Download & Install
Darasa Huru App
DOWNLOAD
TOPIC 2: AREA AND PERIMETER ~ MATHEMATICS FORM 4
The Formula for the Area of any Triangle
Area of triangle is given by½bh, whereby b is the base of the triangle and h is the height of the given triangle. Consider the illustrations below:
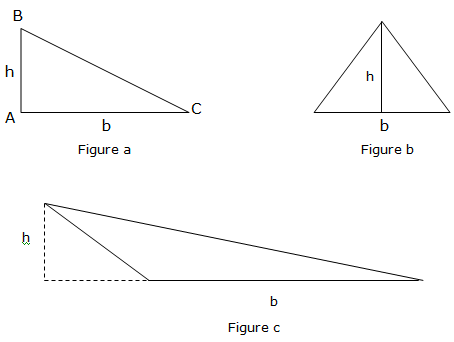
Applying the Formula to find the Area of any Triangle
Apply the formula to find the area of any triangle
Example 1
Solution
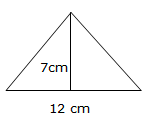
The area of a triangle is given by½bh.
Example 2
Solution:
Area of a Rhombus
The
area of a rhombus is the same as the area of a parallelogram because
rhombus is a special kind of parallelogram. Rhombus is a parallelogram
with equal sides. Consider the figure below of a rhombus with base b and
height h.
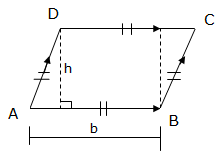
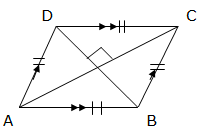
Diagonals
of a rhombus bisect each other at right angles (means the diagonal
lines are half equally), so the area of a rhombus ABCD can be found as
follows:
Area of a triangle ABC = area of a triangle ADC
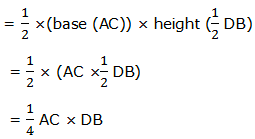
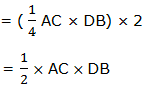
Therefore, the area of a rhombus is equal to half the product of the length of the diagonals.
Consider the trapezium with constructed lines as shown in the figure below:
Download & Install
Darasa Huru App
DOWNLOAD
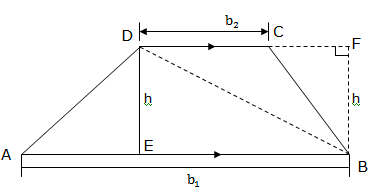
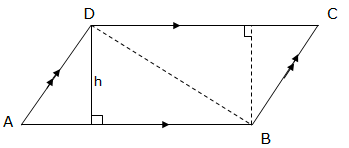
In order to find the area of a trapezium, first let us find the area of the triangles ABD and BDF with the same height h.
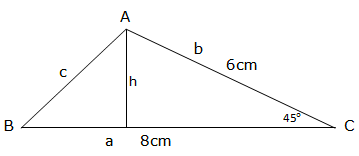
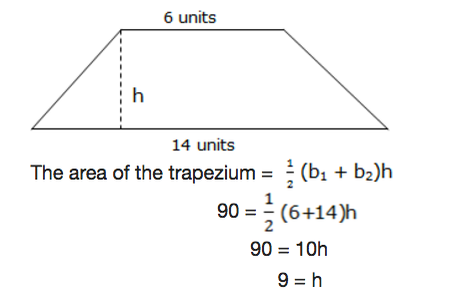
Example 3
Find the height of the trapezium with area 90 square units and bases of 6 units and 14 units
The
area of the parallelogram can be formed from the formula for the area
of the trapezium. The important thing to note is that the bases for a
parallelogram are equal.
Consider the rectangle below:
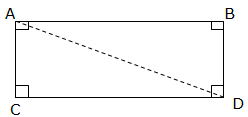
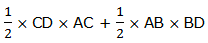
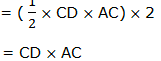
If CD is the length ‘l’of the Rectangle and AC is the width ‘w‘ of the Rectangle, then, the area of ABCD = l×w or lw
Square is a special rectangle with equal sides. Therefore the area of
the square is the product of its lengths. i.e. Area of a square = l × l=l2.
We can also find the area of a square by using the length of the diagonals. Consider the square below with diagonals AC and DB:
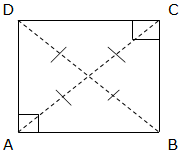
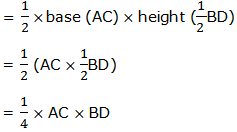
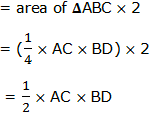
Since the length of the diagonals are equal, then AC = BD.So, the area of ABCD = ½ (AC)2
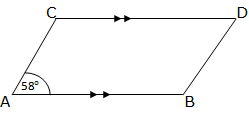
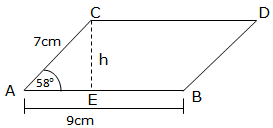
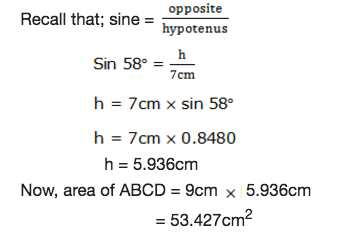
Example 4
Perimeter of a Regular Polygon
we sum up the lengths of the sides of the polygon we obtain what is
called perimeter of a polygon. Therefore, perimeter of a regular polygon
is the sum of the lengths of the sides of the polygon.
inscribed polygon is the one whose vertices lie on the circle. If the
lengths of the sides of the polygon are the same we say that the polygon
is an inscribed Regular Polygon.
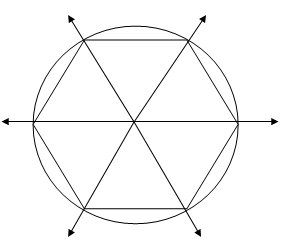
For
example, if you want to construct an inscribed regular hexagon (6
sides), first draw a circle and locate the center of the circle. Then
draw rays that intersect the circle in six points from the center of the
circle. Each angle at the center will measure 360°/6 = 60°. Connect the
points of intersection on the circle by line segments. The figure
formed is an inscribed regular polygon. See the figure below:
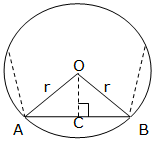
to obtain the formula of finding the perimeter of a regular polygon
inscribed in a circle with radius r and center O, let AB be the side of
the polygon and OC the perpendicular from O to AB as shown in the figure
below:
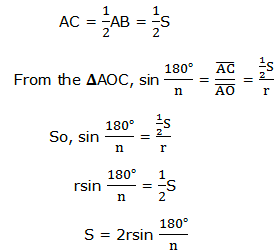
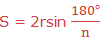

the concept of perimeter that perimeter of a regular polygon is the sum
of the lengths of the sides of the polygon , if we have n sides each
with length ‘S’ then the sum of the lengths of these sides will be nS.
Therefore, Perimeter P of a regular polygon of n sides each with length S
is given by:

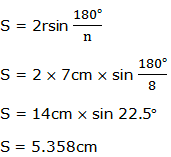
Therefore the length of one side of eight-sided regular polygon with radius of 7cm is 5.358cm
Area of a Regular Polygon
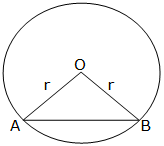
Consider the regular polygon with n sides inscribed in a circle of radius r and center O as shown below:
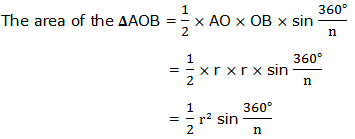
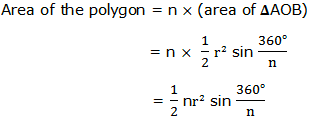
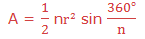
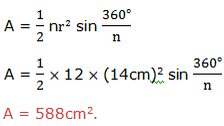
Circumference and area of a circle
Download & Install
Darasa Huru App
DOWNLOAD
Circumference
of a circle is the distance around it. Circumference of a circle can be
estimated by using a regular polygon with many sides inscribed in a
circle with radius r.
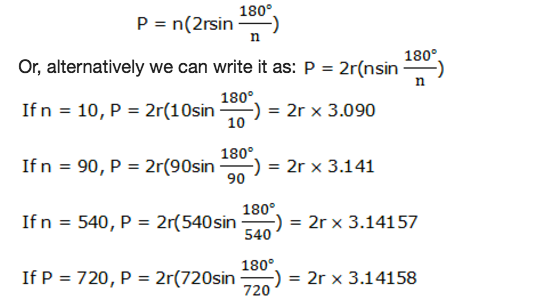
Here
we see that, as n increases the value of nsin 180°/napproaches the
value ofπ.When n is very large the perimeter of a regular polygon
approaches the circumference of the circle. The value ofnsin 180°/ncan
be replaced byπbecause it approaches the value ofπwhen n is very large.
Area of a Circle – AREA AND PERIMETER
In
similar way we can generate the formula of calculating the area of a
circle by considering area of a regular polygon inscribed in a circle of
radius r.
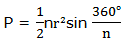
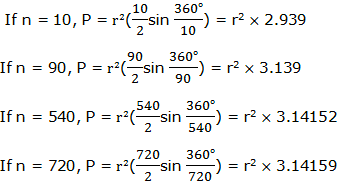
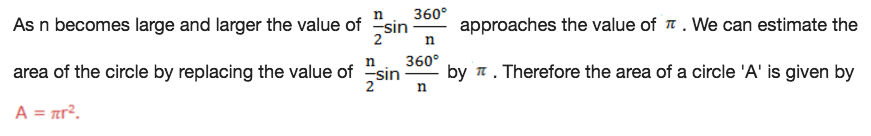
Let ABC and A’ B’ C’ be two similar triangles:
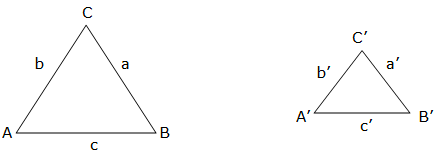
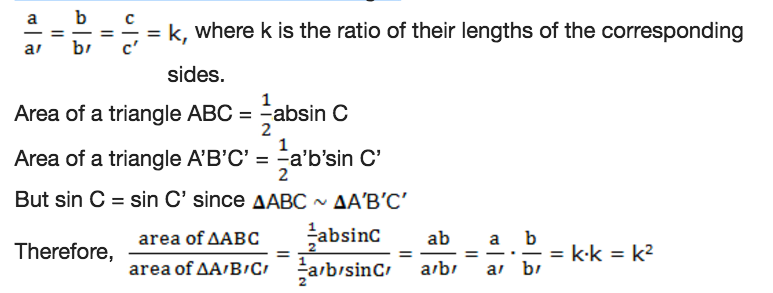
Generally,
if the ratio of the lengths of the corresponding sides of two similar
polygons is k, then the ratio of their areas is k2.
Example 8
We
are given two triangles which are similar. The length of one side is
8cm and the length of the corresponding side is 14cm. if the area of a
smaller triangle is 24cm2find the area of the other triangle.

Therefore the area of the other triangle is 73.5cm2.
Example 9
The
ratio of the areas of two similar polygons is 36:48. The length of a
side of the smaller polygon is 10cm. find the length of the
corresponding side of the other polygon.





