Present Perfect Tense
The Present Perfect tense is a rather important tense in English, but it gives speakers of some languages a difficult time. That is because it uses concepts or ideas that do not exist in those languages.
In fact, the structure of the Present Perfect is very simple. The problems come with the use of the tense. In addition, there are some differences in usage between British and American English.
In this lesson we look at the structure and use of the Present Perfect tense, as well as the use of for and since, followed by a quiz to check your understanding.
How do we make the Present Perfect tense?
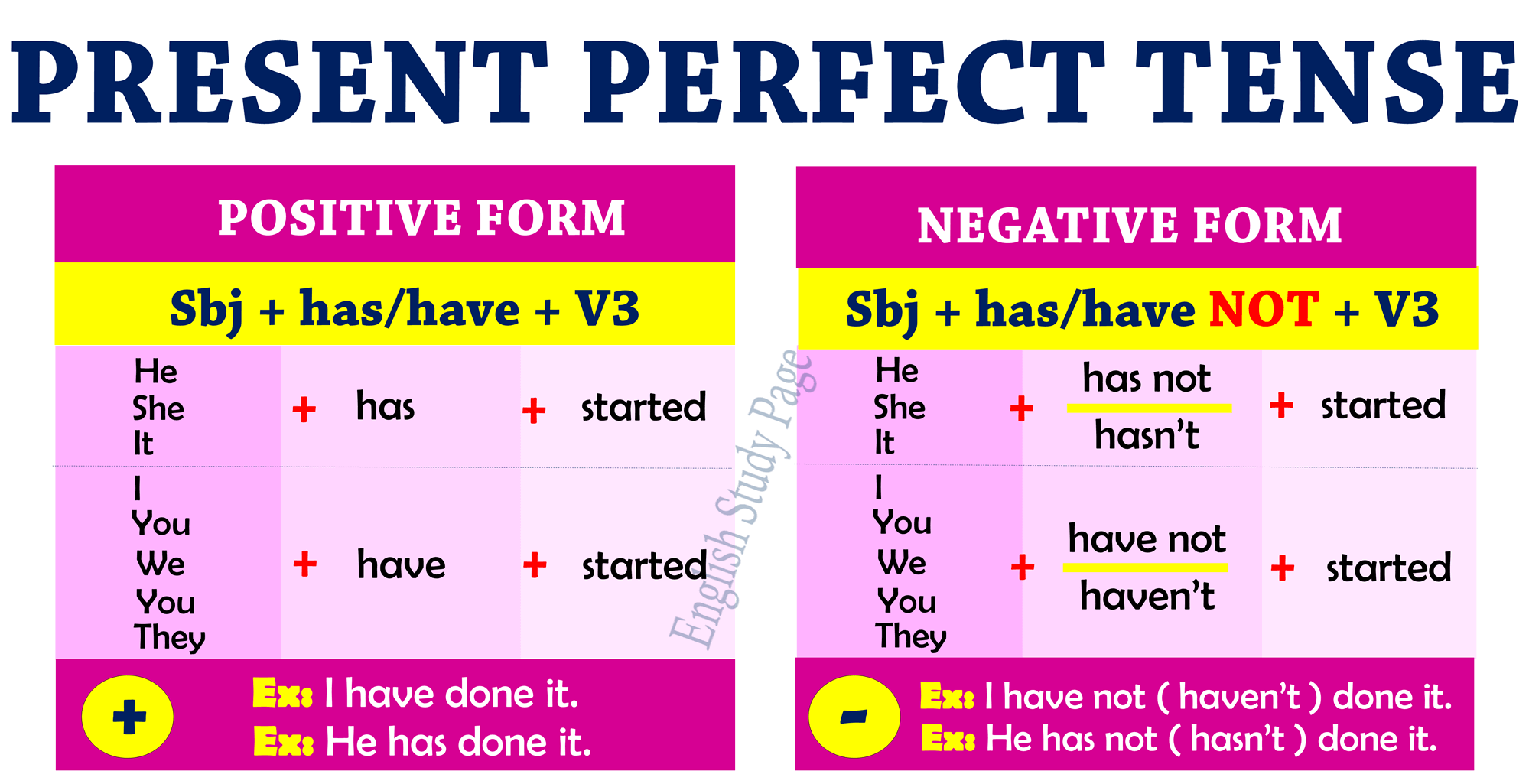
The structure of the Present Perfect is:
| subject | + | auxiliary have | + | main verb |
| conjugated in Present Simple | ||||
| have, has | past participle |
The auxiliary verb (have) is conjugated in the Present Simple: have, has
The main verb is invariable in past participle form: -ed (or irregular)
For negative sentences we insert not between the auxiliary verb and the main verb.
For question sentences, we exchange the subject and the auxiliary verb.
Look at these example sentences with the Present Perfect tense:
| subject | auxiliary verb | main verb | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| + | I | have | seen | ET. | |
| + | You | have | eaten | mine. | |
| – | She | has | not | been | to Rome. |
| – | We | have | not | played | football. |
| ? | Have | you | finished? | ||
| ? | Have | they | done | it? |
Contraction with Present Perfect
When we use the Present Perfect in speaking, we often contract the subject and auxiliary verb. We also sometimes do this in informal writing.
| I have | I’ve |
| You have | You’ve |
| He has She has It has John has The car has |
He’s She’s It’s John’s The car’s |
| We have | We’ve |
| They have | They’ve |
- You’ve told me that before.
- John’s seen Harry Potter.
In negative sentences, we may contract the auxiliary verb and “not”:
- You haven’t won the contest.
- She hasn’t heard from him.
He’s or he’s??? Be careful! The ‘s contraction is used for the auxiliary verbs have and be. For example, “It’s eaten” can mean:
- It has eaten. (Present Perfect tense, active voice)
- It is eaten. (Present Simple tense, passive voice)
It is usually clear from the context.
How do we use the Present Perfect tense?
This tense is called the Present Perfect tense. There is always a connection with the past and with the present.
We use the Present Perfect to talk about:
- experience
- change
- continuing situation
Present Perfect for experience
We often use the Present Perfect to talk about experience from the past. We are not interested in when you did something. We only want to know if you did it:
| I have seen an alien. He has lived in Bangkok. Have you been there? We have never eaten caviar. |
|||||
| past | present | future | |||
|
|||||
| The action or state was in the past. | In my head, I have a memory now. | ||||
Connection with past: the event was in the past
Connection with present: in my head, now, I have a memory of the event; I know something about the event; I have experience of it
Present Perfect for change
We also use the Present Perfect to talk about a change, or new information:
| I have bought a car. | ||
| past | present | future |
| – | + | |
| Last week I didn’t have a car. | Now I have a car. | |
| John has broken his leg. | ||
| past | present | future |
| + | – | |
| Yesterday John had a good leg. | Now he has a bad leg. | |
| Has the price gone up? | ||
| past | present | future |
| + | – | |
| Was the price $1.50 yesterday? | Is the price $1.70 today? | |
| The police have arrested the killer. | ||
| past | present | future |
| – | + | |
| Yesterday the killer was free. | Now he is in prison. | |
Present Perfect for continuing situation
We often use the Present Perfect to talk about a continuing situation. This is a state that started in the past and continues in the present (and will probably continue into the future). This is a situation (not an action). We usually use for or since with this structure.
| I have worked here since June. He has been ill for 2 days. How long have you known Tara (for)? |
|||||||
| past | present | future | |||||
|
|
|||||||
| The situation started in the past. | It continues up to now. | (It will probably continue into the future.) | |||||
For and Since with Present Perfect tense
We often use for and since with perfect tenses:
- We use for to talk about a period of time: five minutes, two weeks, six years
- We use since to talk about a point in past time: 9 o’clock, 1st January, Monday
| for | since |
| a period of time | a point in past time |
| – – – – – – – – – – – – | – • – – – – – – – – – – |
| 20 minutes | 6.15pm |
| three days | Monday |
| 6 months | January |
| 4 years | 1994 |
| 2 centuries | 1800 |
| a long time | I left school |
| ever | the beginning of time |
| etc | etc |
Look at these example sentences using for and since with the Present Perfect tense:
I have been here for twenty minutes.
I have been here since 9 o’clock.
John hasn’t called for six months.
John hasn’t called since February.
He has worked in New York for a long time.
He has worked in New York since he left school.
Present Perfect Quiz
You can do this grammar quiz. It tests what you learned on the Present Perfect page.





































































Enjoyed every bit of your article. Thanks Again. Fantastic.
Thanks again for the blog article.Thanks Again. Really Cool.