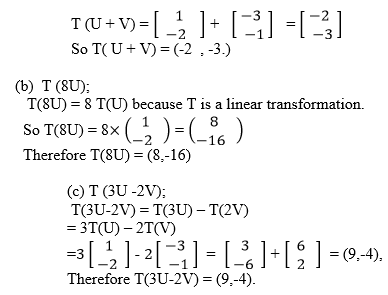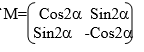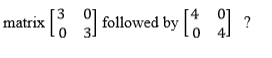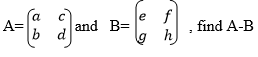Download & Install
Darasa Huru App
DOWNLOAD
TOPIC 7: MATRICES AND TRANSFORMATION ~ MATHEMATICS FORM 4
Operations on Matrices
Explain the concept of a matrix
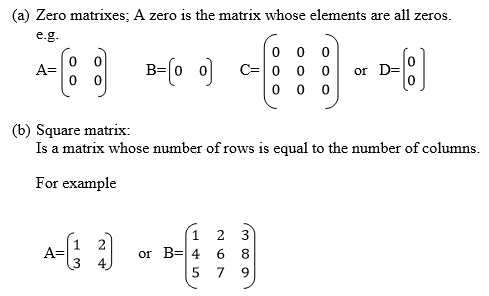
A matrix is an array or an Orderly arrangement of objects in rows and columns.
Consider the following table showing the number of students in each stream in each form.
| Form | I | II | III | IV |
| Stream A | 38 | 35 | 40 | 28 |
| Stream B | 36 | 40 | 34 | 39 |
| Stream C | 40 | 37 | 36 | 35 |
From the above table, if we enclose the numbers in brackets without changing
their arrangement, then a matrix is farmed, this can be done by
removing the headings and the bracket enclosing the numbers (elements)
and given a name (normally a capital letter).
Nowthe above information can be presented in a matrix form as

Any matrix has rows and columns but sometimes you may find a matrix with only row without Colum or only column without row.
the matrix A, 34 is the element (entity) in the second row and third
column while 28 lies in the first row and fourth column. The plural form
of matrix is matrices.
Normallymatrices are named by capital letters and their elements by small letters which represent real numbers.

The order of a matrix or size of a matrix is given by the number of its rows and the number of its columns.
It
is important to note that the order of any matrix is given by stating
the number of its rows first and then the number of its columns.
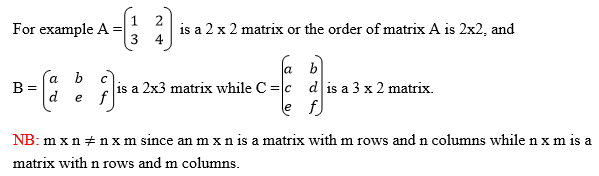
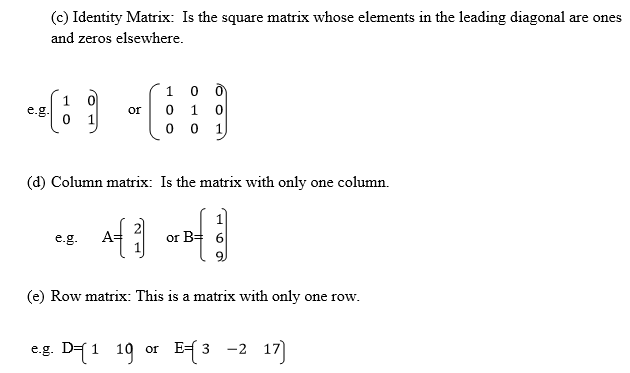
Add matrices of order up to 2 X 2
Example 1
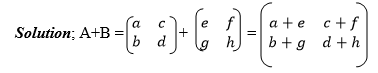
Matrices of order up to 2 X 2
Subtract matrices of order up to 2 X 2
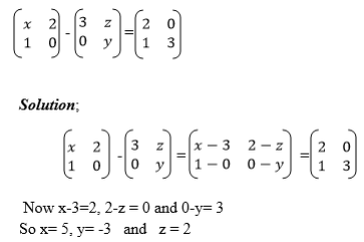
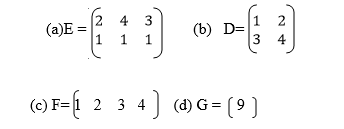
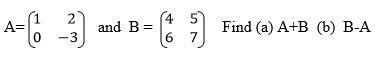
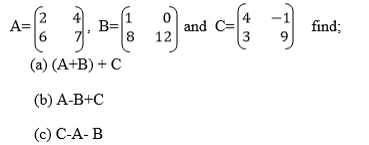
4.
A house wife makes the following purchases during one week: Monday 2kg
of meat and loaf of bread Wednesday, 1kg of meat and Saturday, 1kg of
meat and one loaf of bread. The prices are 6000/= per kg of meat and
500/= per loaf of bread on each purchasing day
- Write a 3×2 matrix of the quantities of items purchased over the three days .
- Write a 2×1 column matrix of the unit prices of meat and bread.
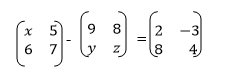

A and B are any matrices with the same order such that A+B = Z, then it
means that either A is an additive inverse of B or B is an additive
inverse of A that is B=-A or A= -B
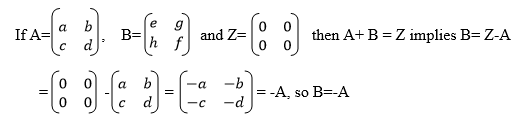
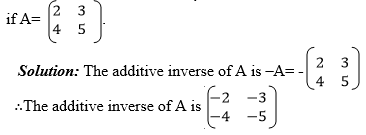
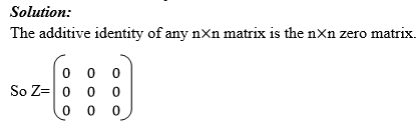
Multiply a matrix of order 2 X 2 by a scalar
Rule: If A is a matrix with elements say a, b, c and d, or
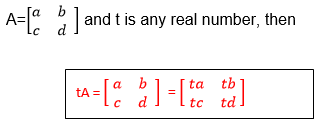
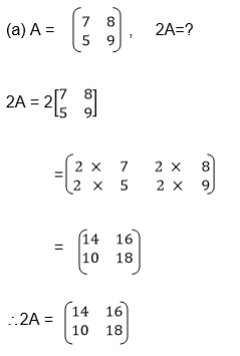
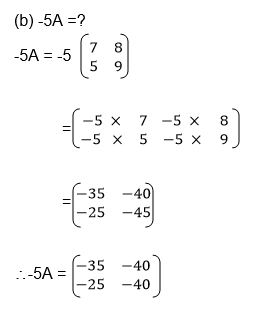
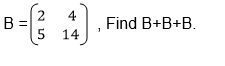
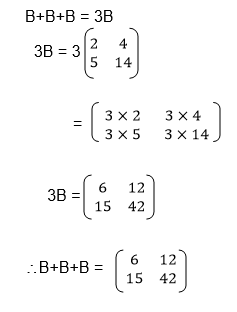
Two Matrices of order up to 2 X 2
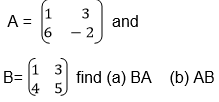
Multiply two matrices of order up to 2 X 2
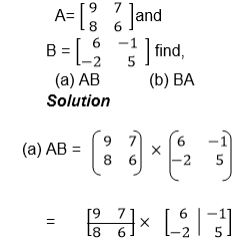
Multiplication of Matrix by another matrix:
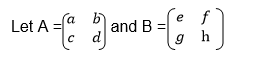
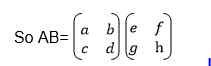
In
AB, matrix A is called a pre-multiplier because it comes first while
matrix B is called the post multiplier because it comes after matrix A.
- The pre –multiplier matrix is divided row wise, that is it is divided according to its rows.
- The post multiplier is divided according to its columns.
- Multiplication is done by taking an element from the row and multiplied by an element from the column.
- In
rule (iii) above, the left most element of the row is multiplied by the
top most element of the column and the right most element from the row
is multiplied by the bottom most element of the column and their sums
are taken:

it can be concluded that matrix by matrix multiplication is only
possible if the number of columns in the pre-multiplier is equal to the
number of rows in the post multiplier.
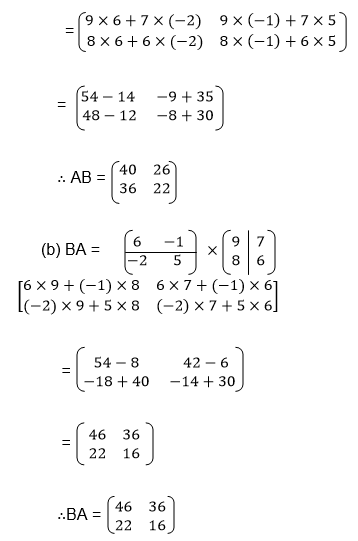
From
the above example it can be noted that AB≠BA, therefore matrix by
matrix multiplication does not obey commutative property except when the
multiplication involves and identity matrix i.e. AI=IA=A
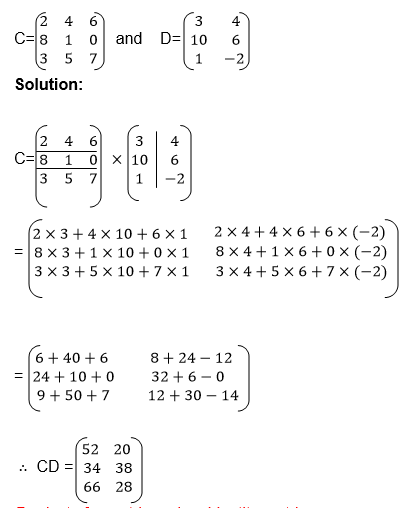
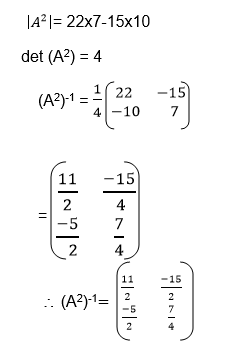
Example 9
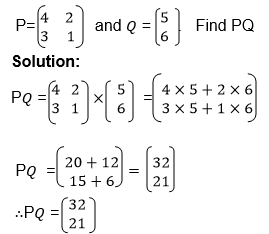


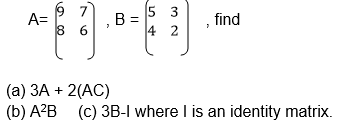
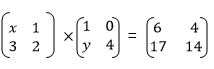
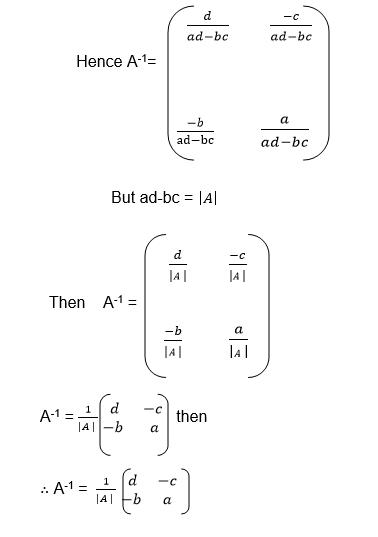
The Determinant of a 2 X 2 Matrix
Calculate the determinant of a 2 X 2 matrix
Determinant of a matrix

the determinant of matrix A is then defined as the difference of the
product of elements in the leading diagonal and the product of the
elements in the main diagonal.

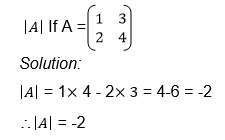
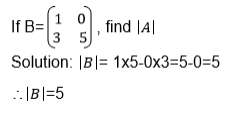


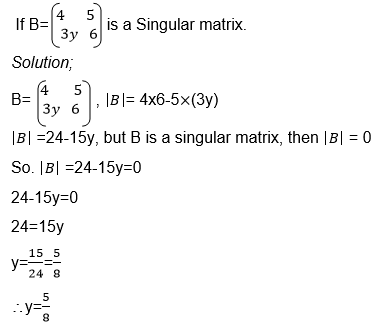
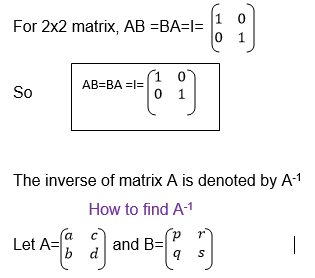
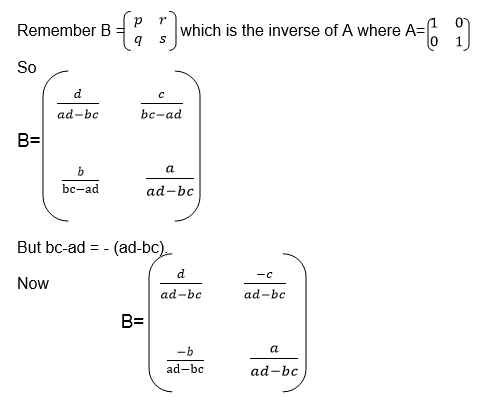
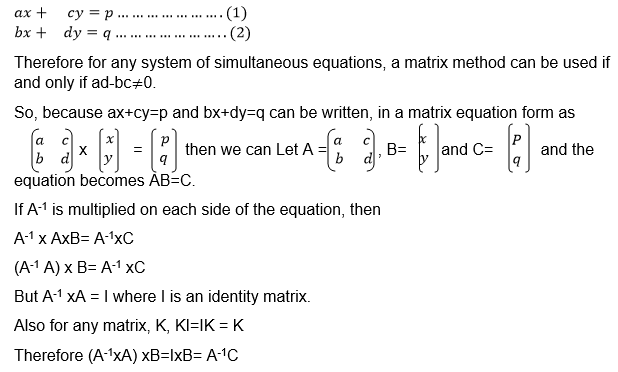
If A is a square matrix and B is another matrix with the same order as
A, then B is the inverse of A if AB=BA=I where I is the identity matrix.

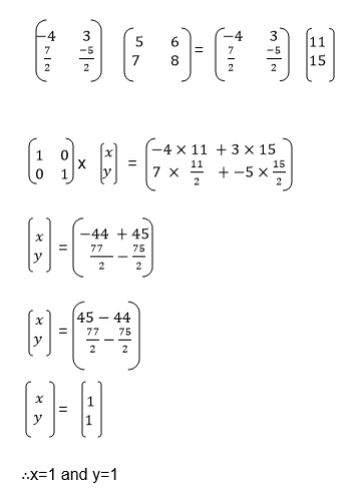
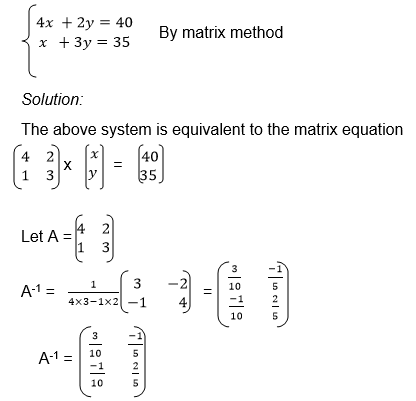
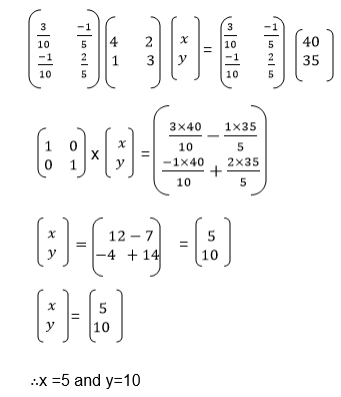
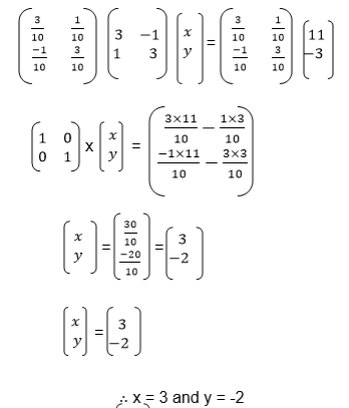
we need the unknown matrix B, we can solve for p and q by using
equations (i) and (iii) and we solve for r and s using equations (ii)
and (iv)

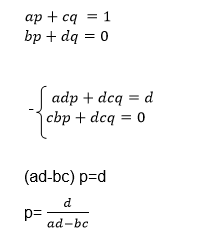
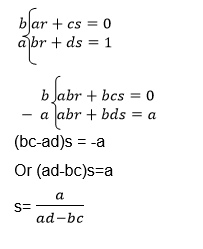
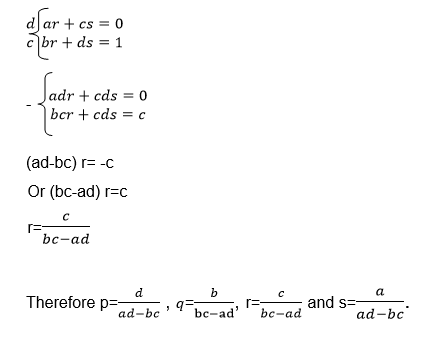
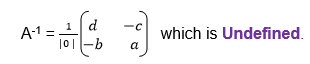
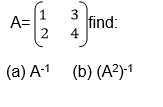
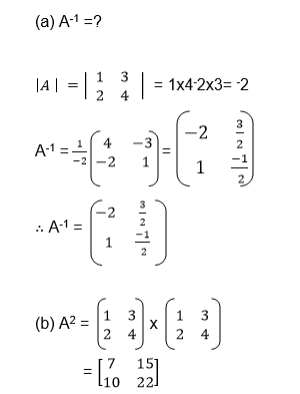

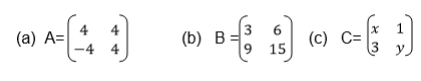
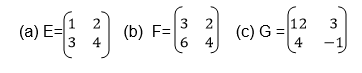
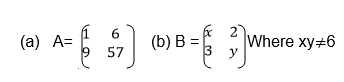
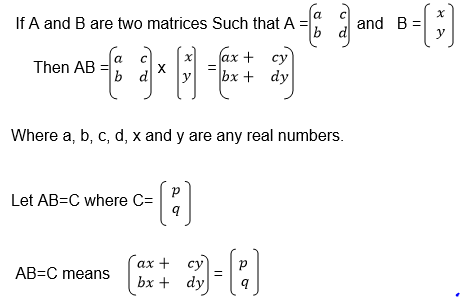
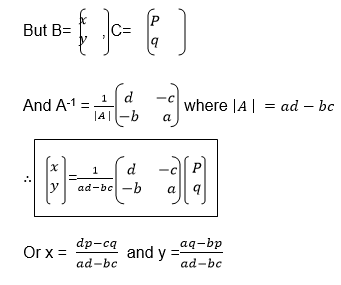
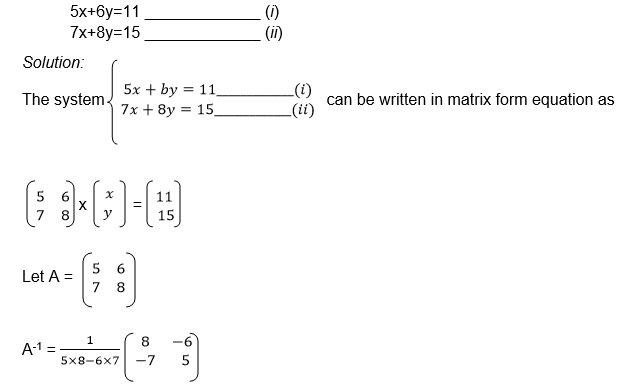
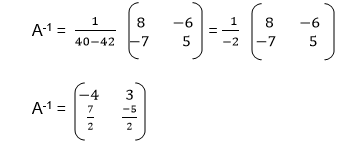



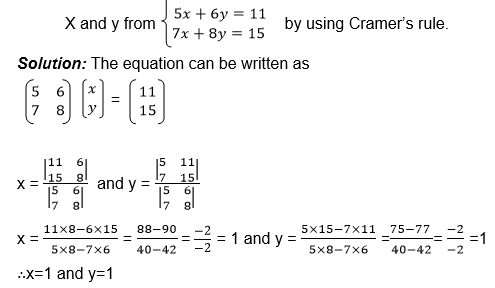
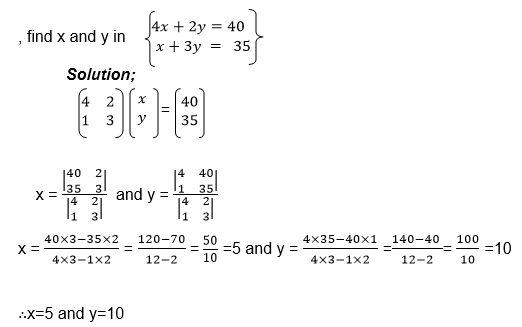
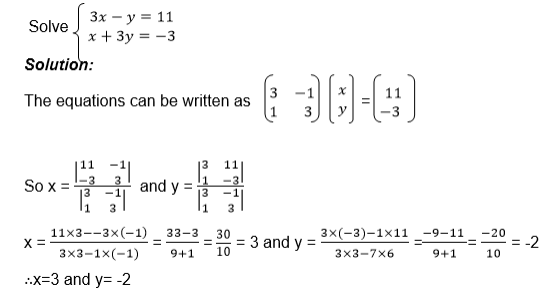
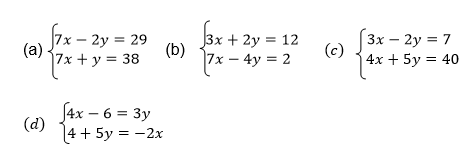
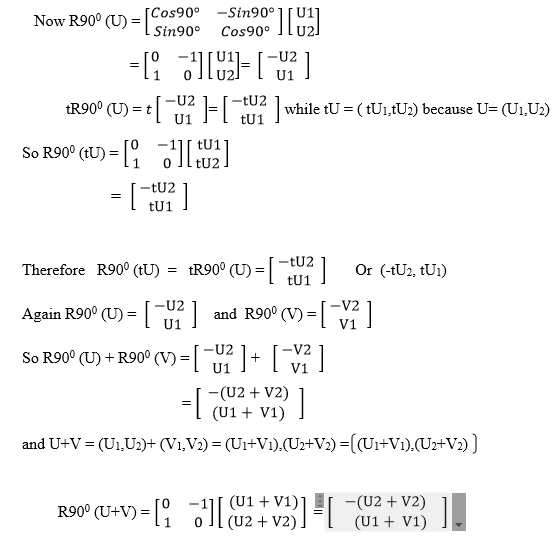
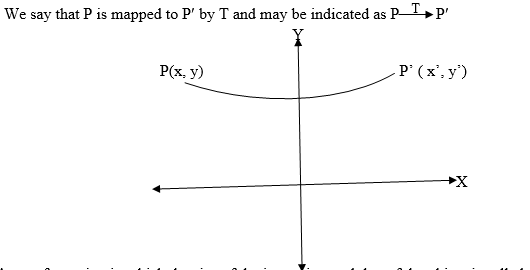
A transformation in a plane is a mapping which moves an object from one
position to another within the plane. Figures on the plane can also be
shifted from one position by a transformation.
you look at yourself in a mirror you seem to see your body behind the
mirror. Your body is in front of the mirror as your image is behind it.
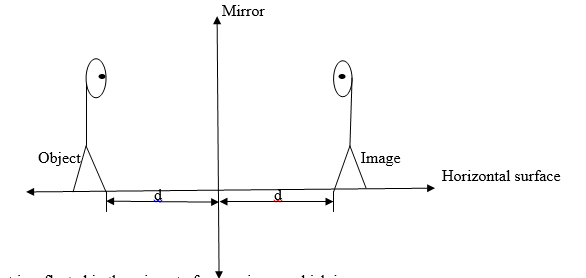
- The same size as the object
- The same distance from the mirror as the object
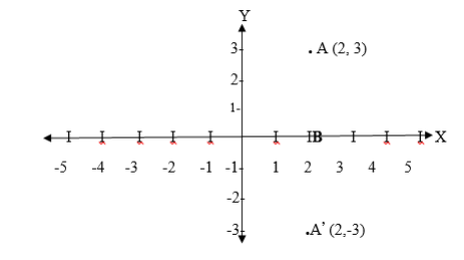
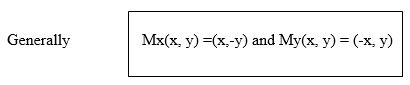
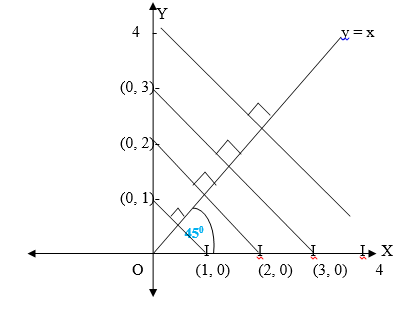
x and y axes. It is the line of symmetry for the angle YOX formed by
two axis. By using isosceles triangle properties, reflection of the
point (1,0) in the line y=x will be ( 0,1) while the reflection of (0,2)
in the line y=x will be ( 2, 0) it can be noticed that the coordinates
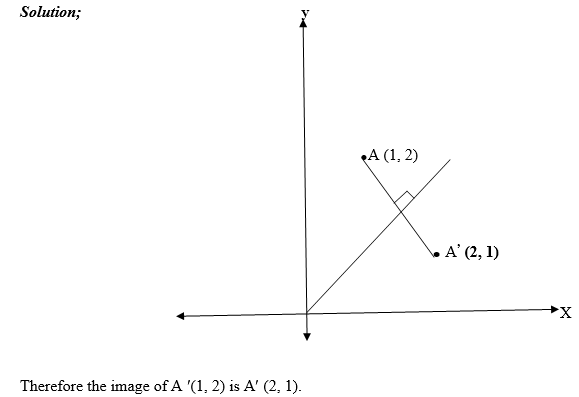
are exchanging positions. Hence the reflection of the point (x,y) in the
line y=x is ( y,x).
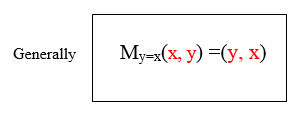
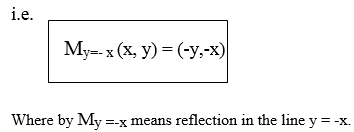
the line passes through the origin and makes an angle a with x – axis
in the positive direction, then its equation is y= xtanα where tanαis
the slope of the line.
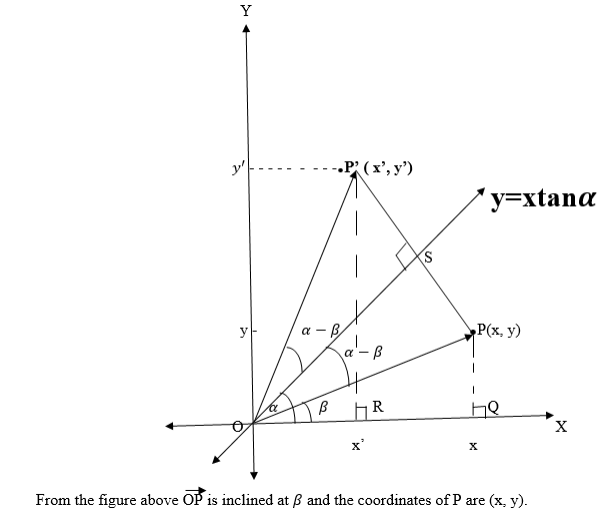

OP¢R is a right angled triangle and the angle P¢QR = a -β + a- β+ β,
this is due to the fact that reflection is an isometric mapping.



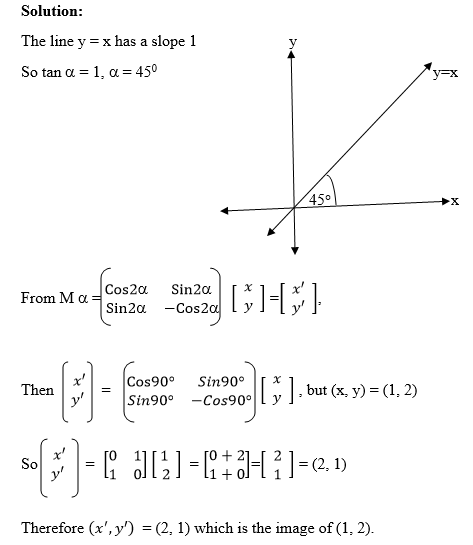


find the image of the line y = 2x + 5, we choose at least two points on
it and find their images, then we use the image points to find the
equation of the image line.
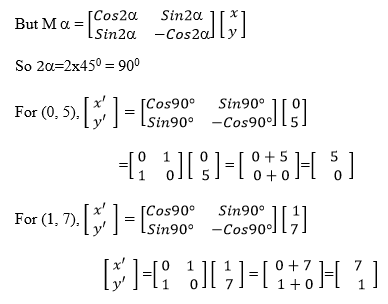
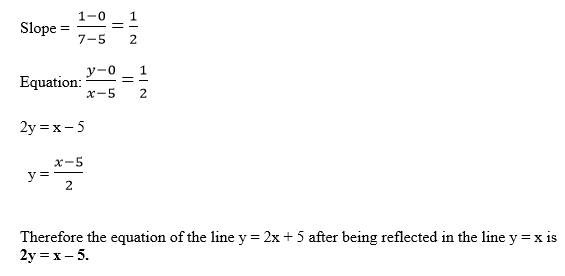
- Find the image of the point D (4,2) under reflection in the x – axis
- Point Q (-4,3) is reflected in the y – axis. Find its image coordinates.
- Reflect the point (5,4) in the line y = x
- Find the image of the point (1,2) after a reflection in the line y = x followed by another reflection in the line y = -x.
- Find the equation of the line y = 3x -1 after being reflected in the line x + y = 0.
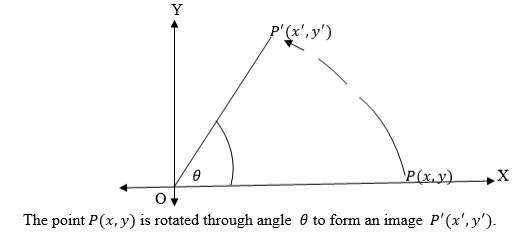
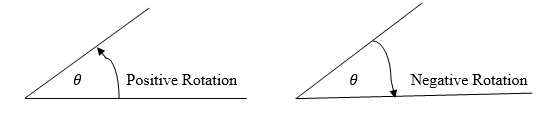
the xy plane, whenθismeasured in the clockwise direction it is negative
and when it is measured in the anticlockwise direction it is positive.
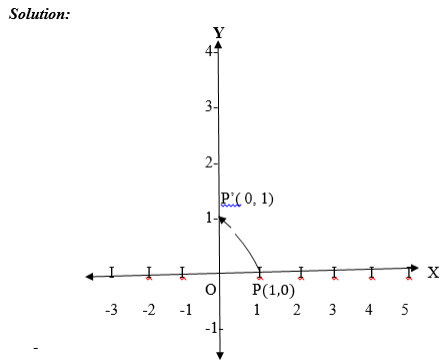
about the origin it will be on the y – axis. Since P is 1unit from O,
P¢ is also 1 unit from O, the coordinates of P¢ (0,1) are P¢ (0,1).
Therefore R 900(1,0) = (0,1).
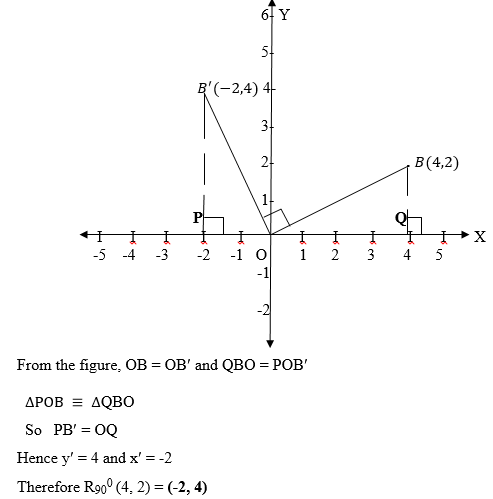
- 900 about the origin
- 450 about the origin
- 2700 about the origin
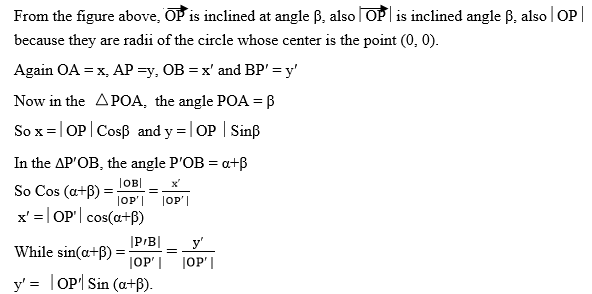
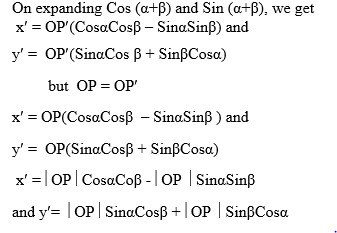
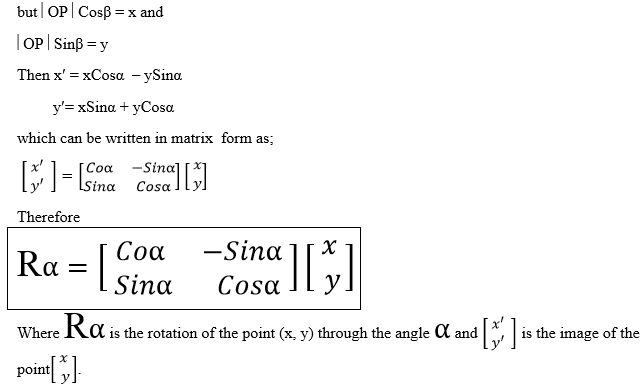


A translation is a mapping of a point P (x, y) into P’ (x’, y’) by the
Vector (a, b) such that (x’, y’) = (x, y) + (a, b), translation is
denoted by the letter T. So T maps a point (x, y) into x’, y’)
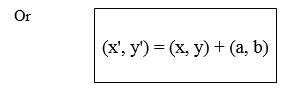
the triangle OPQ whose vertices are (0,0), (3,1) and (3,0) respectively
which is mapped into triangle O¢P¢Q¢ by moving it 2 units in the
positive x direction and 3 units in the positive y direction
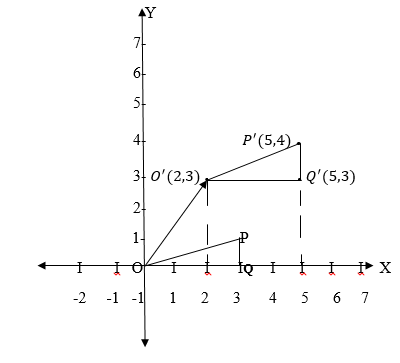

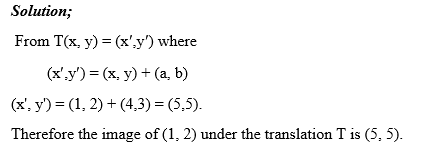
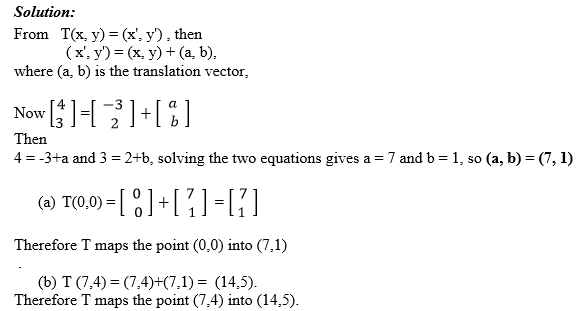
Enlargement is the transformation which magnifies an object such that
its image is proportionally increases on decreased in size by some
factor k. The general matrix of enlargement
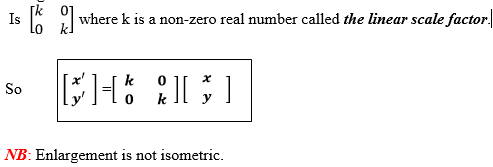

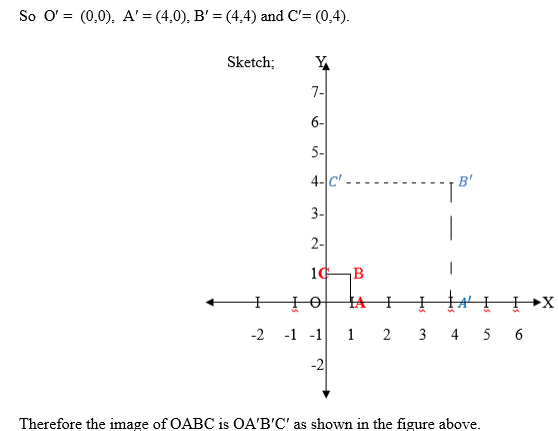


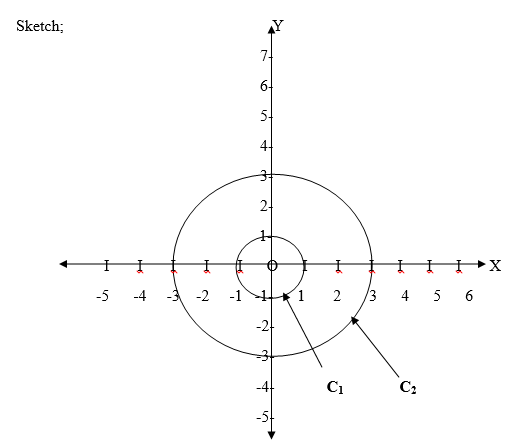
the images of these points are (0,3), (3,0), (0,-3), (-3,0) and other
points respectively, where the centre remains (0,0) and the radius
becomes 3 units.