Download & Install
Darasa Huru App
DOWNLOAD
TOPIC 6: REPRODUCTION | BIOLOGY FORM 3
Concept of Reproduction
Reproduction is the ability of living organisms to form new individuals of the same species from those already in existence. Here, the new organisms replace those that have died and so life continues. It can also be defined as the process whereby organisms produce new individuals of the same species. It is one of the important features of living things.
is a type of reproduction in which new organism is produced when a male
gamete fuses with a female gamete. Sexual reproduction involves the
fusion of two gametes. The process of fusion of gametes is called
fertilization.
These
two gametes differ in form and function and each is produced from a
different organ. In animals the gametes producing organs are called
gonads. These include the ovaries and testes. In flowering plant
structures concerned with the production of gametes are the ovaries and
anthers. The testes and anthers produce the male gametes while ovaries
produce the female gametes.
- It ensures genetic stability
- It ensures perpetuation of life
- It brings variation
- Leads to the interaction among organisms
- Offspring have a great chance of inheriting diseases from the parent
- The reproduction takes long time
- It needs energy
- The sexual reproduction produces few numbers of offspring
- It depends on presences of two parents
- It leads to great chance of spreading diseases
- It takes a long time until offspring are produced
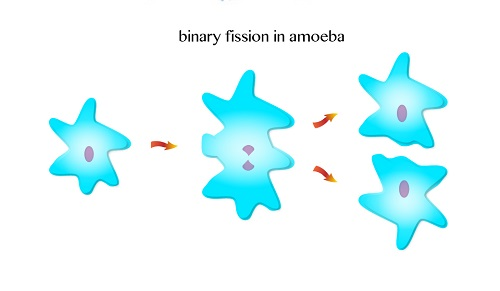
is the type of reproduction whereby production of offspring is from
single organism without the production of gametes. There is no fusion of
gametes.
of organisms who produce asexually are amoeba and bacteria. Asexual
reproduction involves only one individual organism. That means no change
of genetic material is passed from a parent to an offspring. The
offspring are also identical to their parents.
- Fission
- Sporulation/Spore formation
- Budding
- Fragmentation
- Vegetative propagation
- Binnary Fission (Splitting)
- Suckers
- Bulbils
is a form of asexual reproduction in which organisms (parent) breaks
into two or more parts. Fragments grow and develop into a new organism
with identical features as the parent. Example worms such as Nematodes
and flat worms.
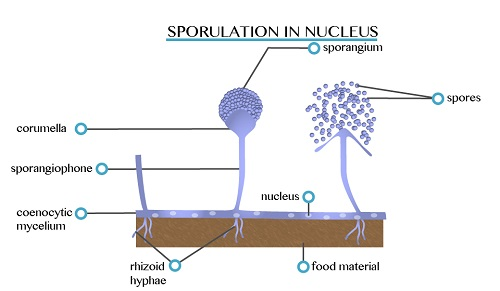
is asexual reproduction by the use of spores. The spore develops from
single cell as a result of mitosis, forming a structure known as
sporangium. When the sporangium is truly developed, the wall bursts to
release the spores which when placed in suitable area they germinate
into new organisms.
is a type of asexual reproduction in which a new organism arises as an
outgrowth (bud) of the older organism (parent). The bud later separates
from the parent and grows to become an independent organism to attain
the size of the parent. Examples: yeast and hydra

flowering plants reproduce through the formation of structure called
buds. Roots may form such buds, leaves or underground stems and such
buds sprout to form new independent plants.
propagation is a form of asexual reproduction found in plants in which a
bud grows and develops into a new plant. The detached plant, root, stem
or leaves at some stages grows and develops into an independent plant.
This is vegetative propagation, which occurs through man’s
manipulation. Man can learn from plants’ natural vegetative propagation
and can intervene and make propagation of plants artificially.
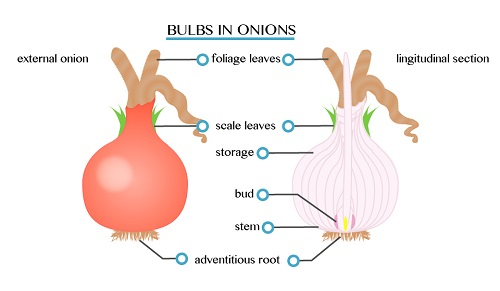
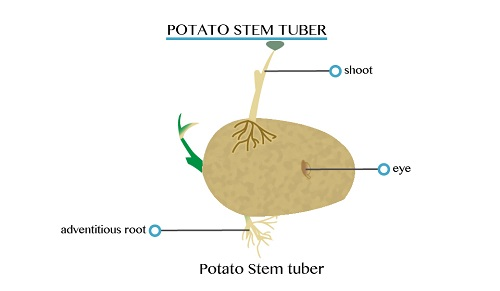
are short swollen underground storage organs formed from a stem or a
root. New tubers are made at the end of the growing season but do not
arise from old tubers.
are short swollen underground stems, which store food, such as starch.
Normally, yam plants form a number of tubers each of which can rise to a
new plant. Such new plant continues to live after the death of the
parent.
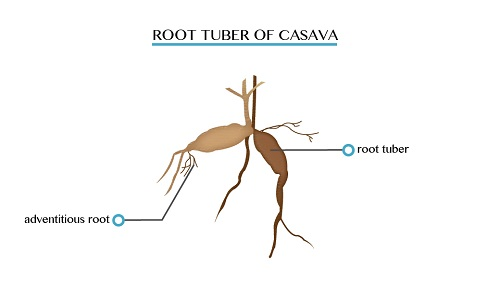
are swollen adventitious underground roots. Roots tubers such as sweet
potatoes and cassava store their food in root tubers and do not bear
leaves or bud.
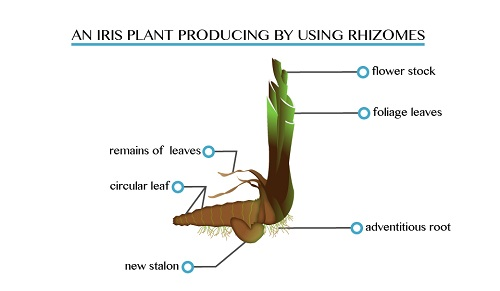
are horizontally growing underground stems, bearing leaves, buds and
adventitious roots. Examples are lilies, ferns and grass.
are slender stems, creeping horizontally as they grow along the ground
surface. Examples: strawberries, black currant and oxalis.

are short horizontal branches, arising from the main stem or just below
ground level. Suckers contain food reserves. Examples: Bananas, sisal
and pineapples
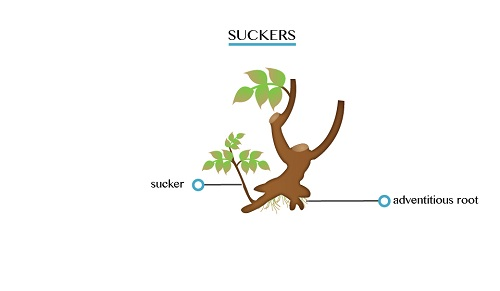
are collection of shoots. Grass plants consist of a number of tillers.
Each tiller has a number of leaves, which arise from the stem of nodes
at the base of the leaves.
plants such as cactus propagate vegetative using leaves. When the
leaves fall off from a plant they develop adventitious roots and buds,
which later may grow and develop into mature plants.
- Asexual reproduction results into an individual with the same genetic constitution as their parent.
- Its offspring matures faster than sexually reproduced organisms
- It does not depend on processes of pollination, seed or fruit dispersal
- Asexually reproducing organisms are at a great risk to perish or get destructed when environmental conditions are unfavorable
- The
parents may pass undesirable characteristics to the offspring since
only one individual organism is involved in asexual reproduction - Competition for resources such as food and shelter may occur due to large number of organisms being produced
involves the transmission of genetic materials from one generation to
the next insuring that species survive. The process of reproduction
involves meiosis.
this type of cell division the parent cells has diploid number of
chromosomes. However the daughter cell arising from the cell division
has the half number of chromosomes a condition known as haploid state.
leads to the formation of reproductive cells (Gametes) such as ova and
sperms each with half number of chromosomes of the parent cells in
organisms reproducing through sexual reproduction.
involves the possibility of exchange of pieces of genetic information
between the paternal and maternal chromosomes of each pair leading to
new combination of characteristics in the gametes.
brings about variation when the members of each pair of chromosomes are
separated from each other independently (Random assortment)
leads to new combination of genes through the process of independent
assortment of chromosomes occurring during meiosis I
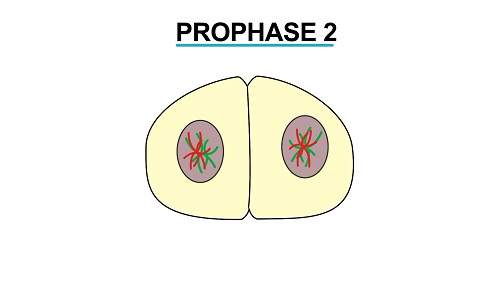
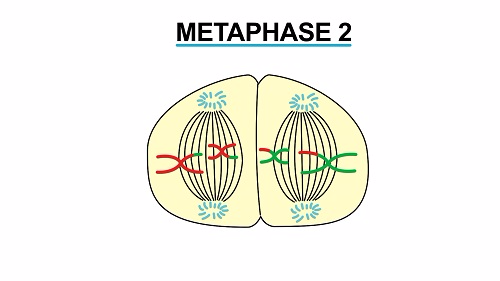
involves number of processes from prophase, metaphase, anaphase and
telephase. There are two meiotic divisions, the first and the second
division. All the above named processes occur in both the first meiotic
division and the second meiotic division.
- Prophase I
- Metaphase I
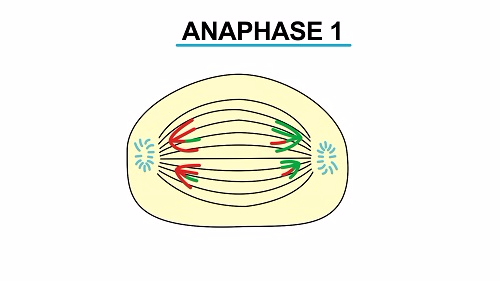
- Anaphase I
- Telophase I
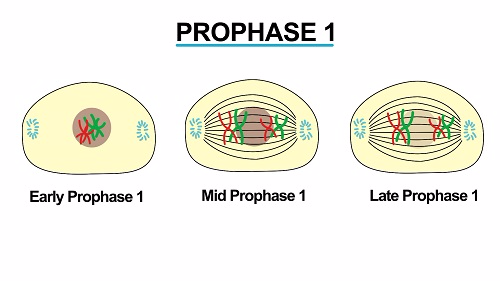
- The nucleus disappears and the centrioles if present migrate to the poles
- Chromosomes condenses and the spindle is formed
- As
prophase proceed homologous chromosomes come to lie side by side and
there after become intertwined by the process called synapsis
synapsis homologous chromosomes is referred to as crossing over. The
point at which homologous chromosomes exchange genetic materials is
known as chiasmata
- Chromosomes contract, thickening, shortening and become more visible
- Nucleus disintegrate and disappear
- Homologous chromosomes come together (synapses) forming a bivalent
- Chromatids cross over by chiasmata which results into exchange of genetic materials
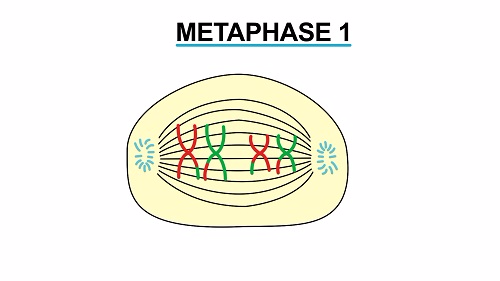
- Bivalent homologous chromosomes moves to the equator of the spindle
- The two homologous chromosomes part company and migrate to opposite poles of the spindle
- The centromeres of the homologous pairs migrate towards the opposite poles where they are attracted.
- The chromosomes reach their destination
- The spindle apparatuses breaks down and disintegrates
- Then the nucleus membrane reforms around each set of chromosomes
- The cell constricts across the membrane and divides into two
- At the end of this prophase the number of chromosomes in each cell is half the chromosomes number cell.
- This is the reason why first meiotic division is referred to as Reduction division
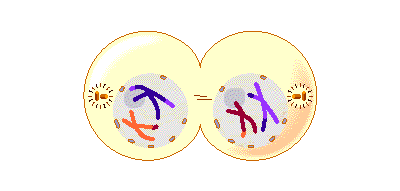
- Sister chromatids part company and migrate to opposite poles of the cell
- The spindle apparatuses disappears
- The nucleus repairs and a new nucleus membrane is formed around each set of chromatids
- The chromatids uncoil and the cell divides into two
- Chromosomes
regain their thread like structure and the cell enter interphase.
Meiosis results into the formation of four daughter cells each with
haploid set of chromosomes - It should be stressed that the four
daughter cells formed has the half number of chromosomes present in the
original parent cell.
plants use flowers to reproduce. The flowers contain all the parts
needed for the reproduction process. Sexual reproduction in flowering
plants takes place in the flower. Within a flower, there are usually
structures that produce both male gametes and female gametes.
flowering plant is an angiosperm, which is any plant that produces a
flower or fruit. The sole purpose of the flower is to allow the plant to
reproduce. Each part of the flower plays a role in the steps of
reproduction. There are male gametes and female gametes. They are both
directly involved with sexual reproduction. Pollen may spread from plant
to plant but can only reproduce with the same species of plants. Let’s
take a look at the different parts of the flower.
start with the sterile parts of the flower, or those parts that are
neither male nor female. These sterile parts are not directly involved
in the fertilization process. Technically, a flowering plant can
reproduce without them; however, they do play important roles in helping
with reproduction.
- Pedicel:The
pedicel is a small stalk or stalk-like part bearing a single flower in
an inflorescence. The Some flowers have no stalk and are directly
attached to the stem of the plant. - Receptacle:The
receptacle is the place on the stem where floral organs originate and
attach.It is the axis (stem) to which the floral organs are attached. In
most angiosperms, floral organs are attached in alternating successive
whorls. A whorl is an arrangement of sepals, petals, leaves, stipules or
branches that radiate from a single point and surround or wrap around
the stem. - Sepals:Sepals are the parts
that look like little leaves that cover the flower before it blooms.
They cup the flower to protect it while it grows. Sepals are mostly
green and in most flowers they resemble leaves. A flower bud is
protected by sepals. Collectively, all of the sepals form the
calyx.Sepals may be hairy, for example in roses, or smooth, for example
in hibiscus.Some flowers have sepal-like structures beneath the calyx
known as epicalyx, for example the hibiscus flower. - Petals:Petals
are the delicate and usually brightly coloured part that gives the
flower its character. Flowers have more than one petal, and the flower
petals are collectively called the corolla. The colour and scent
attracts the agents of pollination such as birds and insects. Fused
petals form a corolla that can be tubular or funnel-shaped as in the
flowers of sweet potato and pumpkin plants. Some of the petals of
leguminous plants are keel-like and they enclose stamens and
carpels.Sepals and petals are collectively referred to as the perianth.
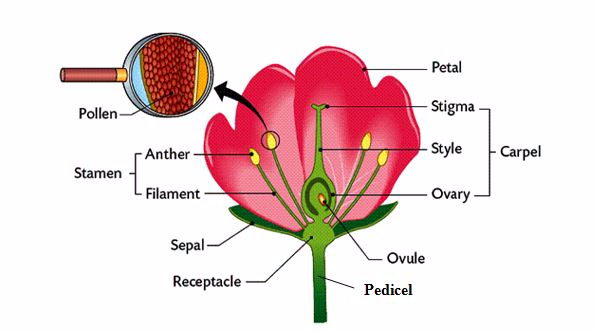
flower is the reproductive unit of some plants (angiosperms). Parts of
the flower include petals, sepals, one or more carpels (the female
reproductive organs), and stamens (the male reproductive organs).
pistil is the collective term for the carpel(s). A carpel is actually
three parts fused into one: stigma, style, and ovary. The stigma is at
the top of the flower. It is sticky to catch the pollen. Each carpel
includes an ovary (where the ovules are produced; ovules are the female
reproductive cells, the eggs), a style (a tube on top of the ovary), and
a stigma (which receives the pollen during fertilization).
ovary is at the base of the flower. From the ovary, extends a tubular
structure called the style and on the top of the style is a surface
receptive to pollen called the stigma. The stigma can take many
different forms, most of them designed to help trap pollen.
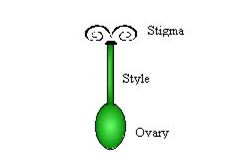
- Ovary:The
ovary contains ovules. Ovules are unfertilized female gametes. The
position of the ovary in relation to the receptacle varies from one
flower to another. The ovary could be either superior or inferior in
relation to the position of the receptacle. A superior ovary is one that
is positioned above the receptacle, for example the ovary of a bean
flower. An inferior ovary is one that is positioned below or enclosed
within the receptacle. Examples are the ovaries of a rose and a black
jack flower. - Style:The style is a long
tube that attaches the stigma to the ovary. The length of the style
varies from one flower to another. This length determines the position
of the stigma. In the maize plants, the style and the stigma hand
outside the flower. - Stigma:The stigma
is a glandular sticky structure at the tip of the carpel. The stigma is
the tissue into which the pollen grains are deposited. The branches of
the stigma correspond to the number of carpels. Five branches of the
stigma indicate the presence of five carpels.
male parts of a flower consist of one or more stamens. Stamens are the
male reproductive parts of flowers. A stamen consists of an anther
(which produces pollen) and a filament. The pollen consists of the male
reproductive cells; they fertilize ovules.
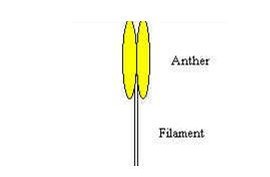
- Filament:The
filament is a slender stalk that supports the anther. The filament may
arise from the receptacle or the petals. It supports the anther. - Anther:The
anther is attached to the apex of the filament. It produces the pollen
grains that contain the sperm needed for fertilization.
flowers have sepals, petals stamens and carpels. A flower with both
stamens and carpel is said to be bisexual. The hibiscus flower is
bisexual.
flowers lack some of the floral parts. Flowers that have carpels only
are referred to as pistillate flowers. Flowers that have stamens only
are referred to as staminate flowers.
is the transfer of pollen grains from the anthers to the stigma of a
flower. Pollen grains from the anthers are carried to the stigma by
wind, insects or birds. These are referred to as the agents of
pollination.Pollination, an important step in the reproduction of seed
plants, is the transfer of pollen grains (male gametes) from the male
reproductive organ to the female reproductive organ that contains the
ovule (female gamete) or transfers it to the ovule itself.
is a very important part of the life cycle of a flowering plant. It is
part of the sexual reproduction process of flowering plants, which
results in seeds that will grow into new plants.
- Self pollination:This is the transfer of pollen grains from the anthers to the stigma of the same flower.
- Cross pollination:This is the transfer of pollen grains from the anthers of the flower to the stigma of another flower of the same species.
potential drawback is that both gametes come from the same parent. If
the plant is well adapted to a stable environment, the production of
uniform offspring may be advantageous. However, inbreeding will result
and if there are disadvantageous recessive characteristics in the
parent, they are much more likely to be exposed than if the plant
cross-pollinates.
is less reliable and more wasteful than self-pollination, but it is
genetically favourable because genes are transferred and variation
increases
- Dioecious plants: Some plants have flowers that are only male – they have onlystamen. Other plants of the same species have flowers that are only female – they have only carpels.
- Monoecious plants:
Some flowers on a plant are only male; other flowers on the same plant
are only female. So, self pollination is avoided by a difference in the
timing of their development. - Protandry: Anthers on some plants mature first. Pollination of immature stigma on the same plant is therefore not possible.
- Protogyny: The stigmas mature first.
- Self-incompatibility: Pollination can occur but the pollen tube doesn’t grow well, if at all, so no fertilisation takes place.
are organisms or physical conditions that facilitate transfer of pollen
grains from the anthers to stigmas. Plants, being immobile, normally
require agents for the transport of pollen, which are commonly wind,
insects, birds, mammals (bats, rodents, primates), and water. Insects
are the most common animals that will pollinate a carpel. The main
agents of pollination are wind, insects and birds.
flowers are also those flowers whose pollen is transferred by wind from
anthers to stigmas. Wind picks pollen grains from the anthers and
transfers them to the stigma.
anthers and stigma of wind-pollinated flowers are exposed. This makes
sit easy for wind to blow the pollen that can then easily land on the
stigma. Flowers of grasses are a representative of wind pollinated
flowers.
that depend on wind for pollination are adapted in various ways. Plants
that are pollinated by wind have the following characteristics:
- Small
petals with exposed anthers and stigma. In some plants the petals are
often absent or have dull-coloured petals that do not attract insects or
birds. The petals and sepals are very similar in shape and size. - Large
anthers which produce large amounts of pollen grains. Very large
quantities of pollen are produced to increase chances of pollination as
much will be lost while blown about. - Anthers are loosely attached to the filaments and hang freely to allow the anthers to be easily shaken by the wind.
- The
pollen grains are small, smooth, dry and light in weight and therefore
easily carried in the air by wind. Some pollen grains have bladder-like
structures that contain air, thus, increasing their buoyancy. - Feathery stigmas with a large sticky surface so they are more likely to catch pollen from the air.
- Large
and feathery stigmas, freely hanging out of the flowers, which provide a
large surface area on which the pollen grains can land. The stigma may
be branched or hairy to increase the surface area. - Long, hairy style to expose the stigma outside the flower.
- No nectar produced because they is no need to attract pollinators to the flower.
- Not scented as the flowers do not attract insects.
- Filaments grow long so stamens hang out of the flower and shake in the wind to disperse pollen.

flowers are also referred to as entomophilous flower. The term
entomophilous is derived from the word entomophily- which means to be
carried by insects. Features of insect pollinated flowers include the
following:
- Large,
brightly-coloured petals which attract insects. Flower structure may be
adapted for one particular of insect, allowing them to land and feed. - Usually scented; therefore they attract insects to the flower.
- Nectarines
which contain nectar, for example, mango flowers have nectarines from
which bees collect nectar for making honey, and while doing so transfer
the pollen. The insects are guided to the nectarines by the nectar
guides. - Sticky stigma that insects come into contact with and
deposit pollen while collecting nectar. The pollen grains picked by
insects from other flowers stick onto the stigma. - The stigma and
anthers are held firmly in position within the flower. This ensures
that when an insect lands on a flower, the stigma is not broken. The
stigma and anthers are located inside the flower where pollinators are
more likely to pick up pollen. - The anthers are small in size and produce few but large pollen grains.
- The
pollen grains are fairly large, heavy, sticky and with small spines.
This enables them to adhere to bodies of pollinators (insects or birds).
pollinate flowers when they search for nectar. Birds such as sunbirds
have long slender and slightly curved beaks that they use to probe into
the flower. Pollen grains stick on the beak. The pollen grains are
deposited on the stigma of another flower of the same species by the
bird as the bird feeds.

is the union of the male and female gametes to form a zygote. Pollen
must fertilise an ovule to produce a viable seed. Fertilisation starts
when a pollen grain lands on the stigma. Only after pollination, when
pollen has landed on the stigma of a suitable flower of the same
species, can a chain of events happen that ends in the making of seeds.
a male’s pollen grains have landed on the stigma during fertilization,
pollen tubes develop within the style, burrowing down to the ovary,
where the sperm fertilizes an ovum (an egg cell), in the ovule. A pollen
tube emerges from the grain, its growth being controlled by the tube
nucleus at the tip of the tube. It may grow downwards in response to
chemicals made by the ovary (a response known as chemotropism).
a process called fertilisation, the two gametes join and their
chromosomes combine, so that the fertilised cell contains a normal
complement of chromosomes, with some from each parent flower. The
fertilised ovule goes on to form a seed, which contains a food store and
an embryo that will later grow into a new plant. The ovary develops
into a fruit to protect the seed. Some flowers, such as avocados, only
have one ovule in their ovary, so their fruit only has one seed. Many
flowers have lots of ovules in their ovary, so their fruit contains many
seeds.
are 2 types of seeds. Some are endospermic while others are
non-endospermic. In endospermic seeds the food reserve is the endosperm,
which is outside the plant embryo. Examples of this type of seed are
maize and wheat. Non-endospermic seeds have food reserve within the
cotyledon(s) of the plant embryo. This occurs in broad beans.
The pollen tube enters the ovule through the micropyle and penetrates
the embryo sac wall. Then, the tip of the tube bursts open, the tube
nucleus disintegrates, creating a passage for the male nuclei and what
follows is calleddouble fertilisation
- 1 male gamete fuses with the egg cell to produce adiploid zygote which undergoes mitosis to form a diploid embryo.
- 1 male gamete fuses with both the polar nuclei to produce thetriploid primary endosperm nucleus. The triploid nucleus undergoes mitosis to form the endosperm. The endosperm stores food materials that the embryo utilizes for growth and during germination.
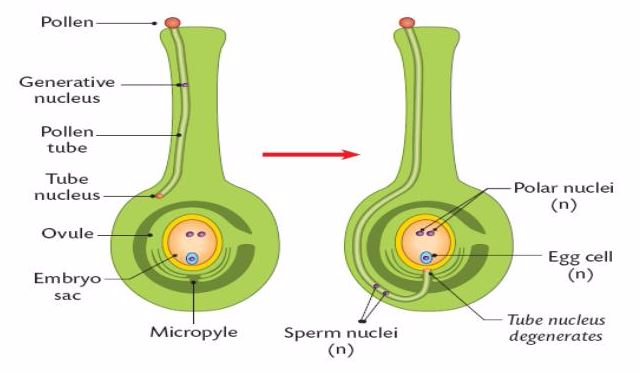
- The zygote divides many times by mitosis to produce anembryo. It differentiates to become aplumule(young shoot),radicle(young root) and either 1 or 2cotyledons(seed leaves). It is attached to the wall of the embryo sac by a suspensor.
- The primary endosperm nucleus divides many times by mitosis to produceendosperm tissue.
In some seeds this endosperm is a food store for later use by the seed.
In others it may gradually disappear as the cotyledons develop. - To
accommodate all this growth the embryo sac expands and the nucellus is
crushed out of existence, giving its nutrients to the embryo and
endosperm. - The integuments surrounding the embryo sac become the tough and protectivetesta (seed coat). The micropyle remains though so that oxygen and water can be taken in during seed germination.
- The water content of the seed decreases drastically so the seed is prepared for dormancy.
- The ovary wall becomes thepericarp–
the fruit wall, the whole ovary now being the fruit. The function of
the fruit is to protect the seeds and to aid in their dispersal, e.g. by
an animal. That is why they can be brightly coloured and sweet; animals
will eat them and scatter the seeds either at the time of eating or
when they are passed out of the gut in defecation, unharmed.
- Formation of the testa:The
testa is also referred to as the seed coat. The two integuments of the
embryo sac fuse to form one seed coat. The seed coat thickens and
hardens. Sometimes the outer integument forms the hard thick testa while
the inner integument remains thin and transparent. The thin transparent
inner integument is referred to as the tegmen.The testa protects the
seed against dehydration, physical damage and invasion by
microorganisms. The microphyle permits oxygen and water to enter the
seed during germination. The hilum is a scar on the testa that marks the
point of attachment to the fruit. - The formation of the embryo:The
egg cell nucleus fuses with the male nucleus to form a zygote. The
zygote undergoes mitosis to form the embryo. An embryo is a rudimentary
plant comprising the plumule, radicle and cotyledons. - Formation of the pericarp:The
ovary wall becomes thick and swells up with food substances. The
pericarp develops from the ovary wall. The pericarp is often the edible
layer in fruits. In mature fruit it may dry up or remain fleshy. - Disintegration of the floral parts:The
sepals, petals, stigma and style wither, dry up and fall off. In some
cases, some of the floral parts may become fleshy and form part of the
fruit. The fruit retains scars at the points of attachment to the
pedicel and style.
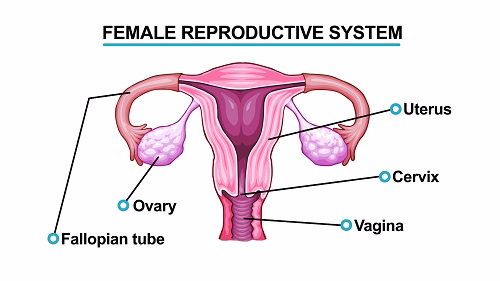
- Ovaries: Ovary is situated near each kidney. Ovary produces ova, estrogen and progesterone as female sex hormones.
- Fallopian tube: It is also known as egg tube/oviduct, it is a funnel shaped opening. Fertilization normally takes place within this tube.
- Uterus:The
two fallopian tubes unite to form an expanded tubular organ called
uterus womb. It is there that fertilized ova implant and develop into an
embryo. N.B. Placenta is formed as an embryo develops, so as to allow
penetration of nutrients, gases (oxygen and carbon dioxide) and waste
products of metabolism An embryo receives nutrient and oxygen gases from
maternal blood circulation and give out waste product through placenta
into maternal blood system. - Vagina: This is
the posterior part of the female reproductive duct connecting the uterus
with the exterior. It is in this region that sperms are deposited. N.B.
Placenta with an endocrine at the last period of pregnancy, it secretes
progesterone like ovaries, which prevent production of ova and
contractions of the uterine walls.
- Testicles:
These are situated in a pouch of skin called scrotum. They produce
sperms as endocrine gland it produces secretes male sex hormone called
testosterone. Testosterone influences male secondary characteristics
during puberty in males. - Sperm duct: It Is
attached to each testicle, it acts as a temporary store for sperms. Each
epididymis leads into a duct called sperm duct or vas di deferens. - Vas deferens: Is the structure, which carries sperms away from the epididymis to penis
- Seminal vesicles and prostate glands:These
are situated just below the urinary bladder and two structures called
seminal vesicles. Each seminal vesicle has a tube which leads to the
sperm duct. Around the junction of urinary bladder and urethra is a
gland called prostate gland

average, female attain puberty (Sexual Maturity) when they are 14 years
old and male when they are 16 years old. In both sexes, attainment of
puberty is accompanied by certain behavioral changes as well as
development of certain structures.
Puberty can be defined as the period when male/female changes from
childhood to adulthood. These changes are influenced by sex hormones
that are testosterone in males, progesterone and estrogen in females.
- Hairs on their chins and pubic region
- Shoulders widen
- Voice deepens
- Pay more attention to female sex
- Enlargement of the mammary gland and hips
- Deposition of fat which gives them more round appearance
- Development of pubic hair
- Menstruation cycle
- Pay more attention to males (young men)
puberty stage is when both males and females are able to produce
fertile cells which united (of male and female) can cause pregnancy.
is believed that female gametes are produced before puberty but after
puberty is when they are fully matured and fertile while male gamete at
large are produced during and after puberty that is when can cause
pregnancy when united with female gamete.
It refers to the release of ova/ovum from ovaries to the uterus. It is
expected to occur at the middle of the menstruation cycle.
The menstruation and liberation of ova every 28 days alternates between
the two ovaries whereby in humans is called menstrual cycle and in
non-human mammals is called oestrus cycle.
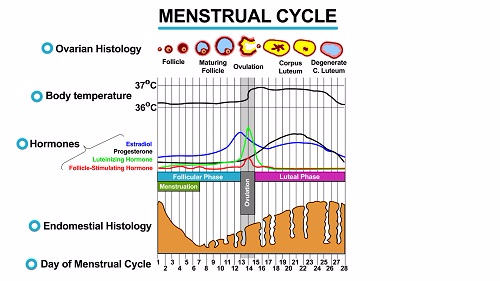
menstruation oestrogen secretion increases, follicle stimulating
hormone secreted to encourage production of ovarian follicle.
hormone is for maturation and ovulation of follicle while oestrogen
prepares (thickening) the uterine for implantation when fertilization
takes place.
(middle) day is when ovulation can take place and secretion of
progesterone increases so as to thicken the uterine wall ready for
pregnancy.
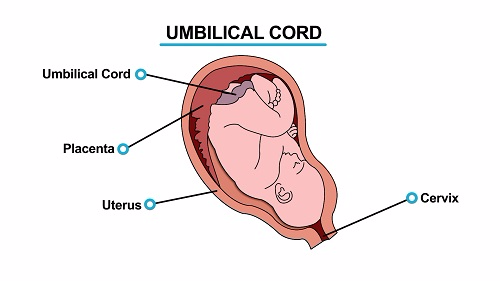
is the portion of uterus, which is invaded by the villi and the
thickened portion of the chorion. The chorion like amnion is a thin
membrane but it has a thick portion called villi, finger-like
projection.
- It connects the developing embryo to placenta to the maternal blood system
- It carries two arteries and a vein of blood circulation of an embryo
- AN
embryo uses umbilical cord for gas exchange, receiving nutrients and
removal of waste products via placenta into maternal blood system
- It
starts by a sudden fall in the level of oestrogen and progesterone
resulting in periodic contractions of muscular walls of the uterus which
cause pains called labour pains - Under the influence of hormones a child is given out through vagina
- When
a male is sexually stimulated, the spongy penis is filled with blood
and becomes erect. The erect penis is inserted into the vagina and moved
back and forth, this movement stimulates sense organs in the penis and
ejaculation occurs. - Ejaculation refers to the release of sperm
into the vagina; it can cause pregnancy when the fertile sperm unites
with fertile ova.
can be defined as the process of uniting male and female gametes to
form a zygote. The sperms remain alive for up to 48 hours while ova
remains alive for up to 36 hours.
refers to the situation when a female conceives. That is fertilization
takes place to form zygote. Soon after zygote is formed its cell starts
to divide into many cells called embryo. It takes 3-5 days for the
zygote to reach to uterus for implantation.
- Refers to the process whereby an embryo attaches itself to the uterine wall
- It takes 3 – 5 days to implant fully
- After implantation envelope is formed, the outer chorion, inner amnion
- Between
these membranes of envelop there are fluids called chorionic fluids and
amniotic fluids respectively, both fluids act as shock absorbers,
protecting embryo from physical damage
normal couple that is trying to start a family will usually be
successful after a few months. However, at least one in ten couples do
not conceive after a year or more of trying.
- Ova are not released in normal monthly cycle
- The fallopian tubes may be blocked/twisted
- The women may make antibodies that destroy the sperm
- The vas deferens may be blocked
- A high proportion of the sperm produced are abnormal
- Very few sperms are produced in one ejaculation
- In – Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
- Fertility Drugs
- Artificial Insemination
insemination, also known as AI, is a procedure used to
treatinfertilitythat involves direct insertion of semen into a woman’s
womb. It is a process originally used on livestock that has been adapted
for human use. In human use, the sperm could originate from the woman’s
male partner, unless the male is infertile or there is no male partner
(i.e. single woman or woman in same sex relationship).
most commonly used method of artificial insemination, is IUI
(Intrauterine Insemination), as it has the best success rate. Other
types of AI are:
- IUTPI (Intrauterine tuboperitoneal insemination
- ICI (Intracervical insemination)
- ITI (Intratubal insemination)
insemination is beneficial to couples or individuals in many
circumstances. For example a couple may be producing healthy sperm and
eggs but not necessarily be able to have intercourse (maybe due to a
medical condition). Some other scenarios where artificial insemination
could be beneficial are listed below.
- A woman may want to raise a child alone – in this case she would request a sperm donor to be artificially inseminated.
- The female may be infertile due tocervical factor infertility–
the cervix is supposed to produce a mucus that helps sperm travel to
the womb. With cervical factor infertility, the cervix is either not
producing enough of this mucus, or it is producing mucus containing
sperm killing substances. - The woman may be sufferingEndometriosis–
this is when cells from the womb lining start to grow in places they
should not within the woman’s reproductive system e.g. ovaries or
fallopian tubes. One of the possible results of this condition is
infertility. Artificial insemination can be successful in mild to
moderate cases of this. - The female could have semen allergy –
this is rare but can still happen, due to certain proteins in the sperm
the woman may suffer an allergic reaction when the sperm makes contact.
With IUI most of the proteins would be removed before sperm insertion. - The male is unable to produce enough sperm for successful fertilization.
- The man is impotent(erectile dysfunction)– and would therefore be unable to perform sexual intercourse.
- The
male could be infertile as a result of a medical treatment – some
treatments carry the risk of infertility e.g.radiotherapy. Before the
treatment the male would have been given the chance to freeze some of
his sperm. - The couple could be in same sex relationship – two
women who want to raise a child together would use sperm from a donor,
which one of the women would receive via artificial insemination. - Reason
for infertility cannot be determined – IUI may be recommended to a
couple that cannot conceive even if no underlying reason for the
infertility can be identified.
pregnancy refers to a situation when more than one ovum is released
into the reproductive tract of the female. On this occasion it is
possible for more than one ovum to be fertilized, consequently several
viable embryos may enter the uterus where they are implanted and
developed.
pregnancies may occur naturally or arise as a result of reproductive
technology involving fertility drug or during an IVF program.
- More than one ovum released into the reproductive track
- One fertilized ovum splitting up into more than one embryo resulting to twins
are fully identical since they come from a single fertilized ovum,
which has split to give two or four embryos and developing to give
babies. They have the same sex and appearance.
when more than one ovum (ova) are released at a time and are
fertilized. They may have the same sex but not identical at all.
system is the one dealing with the birth of a child. We have two types
of reproductive systems, which are male reproductive system and female
reproductive system. The main function of reproductive system is to fuse
the gamete causing fertilization. Conserving the baby in a mother’s
womb till the day of bearing a child. Also is the one providing
birth/bearing of a child.
are many disorders that affect the reproductive system. These problems
may be found in both male and female reproductive systems. Disorders
affecting male reproductive system are Impotence, Premature Ejaculation,
Inflammation and Autoimmunity. Female disorders of the reproductive
system are Damage to the Oviducts (inflammation), Pelvic Inflammatory
Diseases (PID), Congenital Malformation and Functional Disorder.
is the inability to achieve or maintain an erection of the penis. A
male could not erect the penis even though he will touch the sex organs.
- Impotence is usually psychological disturbance. It may occur any time during the life time of a male
- Strong alcohol consumption and use of drugs
- Diseases also may cause impotence
- Impotence causes failure in performing the social act, thus one cannot have children
- May cause psychological disturbances to the person
- If an impotent person in married, impotence may lead to the break of that marriage
- It
may lead to the contamination of diseases such as HIV/AIDS, gonorrhea
when a couple get out of marriage to get sexual satisfaction
ejaculation is the situation where a man reaches orgasm before
penetration of the penis into the female track. Before inserting penis
into the female track the male ejaculated long time outside the female
track.
- Fear, anxiety and sometimes is the first time to have sexual intercourse
- Psychological factors may also lead to a problem
- The person (male) fails to satisfy a woman
- May lead to the breakage of marriage when a woman finds another male for sexual satisfaction
- May cause psychological disturbances in the man’s mind
is a situation in which antibodies are made, which attacks own sperm,
thus reducing the number of sperms. It may lead to have small number of
sperms in the sperm store area.
- It causes infertility to a person
- May cause psychological effects to the person who suffering from this problem
- No more production of children
- May be caused by swelling of the prostate gland
- Also inflammation may cause the problem
- Inflammation may lead to sterility (infertility)
- May cause psychological problems to the person
- May cause severe pain during sexual intercourse as one/man wants to ejaculate but sperms fail to pass through urethra
may be caused by the infections due to different diseases. The
infections may cause scarring, thus leading to partial or complete
blockage of the oviduct.
causes infertility to the female. A female may not have the ability to
carry/conceive a child due to failure of fertilization of an egg in the
fallopian tube.
is the pelvic infection caused by bacteria.This condition causes damage
to the oviducts.It occurs commonly to women with many sexual partners
and women who use the coil contraceptive method
- The cause may be psychological
- Also may be biological one
- May cause someone to stay away not conducting sexual intercourse
- May lead to end in marriage
- If the causes of impotence are psychological, counseling may help to cure it
- If the cause is biological, one has to attend hospital for medical check up
- Counseling is the most effective way to be adopted to treat the problem
- Medical treatment may be applied to stop the problem
- If a woman feels she has PID she should have to go to the hospital for the right treatment
- Abstaining from many sexual partners so as to overcome more infections/problem
- Counseling is the most effective way that may be used to help the patient regain their confidence
- Patients may go to the hospital for further checks and treatment
women give birth normally and perfectly but some problems can and do
occur in their reproductive system and causes effects to the newly
formed embryo.The problems/complications are abortion/miscarriage,
ectopic pregnancy and still births also breech birth.
- Miscarriage:This
is the loss of a developing embryo before six months are over.
Medically, miscarriage is considered as the natural abortion. It may
result from foetus not being fully developed, failure of the embryo to
implant properly or due to deformed embryo. - Ectopic Pregnancy:Occasionally
the fertilized ovum fails to reach the uterus and instead implants else
where in the reproductive track. For example it can be implanted in the
fallopian tube instead of uterus. This situation is known as ectopic
pregnancy.Only 1 out of 50,000 ectopic pregnancies may be delivered
safely. - Abortion:Refers to the premature termination of pregnancy. Abortion may occur naturally (miscarriage) or be induced.Induced Abortionis the abortion that is deliberately brought out for medical reasons.Spontaneous Abortiois
the kind of abortion that occurs without humans or medical
intervention. That is not induced in any way. It is also referred to as
miscarriage. - Breech Birth:This is the situation
where a baby is born feet or buttocks first. In such cases, duration of
delivery is critical, too fast delivery may result in damage and too
long delivery may cause oxygen deprivation and if left for a longtime
may result to death of the baby.Sometimes it becomes necessary to remove
the baby by other means such as forceps (surgical tongs) or Caesarian
(C) section - Caesarian Delivery:This is the
removal of the baby from the uterus using surgical means through making
an incision in the abdominal and uterine wall. Caesarian delivery can be
done when either the baby is too big to pass the female reproductive
structures or the mother’s reproductive structures are too small.
complications that occasionally arise during childbirth and generally
require management by an obstetrician may be described as follows:
- Non-progression
of labour (long-term contractions without adequate cervical dilation)
is generally treated with cervical prostaglandin gel or intravenous
synthetic oxytocin preparations. If this is ineffective Caesarian
section may be necessary. - Fetal distress is the development of
signs of distress by the child. These may include rising or decreasing
heartbeat (monitored on cardiotocography). Shedding of meconium in the
amniotic fluid and other signs. - Non-progression of expulsion
(the head or presenting parts are not delivered despite adequate
contractions); this can require interventions such as vacuum extraction
forceps extraction and Caesarian section.In the past a great many women
died during or shortly after childbirth but modern medical techniques
available in industrialized countries have greatly reduced this totally. - Unanticipated heavy bleedingduring
or after childbirth is potentially lethal n places without immediate
access to high-level emergency care. Heavy blood loss leads to
hypovolemic shock, insufficient perfusion of vital organs and death if
not rapidly treated by stemming the blood loss and blood transfusion.
complications that occasionally arise during childbirth and generally
require management by an obstetrician may be described as follows:
- Non-progression
of labour (long-term contractions without adequate cervical dilation)
is generally treated with cervical prostaglandin gel or intravenous
synthetic oxytocin preparations. If this is ineffective Caesarian
section may be necessary. - Fetal distress is the development of
signs of distress by the child. These may include rising or decreasing
heartbeat (monitored on cardiotocography). Shedding of meconium in the
amniotic fluid and other signs. - Non-progression of expulsion
(the head or presenting parts are not delivered despite adequate
contractions); this can require interventions such as vacuum extraction
forceps extraction and Caesarian section.In the past a great many women
died during or shortly after childbirth but modern medical techniques
available in industrialized countries have greatly reduced this totally. - Unanticipated heavy bleedingduring
or after childbirth is potentially lethal n places without immediate
access to high-level emergency care. Heavy blood loss leads to
hypovolemic shock, insufficient perfusion of vital organs and death if
not rapidly treated by stemming the blood loss and blood transfusion.
- Stop/minimizing
amount of alcohol that we take/drink may keep us away from impotence
and other infections that may lead to disorders in reproductive systems - Practicing
different duties/activities and participating in exercises also sports
and games helps to reduce psychological problems which may lead to
disorders in the reproductive system - Medical check up between
the partners who want to get married to know their Rhesus factors, blood
groups, infections and HIV/AIDS in order to minimize the death or
miscarriage during pregnancy - Getting early treatment of any
infections like gonorrhea, syphilis, bilharziasis, which may cause
damage to the fallopian tubes and urethra in male and female.
- How you feel about yourself as a person
- How you feel being a man or woman
- How you get along with member of the same or opposite sex
- It also includes genital and reproductive processes such as intercourse and child bearing
- Start at infantry when children shown their own bodies
- Also sexuality is shown at early age (play age)
- Children also do and learn from their fellow children on different sexual matters
- Education – in school and community
- Initiation rites
- Religious beliefs
- Mass Media
- Economic status – both poor and rich
- Early marriage
- Social pressure (tradition of being independent)
- Drug addiction – it can stimulate or depress the sexual practice
- Peer pressure
- Education – school and community
- Moral decay
- Marriage breakdown and problems
- Poverty
- Mass Media
- Lack of proper guidance and counseling
sexual behaviours are the behaviours, which are acceptable in the
societies to elicit or trigger sexual activity like marriage.
sexual behaviors are those behaviours of an individual, which are not
acceptable by family as well as societies, example use of alcohol and
drugs (drug addiction) and prostitution to trigger sexual activities.
- Becoming pregnant at a tender age, thus losing the opportunity of being officially married or continuing with studies
- Being in danger of contracting fatal venereal disease such as syphilis, HIV/AIDS, gonorrhea etc.
- It may lead to death, when an individual tries to abort an unwanted pregnancy
- Getting a responsibility of caring for a family at an early age
- It
can degrade the personality of a person. For example prostitutes or
rapists have no place to put their faces in some societies
- Breakage of marriage
- Lead to conflict in the family or marriage
- Loss of particular relative if he/she contracts disease like HIV/AIDS
are several measures that can be taken to eradicate irresponsible
sexual behaviours in the family and community. The measures include the
following:
- Old children should not sleep with young children on the same bed without strict follow-up by the parents/guardians.
- Keeping
out of all situations culminating to sexual arousal such as watching
pornographic movies, alcoholism, meeting in isolated places, attending
night clubs and accompanying ill groups of people like homosexuals,
harlots, and rapists. - Adults, guardians, parents, and teachers
should talk openly to children about relationships and sexual-education
matters to make them informed about the aftermath of irresponsible
sexual behaviours. - Close supervision and guidance of children
- Getting
involved in age-appropriate activities (for example, sports, boys/girls
clubs, after-school activities, and craft activities) to help keep
one’s minds out of sexual mood and desires. - Protection for
children from scary or traumatic events, including media coverage of
such events as wars, bombings, or shootings; and - Closely observing what your child watches on television and in the movies or is exposed to in music and on the Internet.
- Following religious teachings on sexuality.
skills are behaviours that enable individuals to adapt to and deal
effectively with the demands and challenges of life. There are many such
skills, but core life skills include the ability to:
- make decisions, solve problems, and think critically and creatively;
- clarify and analyze values;
- communicate ( including listen, build empathy, be assertive, and negotiate);
- cope with emotions and stress; and
- feel empathy (understand and care about other peoples’ needs, desires and feelings) with others and be self-aware.
- Educating
youth about health-related issues, such as alcohol, tobacco, and other
drug use; nutrition; reproductive health; and preventing HIV/AIDS and
other sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Life skills education can
also be effective in preventing school dropout and violence among young
people. - Referring young women to age-appropriate reproductive health services.
- Promoting youth’s livelihood through vocational training, recreation, etc.
- Mobilizing
and empowering individuals, families, and communities in order to
reach, influence, and involve everyone to become a part of the solution. - Parents and teachers strictly supervising teenagers at home and school, respectively.
- Adults and parents inculcating good moral behaviours to adolescents by serving as good examples for them to follow.
refers to prevention of conception that is prevention or preventing the
fusion of the male gamete with the female gamete. Birth control is
broad it includes measures taken to prevent birth after fertilization.
- Artificial Family Planning Methodsincludes sterilization, oral contraceptives, intra-uterine devices, Norplant, diaphragm and condoms
- Natural Family Planning Methodsincludes rhythm, the basal body temperature and withdrawal (coitus interrupt)
refers to the avoidance of sexual intercourse or can be defined as
refusal by sexually active male and female to have sexual intercourse.
- It is the most effective method of preventing conception
- The approximated rate of failure of this method is zero percent
is modified from abstinence. N intercourse is done during the fertile
period. These days can be counted or identified by counting the days
between menstrual period and also by observing certain associated
physical changes such as small changes in body temperature. A woman may
also keep a written chart of her menstrual cycle for certain months and
is taught how to determine the number of days each month when sexual
intercourse must be avoided. Total abstinence is about 7 days in a
month.
- The method is said to be natural and widely acceptable
- It has no cost
- It is said to be 77-87% effective
- The approximate failure rate is 20%
- It requires good knowledge and good record keeping
- It also requires a period of abstinence
- Irregularity of the menstrual period (cycle)
method is based on the changes of a woman’s body’s temperature due to
her menstrual cycle. The temperature is said to drop during the
menstrual period and remains low until the release of an ovum. A rise in
temperature is noted at ovulation and sexual intercourse should be
avoided at this time if conception is not intended.
- The method is said to be 76-80% effective
- It costs nothing
- It does not require fitting and regular checkups
- The approximate failure is said to be 20-24%
- Sperms released to a female tract a few day before ovulation may survive until ovulation
- Irregularity of the ovulation may cause fluctuation of temperature
method is based on the fact that the secretion from the female tract
changes noticeably during the course of her menstrual cycle. The
appearance of clear thin mucus in female tract secretions at ovulation
is noted and sexual intercourse is avoided during these times.
- It is said to be 76-80% effective
- It costs nothing (it is cheap)
- It does not require fitting and regular check ups
interruption or withdrawal is another natural method of birth control
in which a male withdraws his penis from a female tract before
ejaculation. This method is one of the oldest methods of birth control.
Coitus interruption requires unusual degree of will power.
- The method is costless
- It is reliable for 76-80% when practiced
- The method requires some degree of will power
- It has a high failure rate in case fluid released from the penis just before ejaculation may contain viable sperms
- Sperms may leak from penis before is withdrawal even without ejaculation
is a thin rubber sheath, which prevents sperms from entering into the
female tract. Male condom is worn over an erect penis during intercourse
and prevents sperms from being released into the female tract that way
preventing union of sperm and ovum.
- Condoms are said to be 85% to 93% reliable when used properly (handled with care)
- They may help prevention of sexually transmitted diseases such as fungal infection
- They are cheap and easily and obtained
- Condoms can tear and leak. In such cases they become useless
- A condom may slip off the penis after climax
- Condoms may disrupt the act of love making (reduce sensation)
- It is a thin rubber tube with a close end which fits inside the female tract
- Female
condoms are relatively new, so not much is known about them. They give a
woman some control and are said to have the advantages as those f the
male condoms
is another barrier method that prevents entering of sperms into the
female tract.A diaphragm is a flexible rubber, which fits over the
cervix and prevents entry of sperm to uterus. It is applied with
contraceptive jelly (cream) or spermicidal chemicals, which kill sperms.
A doctor must prescribe this method.
- The method is said to be cheap
- It can be inserted a few hours before sexual act
- The diaphragm must be fitted by a doctor and training is required for the woman to fit it
- It disrupts spontaneity
- It occasionally causes pain in the abdomen
- It needs check up after every six (6) months
- It should be left in place six hours after intercourse
are chemicals, which kills sperms. Spermicidal foam, or spermicidal
jelly is placed in an applicator, which is inserted and emptied into the
female tract just before sexual intercourse. These kill sperm and block
cervix.
- It is cheap
- It is effective for about an hour
- It is messy
- It has a high failure rate if used on its own
is one of the most widely used contraceptive methods.The pill is an
oral contraceptive by synthetic oestrogen and progesterone taken daily
by the female.It function by suppressing the normal release of
gonadotropins from the pituitary. These synthetic hormones prevent the
ovulation process, thus hindering fertilization.
- The pill is said to be very effective i.e. it is about 98% successful
- A woman has control over the method
- It has no interference with sexual intercourse
- It is not suitable for all women. There may be increased risk of blood clotting in some women
- It is not recommended for older women or women who smoke
- Short term side effects of the pill include nausea, weight gain, tissue swelling, fluid retention and minor headaches
- To
ensure both partners are healthy and observe medical measures that are
advised, giving enough time for a mother’s full recovery after giving
birth - Ability to cater for the needs of many children
- Couples decide to practice child spacing so that they can cater for their needs
- Helps
to improve the health of a mother by helping women to avoid pregnancy
at early age, unwanted pregnancies and to become pregnant at late age of
35 years
- Some family planning methods help to prevent the transmission of HIV and sexually transmitted infections
- Family planning reduces the need for unsafe abortion
- Family planning reinforces people’s rights to determine the number and spacing of their children
- Family planning helps to build the health of a mother
- Family planning enables the couple to be able to handle the family by catering to the needs of family
Maternal and Child Care
pregnant mother needs a lot of care and consideration for the best of
her health and that of the child. Basically there are two types of care
given to pregnant mother. These are pre-natal and post-natal care. The
care given before birth is called pre-natal care and the care given
during birth is called natal care. But a pregnant mother also needs a
care and support after birth of the child; this kind of care and support
provided after birth is called post-natal care.
- Visit ante-natal clinic for counseling
- Maintain general body cleanliness all the time
- Have enough rest
- Wear lose-fitting dresses and low heeled shoes for comfort
- Eat well balanced diet containing all types of food
- Doing tiresome and manual work. Example lifting heavy loads
- Taking any medicine not prescribed by the doctor
- Taking drugs such as alcohol, cigarettes which could be detrimental to the unborn baby
- Tight clothes and high heeled shoes
- Avoid
situations leading to chances of contracting venereal diseases such as
gonorrhea, syphilis and AIDS which might affect the baby - Avoid stressful situation
period is the period when the pregnant mother gives birth to the child
she has been carrying in her womb for about nine months. A number of
things need to be considered during natal period:
- An
expectant mother needs to undergo labor under supervision of a trained
nurse or trained birth attendant whenever this is possible - If
any complications occur that can not be solved by either a trained nurse
or a trained birth attendant arises, an expectant mother should be
referred to the health center or hospital for medical assistance - Most
births are perfectly normal but problems can and do occur. When
problems arise, modern delivery facilities or techniques such as
Caesarean section and vacuum extraction are used. Care should be taken
not to damage any organ of the baby or the mother - In case a
newborn baby is pre-mature appropriate services should be given to it so
as to help it accomplish a normal pattern of growth and development
are care and services provided to the mother and the newborn child
after birth. After birth a mother has another big responsibility and
role of breast-feeding the child.
a mother should attend post-natal clinic for medical checks and
immunization of the child Balanced diet should be supplied to a
lactating mother so as to ensure that she gets enough nutrition for her
benefit and ultimately that of the child.
nutrition will help her to restore the tissue worn out during the natal
period. This helps also the newborn baby to have enough milk from its
mother. The health of both the mother and her child should be seriously
taken care of.
- It contains antibodies that are much needed to the child
- In case the mother has no health problems such milk is free from contamination
- Mother’s milk also contains much proteins and vitamins which are very important for the child’s growth
- Breast
milk is easily digested than other milk example bottled milk. Therefore
children who take milk from their mother rarely suffer from
constipation - Mother’s milk is said to contain some chemicals which help in development of the nervous system of the child
- Regular
attendance of post-natal clinic for the child is very important. The
child should also get immunized against different infections and
diseases such as polio, measles and other diseases - The mother
should follow medical advice on how to handle the child and in case of
any problems report it to the personnel concerned
- Female Genital Mutilation (FGM):This
is the practice of circumcising women. It is said to have effects
during childbirth. It causes women to experience pain, bleeding, and
shock and may lead to infection. - Local Belief:These
are certain local beliefs and taboos such as banning women to eat
certain types of foods such as protein rich foods, which could help to
build their health and that of the child. - Working
especially hard work such as cultivation: Hard work may cause several
problems to the pregnant woman such as miscarriage or pain. - Alcohol Consumption during pregnancy:In
most cultural practices taking alcohol is considered as a normal
behaviour. But alcohol during pregnancy affects both the health of the
mother and that of the child.
These include the following:
- To ensure frequent medical check up for both maternal and child
- To ensure they get well balanced diet
- Avoid sharing sharp objects like razor blades
- Counseling in order to help them deal with their feelings of loss and grief
- To avoid discrimination for people living with HIV/AIDS
- Ensure the use of polite language when providing care to them
- Wearing of gloves when cleaning their bodies and clothes