,holds together the eight planets of the solar
system. The planets move round the space at speeds that just balance the
sun’s gravitational pull, so they are locked into a permanent path
(orbit) around the sun.
force is actually very weak force.The huge gravitational force of the
nearest star,the sun,holds together the eight planets of the solar
system. The planets move round the space at speeds that just balance the
sun’s gravitational pull, so they are locked into a permanent path
(orbit) around the sun.
Natural
satellites (moons) orbits planets while artificial satellites orbit the
earth in the same way as the moon orbits the planets.
satellites (moons) orbits planets while artificial satellites orbit the
earth in the same way as the moon orbits the planets.
Gravity
is the gravitational force that occurs between the earth and the other
objects.It pulls the objects towards the center of the earth.It holds us
on the ground and causes objects to fall back to the ground after being
thrown uo in the air.
is the gravitational force that occurs between the earth and the other
objects.It pulls the objects towards the center of the earth.It holds us
on the ground and causes objects to fall back to the ground after being
thrown uo in the air.
The
earth gravitational pull extends out into space in all directions. The
further you move away from the center of the earth,the weaker the force
becomes. The measure of the force of gravity on an object on the earth’s
surface is the weight of that object and is measured in newton (N).
earth gravitational pull extends out into space in all directions. The
further you move away from the center of the earth,the weaker the force
becomes. The measure of the force of gravity on an object on the earth’s
surface is the weight of that object and is measured in newton (N).
The weight of an object changes depending on its location in the universe.
The Surface Features and Temperature of the Moon
Describe the surface features and temperature of the moon
The
moon of the earth is the sixth largest in the solar system. It has a
diameter of 3,476km and a mass of 7.35 x 10²²kg. Like the earth, the
moon has an iron core surrounded by a rocky mantle and crust.Unlike the
earth, no part of the moon’s iron core is molten so it does not have a
magnetic field.Surface gravity on the moon is 1/6 that of the earth.
moon of the earth is the sixth largest in the solar system. It has a
diameter of 3,476km and a mass of 7.35 x 10²²kg. Like the earth, the
moon has an iron core surrounded by a rocky mantle and crust.Unlike the
earth, no part of the moon’s iron core is molten so it does not have a
magnetic field.Surface gravity on the moon is 1/6 that of the earth.
The
moon revolves in a anticlockwise direction around the earth in an
elliptical orbit. The moon’s orbit is tilted at 5° relative to the
earth’s orbit around the sun.The distance between the earth and the moon
varies from perigee (nearest the earth) where it is 356,000km to apogee
(furthest from the earth) where it is 406,000km. The average distance
is 384,000km.
moon revolves in a anticlockwise direction around the earth in an
elliptical orbit. The moon’s orbit is tilted at 5° relative to the
earth’s orbit around the sun.The distance between the earth and the moon
varies from perigee (nearest the earth) where it is 356,000km to apogee
(furthest from the earth) where it is 406,000km. The average distance
is 384,000km.
It
take the moon 27.3 earth days to complete one orbit, a period of time
called the Sidereal month.The moon also rotates about its axis at a rate
equal to its rate of revolution. The result of this is that one side of
the moon face the earth. The side which faces the earth is called the
near side while the side which faces away is called the far side.
take the moon 27.3 earth days to complete one orbit, a period of time
called the Sidereal month.The moon also rotates about its axis at a rate
equal to its rate of revolution. The result of this is that one side of
the moon face the earth. The side which faces the earth is called the
near side while the side which faces away is called the far side.
The
spinning of the earth causes the moon to rise and set each day ,just
like the sun. However, because of moons’ orbital motion around the earth
,it(the moon) rises about 50 minutes later each day .As a result, the
moon can be seen at different times of the day and night during a month.
spinning of the earth causes the moon to rise and set each day ,just
like the sun. However, because of moons’ orbital motion around the earth
,it(the moon) rises about 50 minutes later each day .As a result, the
moon can be seen at different times of the day and night during a month.
The temperatures on the surface of the moon are on average 107°C during the day and 53°C during the night.
Surface features of the moon.
There are two primary types of terrain on the moon. These are;
- Heavily cratered very old lunar highlands.
- Relatively smooth and younger Maria.
From the surface of the earth,the moon’s surface appears to have bright and dark regions when viewed with the unaided eye.
The
bright areas are the lunar highlands that have many craters and covered
with a highly reflective layer of fine dust. The highlands are
geologically the oldest parts of the moon’s surface.
bright areas are the lunar highlands that have many craters and covered
with a highly reflective layer of fine dust. The highlands are
geologically the oldest parts of the moon’s surface.
The
dark areas are low areas similar to ocean basins on the earth. They are
with dark solidified lava and are less cratered than the highlands.
Galileo called these areas matia, Italian word for seas, because their
dark smooth surface appears to be large bodies of water.
dark areas are low areas similar to ocean basins on the earth. They are
with dark solidified lava and are less cratered than the highlands.
Galileo called these areas matia, Italian word for seas, because their
dark smooth surface appears to be large bodies of water.
The
maria which makes 16% of the moon’s surface , are huge impact craters
that were later flooded with molten lava. Most of the maria is covered
with regolith,a mixture of fine dust and rocky debris produced by meteor
impact.
maria which makes 16% of the moon’s surface , are huge impact craters
that were later flooded with molten lava. Most of the maria is covered
with regolith,a mixture of fine dust and rocky debris produced by meteor
impact.
The Causes of Ocean Tides
Explain the causes of ocean tides
Tides
are periodic rises and falls of large bodies of water caused mainly by
gravitational interaction between the earth and the moon.
are periodic rises and falls of large bodies of water caused mainly by
gravitational interaction between the earth and the moon.
The
earth and the moon are attracted each other, just like magnets are
attracted to each other. The moon rises to pull at anything on the earth
to bring it closer. But the earth is able to hold onto everything
except the water. Since the water always moving, the earth can’t hold
onto it and the moon is able to pull at it. This results into ocean
tides.
earth and the moon are attracted each other, just like magnets are
attracted to each other. The moon rises to pull at anything on the earth
to bring it closer. But the earth is able to hold onto everything
except the water. Since the water always moving, the earth can’t hold
onto it and the moon is able to pull at it. This results into ocean
tides.
Each
day, there are two high tides and two low tides. The ocean constantly
moves from high tide to low tide, and then back to high tide. There is a
time interval of about 12 hours and 25 minutes between the two high
tides.
day, there are two high tides and two low tides. The ocean constantly
moves from high tide to low tide, and then back to high tide. There is a
time interval of about 12 hours and 25 minutes between the two high
tides.
How tides occur
Gravitational
attraction of the moon causes the oceans to bulge out in the direction
of the moon. Another bulge occurs on the opposite side since the earth
is also being pulled towards the moon (and away from the water on the
far side).
attraction of the moon causes the oceans to bulge out in the direction
of the moon. Another bulge occurs on the opposite side since the earth
is also being pulled towards the moon (and away from the water on the
far side).
Ocean
levels fluctuate daily as the sun, moon and earth interact .As the moon
travels around the earth, and as they together travel around the sun,
the combined gravitational forces cause the world ocean water levels to
rise and fall. Since the earth is rotating while this is happening, two
tides occur each day.
levels fluctuate daily as the sun, moon and earth interact .As the moon
travels around the earth, and as they together travel around the sun,
the combined gravitational forces cause the world ocean water levels to
rise and fall. Since the earth is rotating while this is happening, two
tides occur each day.
Types of tides
There are two types of tides:
Spring tides
They
occur during the full moon and the new moon. During this time, the
earth,the sun and the moon are in a line. The gravitational forces of
the moon and the sun both contribute to the tides.
occur during the full moon and the new moon. During this time, the
earth,the sun and the moon are in a line. The gravitational forces of
the moon and the sun both contribute to the tides.
At
these times, the high tides are very high and the low tides are very
low. These are known as spring high tines and spring low tides
respectively.
these times, the high tides are very high and the low tides are very
low. These are known as spring high tines and spring low tides
respectively.
Spring
tides are especially strong tides.Proxigen spring tide is a rare
unusually high tide. It occurs when the moon is both unusually close to
the earth (at its closest perigee, called the proxigee) and in the new
moon phase(when the moon is between the earth and the sun).
tides are especially strong tides.Proxigen spring tide is a rare
unusually high tide. It occurs when the moon is both unusually close to
the earth (at its closest perigee, called the proxigee) and in the new
moon phase(when the moon is between the earth and the sun).
The proxigen spring spring tide occurs at most once every 1.5 years.
Neap tide
When
the sun and the moon are not aligned, the gravitational forces cancel
each other out, and the tides are not very high or very low. These are
called neap tides.
the sun and the moon are not aligned, the gravitational forces cancel
each other out, and the tides are not very high or very low. These are
called neap tides.
They
occur during quarter moons. During this time, the gravitational forces
of the moon and the sun are perpendicular to one another (with respect
to the earth).
occur during quarter moons. During this time, the gravitational forces
of the moon and the sun are perpendicular to one another (with respect
to the earth).
This
causes the bulges to cancel each other. The result is a smaller
difference between high and low tide and is known as a neap tide. Neap
tides are especially weak tides.
causes the bulges to cancel each other. The result is a smaller
difference between high and low tide and is known as a neap tide. Neap
tides are especially weak tides.


