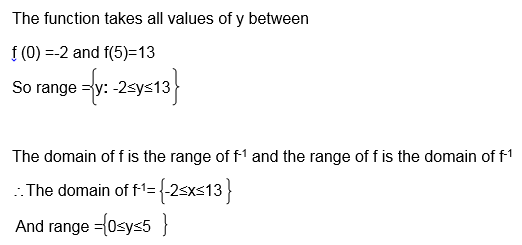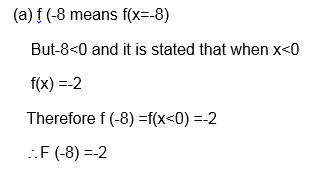Download & Install
Darasa Huru App
DOWNLOAD
TOPIC 2: FUNCTIONS ~ MATHEMATICS FORM 3
Normally relation deals with matching of elements from the first set called
DOMAIN with the element of the second set called RANGE.
function is a relation with a property that for each element in the
domain there is only one corresponding element in the range or co-
domain
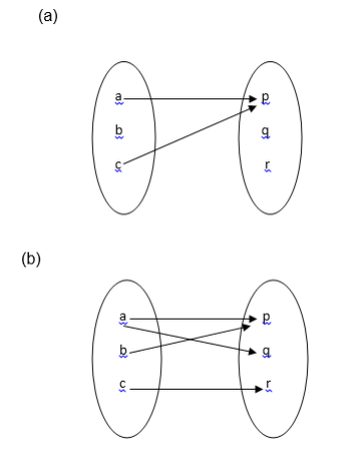
Example 1
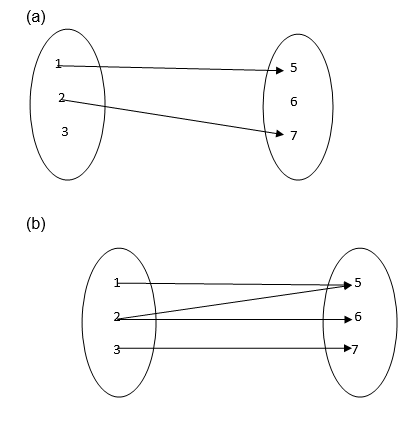
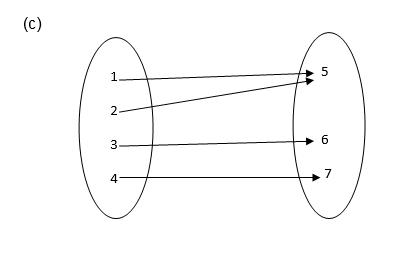
- It is not a function since 3 and 6 remain unmapped.
- It is not a function because 2 has two images ( 5 and 6)
- It is a function because each of 1, 2, 3 and 4 is connected to exactly one of 5, 6 or 7.
Identify functions
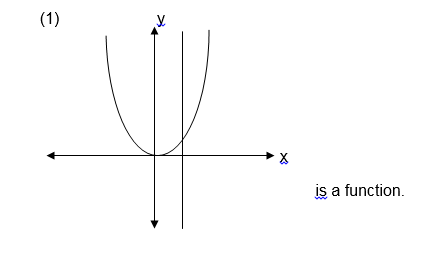
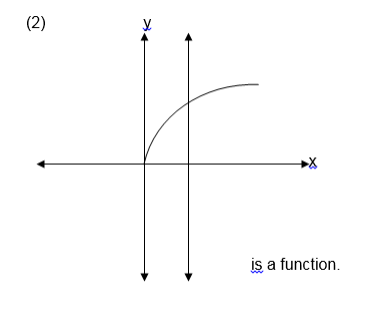
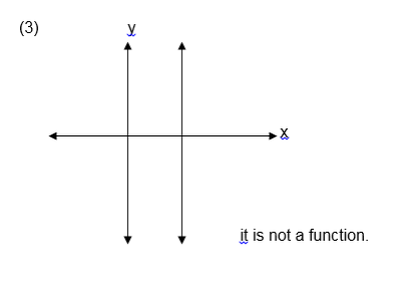
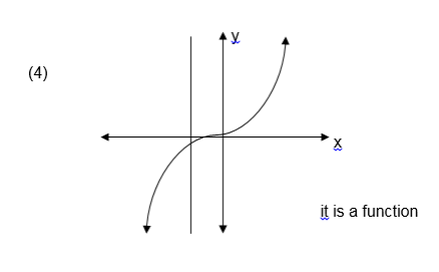
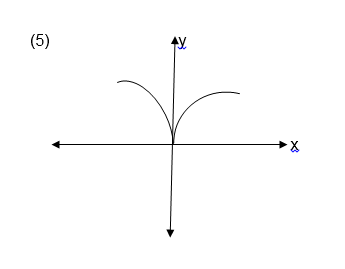
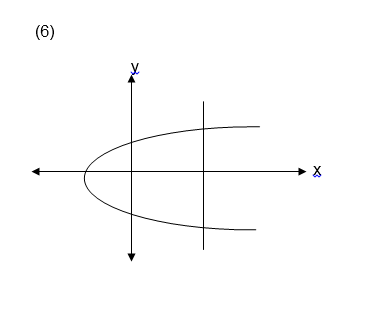
a line parallel to the y-axis is drawn and it passes through two or
more points on the graph of the relation then the relation is not a
function.
Example 2
and B ={ 2, 3, 5, 7 }
B = {1, 2, 3, 4 } which of the following relations are functions ?
- { ( x , y ) : x < y }
- { ( x , y ) : x > y}
- { ( x , y ) : y = x2}
The Domain of a Function
State the domain of a function
Example 3
1. Let f(x) = 3x – 5 for all value of x such that -2 £ x £ 3 find its range
f (x) = y = 3x -5
Example 4
Make x the subject
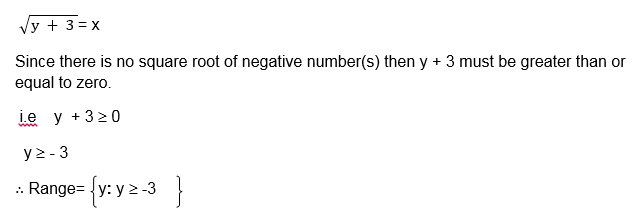
- f(x) = 2x + 7 for 2 £ x £ 5
- f(x) = x – 1 for -4 £ x £ 6
- f(x) = 5 – 3x such that -2 £ f(x) < 8
- f(x) = x2
- f(x) = x2+2
- f(x) = 2x + 1
- f(x) = 1 – x2
- y: -18£ y £3
- y: -3£ y £18
- y: 3 £y £18
- y: -18 £ y £-3
- x: – 3£ x £17
- x: – 2£ x £8
- x: -17 £ x £3
- R = (x, y) : y = for x ≥0
- R= (x, y) : y2 = x-2 for x ≥0
- R= (x, y) : y = for x ≥0 and y ≥0
- R= (x, y) : x = 7 for all values of y
- R = (x, y): -2 £ x £6, 3 £ y<8 and x<y, Where both x and y are integers
- R= (x, y): -2 £ x £6, 3 £ y<8 and x<y, Where both x and y are integers
- R= (x,y): y = √(x+2) for x ≥-2.
- R = (x, y): y=√(2-x) for x ≤2 and y ≤0
- f (-2) < f (0)
- f (3)> f (-4)
- f (-5) = f (5)
- The function crosses , y – axis at 1
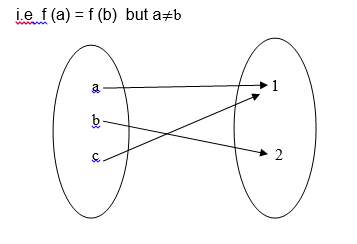
- f (x) = 3x + 2
- f (x) = x + 6
- f (x) = x3 + 1 etc
- f(x) = x2 +1
- f(x) = x4 – 2 etc

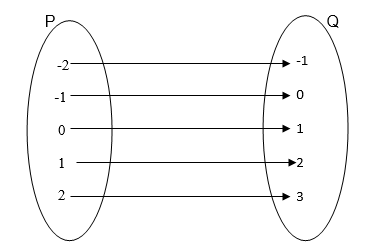
NB:
In example 1, f(x) is not a one to one function because -2 and 2 in A
have the same image in B, that is 4 is the image of both 2 and -2.
Download & Install
Darasa Huru App
DOWNLOAD
Example 7
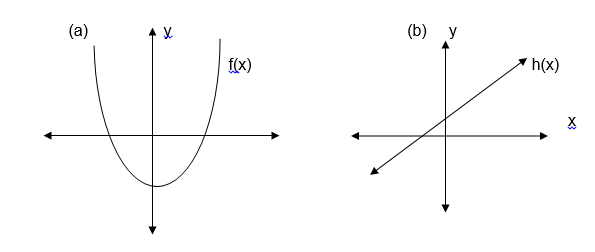
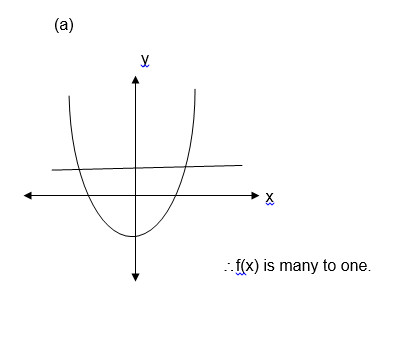
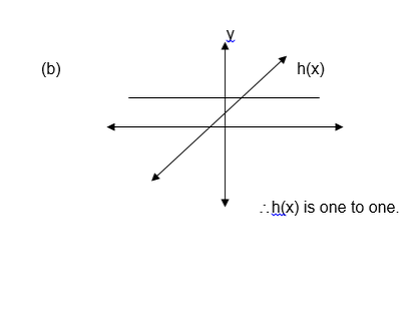
Draw
a line parallel to the x axis and see if it crosses the graph at more
than one points. If it does, then, the function is many to one and if it
crosses at only one point then the graph represents a one to one
function.
Graphs of Functions
Draw graphs of functions
functions are given as equations, this being the case, drawing a graph
of the equation is obtaining the graph of the equation which defines the
function.
that, you can draw a graph of a function if you know the limits of its
independent variables as well as dependent variables. i.e you must know
the domain and range of the given function.
Example 8
- f(x) = 3x -1
- g (x) = x2 – 2x -1
- h (x) = x3
f(x) = 3x – 1
So y = 3x – 1
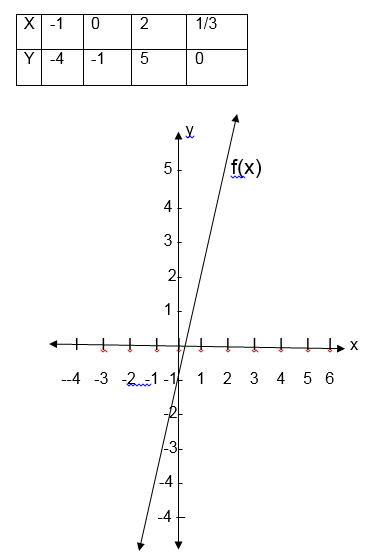
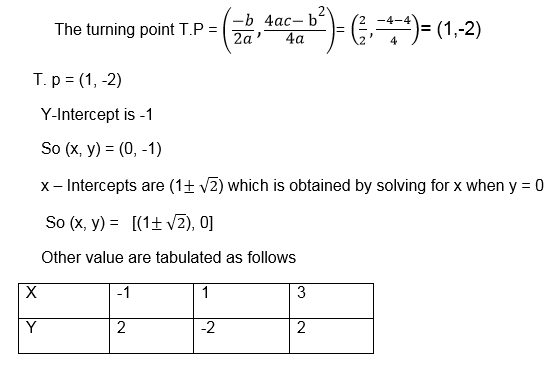
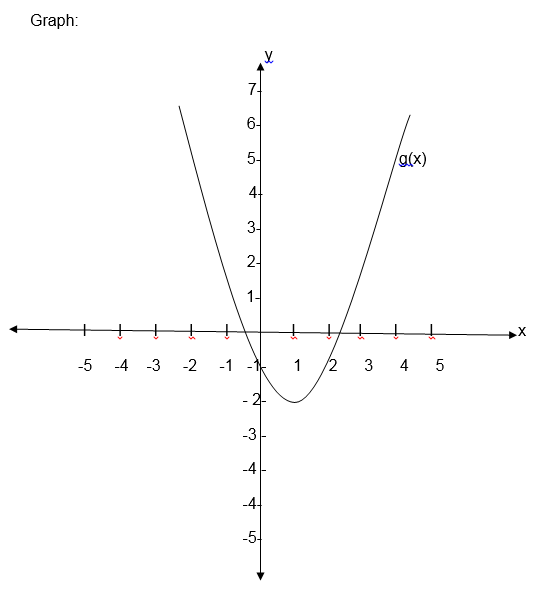
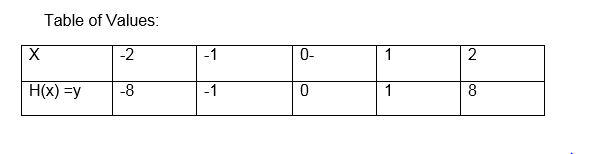
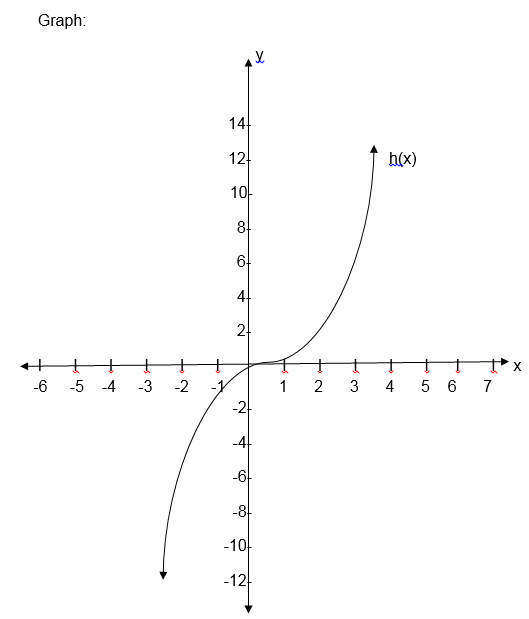
The
first graph is the graph of linear function, the second one is called
the graph of a quadratic function and the last graph is for cubic
function.
Example 9
f(x) = -1 + 6x-x2
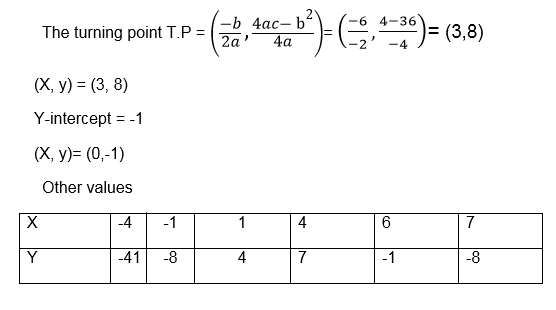
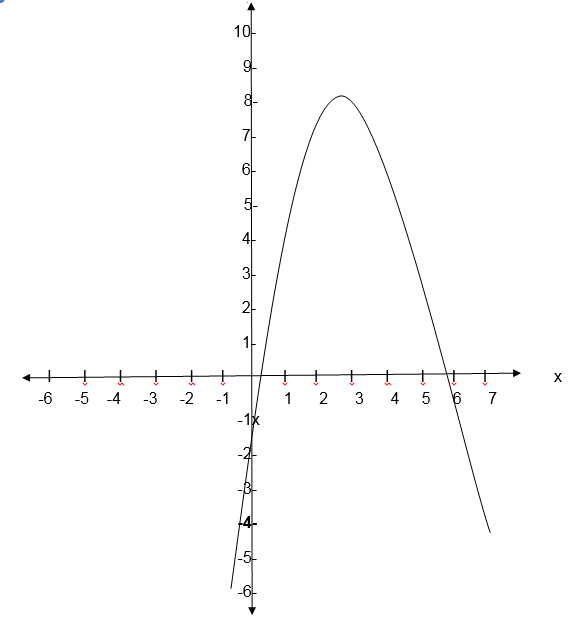
- f(x) = 3x – x2
- g (x) = x-1
- k(x) =x3+1
- f(x) =x+x2+x3
- k(x)=x4
- f(x) = 3x – x2
- h (x) = x+1
- g(x) =x 3– x 2+3
- x=-3 and x=7
- x=8 and x=-6
- x=-3 and x=2
- x=4 and x=-1
- f(x)=x2+2
- f(x) =x4-x2
- f(x)=x5-7
- f(x)=x2+x+2
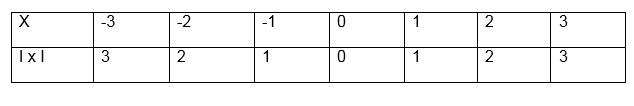
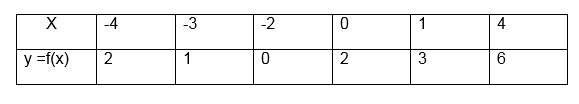
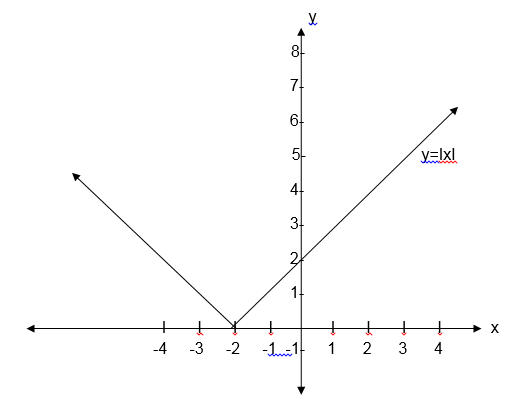
Some functions consist of more than one part. When drawing their graphs draw the parts separately.
the graph includes an end point, indicate it with a solid dot if it
does not include the end point indicate it with a hollow dot.
(a) F(x) x+1 for x>0
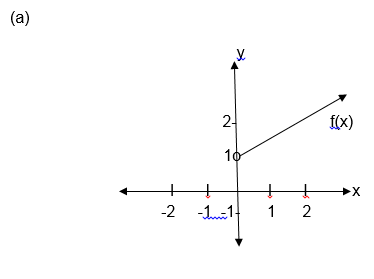
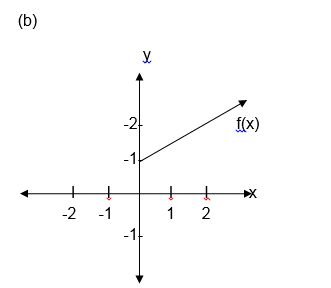
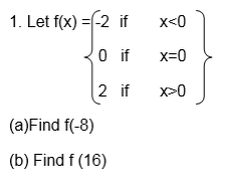
(d) State the domain and range of f
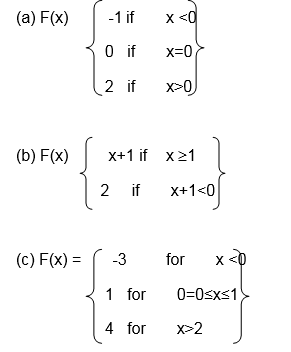
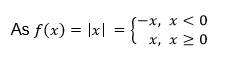
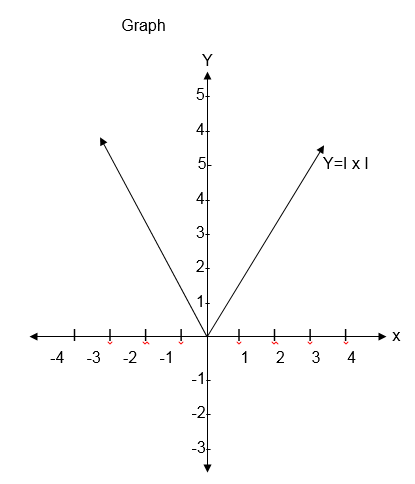



The Inverse of a Function
Explain the inverse of a function
According to the definition of function the inverse of a function is also a function if and only if the function is one to one
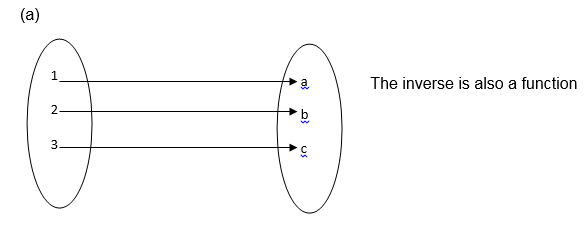
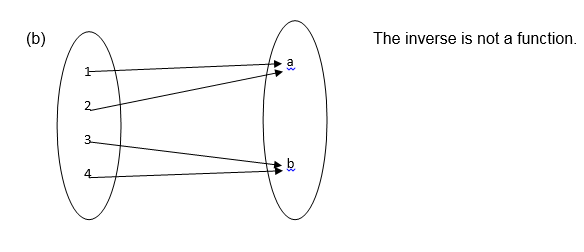
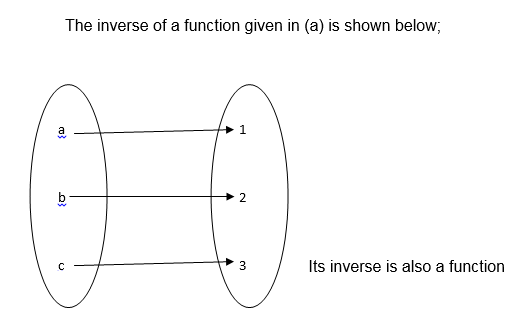
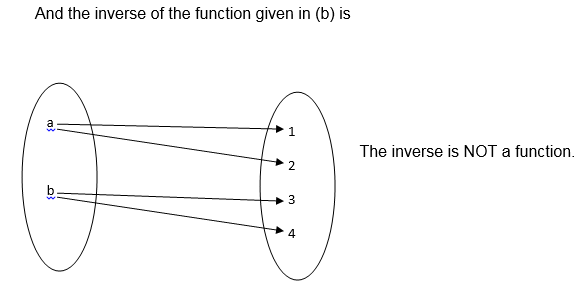
Find the inverse of a function
Example 13
- F(x) = 3x-6
- F(x) =x3
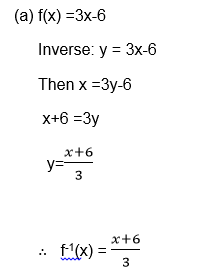
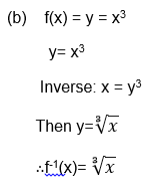
Draw a graph of the inverse of a function
Example 14
find the inverse of the function f(x) = x-5 and then sketch the graph of f-1(x) , also state the domain and range of f-1(x).
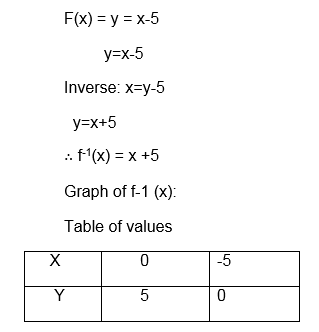
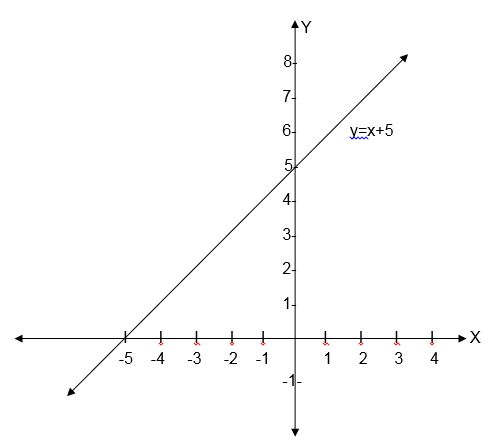
Range = {All real numbers}
The Domain and Range of Inverse of Functions
State the domain and range of inverse of functions